![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is physical hydrology? |
The study of the occurrence, movement and physical properties of water on and below the earths surface, with the exception of oceanic water |
|
|
What are the major water types? |
1) atmospheric water 2) groundwater 3) soil water 4) surface water |
|
|
What is atmospheric water? |
The water that is contained in the air above the land surface. Typically water vapour but may also be liquid water as rain or solid water as snow (ice crystals). Studied in meteorology |
|
|
What is surface water? |
Water at the surface, stored in ponds , lakes, streams or rivers |
|
|
What is ground water? |
The water found in the saturated zone which is below the water table |
|
|
How do we find the water table (WT) |
At some depth below the surface, pores within the soil/ rocks are saturated with water. If we dig a large pit, the level to which the water fills up the hole is the water table |
|
|
What is soil water? |
Water that is found below the land surface but above the water table. (Unsaturated zone) |
|
|
What is the total amount of water on earth? |
1.4×10^18 m^3 |
|
|
Draw way WT is found and label |

|
|
|
How much of the total water is fresh water? What makes up the freshwater percentage? |
2.5%. 69% is in polar ice, 30 is fresh groundwater and 1 is surface water, soil water and atmospheric water combined |
|
|
How much groundwater is brackish? Why? |
About 50% of groundwater is brackish because much GW is in contact with sea water through underground water bearing layers |
|
|
How was the sea level different during the peak of the last ice age? |
120 m lower than today |
|
|
During the warm period how much warmer was it and what was the corresponding seal level |
4° higher caused 6 m higher than today |
|
|
What is the conversion rate from ice to water? |
Water=0.9 × ice |
|
|
What is the area of earths oceans and seas? |
362×10^6 km^2 |
|
|
What Is the hydrological cycle |
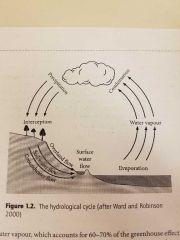
Describes the way in which the water of the ocean is heated by the sun, evaporates and is carried over the earth in atmospheric circulation as water vapour. |
|
|
What is climate? |
Weather averaged over a long period of time, usually 30 years |
|
|
What is the greenhouse effect? |
Greenhouse gases such as water vapour and carbon dioxide allow much of the sun's warming energy to pass through as Shortwave radiation but absorbs the longwave and infrared radiation emitted by the earths surface. This sets the air temp to it's current value, on average 15°C |
|
|
What is the average residence time? |
Average amount of time for which a water molecule resides in a particular place or within a particular system |
|
|
Without greenhouse gases what would the surface temperature be? |
-18°C |
|
|
What are the average residence times of water in the atmosphere and in the ocean. |
Ten days and thousands of years respectively |
|
|
What is Broeker's hypothesis concerning global warming causing an ice age |
The to global warming an increase in fresh meltwater inflow from arctic areas into the north Atlantic Ocean will impede the the flow of water into the north atlantic drift: this will effectively halt the transport of warm ocean water from the equator to higher latitudes |
|
|
What is a drainage basement/ catchment? |
The geographical area that drains into a river or reservoir. Water flow is contained within the drainage basin boundaries and surface water flow moves through the drainage basin outlet |
|
|
What is leakage? |
The loss of quantities of GW through underground water bearing layers, often unknown and may cause a problem when using the drainage basin as a unit |
|
|
What is interception and what is it's formula? |
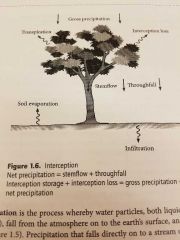
When precipitation lands on vegetation or buildings. |
|
|
What is throughfall and what is stemflow? |
Throughfall: consists of raindrops that fall through spaces in the vegetation canopy and that drip from wet leaves and branches Stemflow: the water that runs down the main stem of a tree |
|
|
What is infiltration and percolation |
Infiltration: when on contact with the soil water trickles into pores or cracks on the soil etc Percolation: when in the unsaturated zone water may move further down into the GW TABLE. |
|
|
What is interception storage and interception loss? |
Storage: water stored on plant surfaces Loss: when water evaporates off of interception surfaces |
|
|
What Is the water balance equation? |

|
|
|
How do we find total amount of water stored? |
= water stored as surface water + water stored as soil water + water stored as GW |
|
|
What does a positive change in storage represent? (◇S>0) |
Signifies that water is taken into storage. The total amount of water stored in the ground is larger at the end of the selected time period than at the beginning. This causes wetter vegetation, a higher surface water level, wetter soil and/or elevated water table |
|
|
What does a negative change instorage signify? |
Decrease of the total water storage in the area. This manifests as drier vegetation, lower surface water level a drier soil and/ or a lowered WT. |

