![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
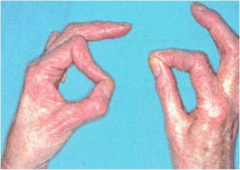
Hx:72yo f c/o progressive weakness with grasp and key pinch in L hand. PE of the hand is significant for decreased sensation on the volar aspect of the 4&5 digits. Dorsal sensation throughout the hand is nl. A clinical photo displaying b/l key pinch is shown in Fig A. What is the most likely cause of compression? 1-Accessory head of the FPL
2-FCU; 3-Osborne's lig; 4-Ganglion within Guyon's canal; 5-Anconeus epitrochlearis |
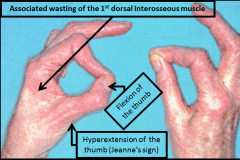
Compression of the ulnar nerve within Guyon's canal, termed ulnar tunnel syndrome, is most commonly caused by a ganglion cyst. A lack of dorsal ulnar sensory deficit helps differentiate entrapment here from at the elbow because the dorsal ulnar cutaneous nerve branches proximal to Guyon's canal. The clinical photo demonstrates Froment's sign where the FPL is used to substitute for the weakened adductor pollicis resulting in flexion of the thumb at the interphalangeal joint, and MCP joint hyperextension. The AIN can be compressed by the accssory head of the FPL (Gantzer's muscle) which results in loss of FPL, index FDP and PQ motor function and no sensory deficits. Ulnar nerve compression at Osborne's ligament, the two heads of the FCU, or by the anconeus epitrochlearis will classically result in volar and dorsal ulnar sensory loss of the affected hand.Ans4
|
|
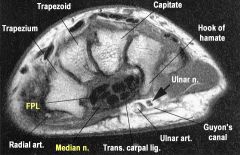
Hx50yo F is diagnosed with CTS She is prescribed a cock-up wrist splint at 30 deg of extension to wear at night. This splint has what effect on the carpal tunnel? 1-Decreases carpal tunnel pressure; 2-Increases carpal tunnel pressure; 3-No effect on carpal tunnel pressure; 4-Enlarges the carpal tunnel volume
5-Improves nerve conduction studies |
carpal tunnel canal pressure varies with wrist position. Use of neutral wrist splints for carpal tunnel syndrome is most useful for improving noctural sx. The reason for this is the functional position of the wrist is approximately 30 deg of extension, and the neutral splints can be functionally limiting when used during productive daytime hours, Weiss et al showed that carpal tunnel pressures are elevated when the wrist is in extension, and are lowest at near neutral. If one couples this with the inherent tunnel pressure increase from the disease itself, its easy to see that extension splinting is a double hit and can lead to increased symptoms.Ans2
|
|
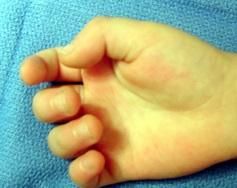
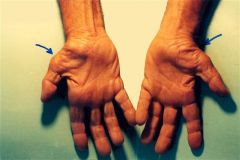
Hx:2yo C has a flex deformity of the IPJ of his thumb Fig A. Surgical correction of this deformity places what structure most at risk as it crosses the surgical field? 1-Princeps pollicis artery; 2-Ulnar digital nerve; 3-Oblique pulley; 4-Ulnar digital artery
5-Radial digital nerv |
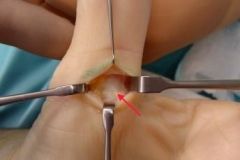
The patient in the scenario has a trigger thumb. Surgical correction of this condition requires the release of the A1 pulley. The A1 pulley is seen at the red arrow in Illustration A. During the dissection, the radial digital nerve crosses the operative field and is at risk. It must be identified and protected, They concluded that trigger thumbs in children will resolve without treatment in >60% of patients. In patients who do not have full resolution, the flexion deformity can be expected to gradually improve with timeAns5
|
|
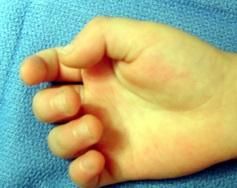
When surgically treating a trigger finger in a child, what structure may need to be released in addition to the A-1 pulley? 1-One or both limbs of the sublimis tendon; 2-A-4 pulley; 3-Lumbrical origin
4-Dorsal interosseous insertion; 5-Anomalous insertion of the MCP joint collateral ligament |
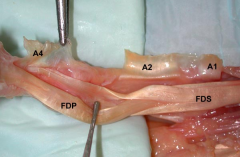
Unlike adults, release of the A-1 pulley in a pediatric trigger finger alone may not resolve triggering symptoms. Trigger finger in the child may be associated with a more proximal decussation of the FDS tendon, nodules in either the FDS or FDP tendon, a thickened A-2 pulley, or a tight A-3 pulley. Cardon et al looked at 16 pediatric pts with 18 trigger fingers and found that 6 fingers continued to trigger after A-1 pulley release. The sublimis decussation and A-3 pulley were found to be the most common cause of this persistent triggering. Bae et al looked at 23 pediatric trigger fingers and found that triggering was noted to occur at the level of the FDS tendon decussation in half the cases. The conclusion was made that all pediatric trigger fingers should be treated with A-1 pulley release and resection of a single FDS tendon slip. Illustration A shows normal decussation of the FDS tendon near the level of the A2 pulley. The FDS decussation may be found to be more proximal in pediatric trigger fingers, necessitating release.Ans1
|
|
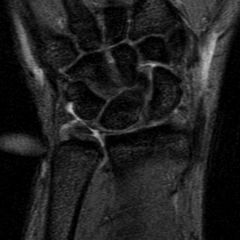
Which of the following structures is an anatomical component of the triangular fibrocartilage complex? 1-Extensor carpi ulnaris tendon sheath
2-Lunotriquetral interosseous ligament 3-Extensor digiti minimi tendon sheath 4-Radioscaphocapitate ligament 5-Flexor carpi ulnaris tendon sheath |
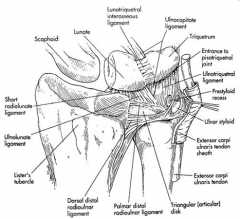
The TFCC was found to be composed of:
-sheath of the extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU), -an articular disc, -the dorsal and volar radioulnar ligaments, -the meniscus homologue, and -ulnar collateral ligament. Biomechanically, they determined that the TFCC functions as a cushion at the ulnocarpal interface, and is a major stabilizer of the DRUJ. They found that the floor of the ECU sheath originated from the dorsal side of the fovea of the ulna, through an arrangement of Sharpey's fibers. Ans1 |

