![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the dorsal surface of the foot |
where your shoelaces are |
|
|
define the ankle mortise |
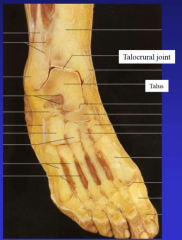
ankle joint tibia and fibula into ankle talocrural joint (ankle joint) |
|
|
what are the bones of the foot |
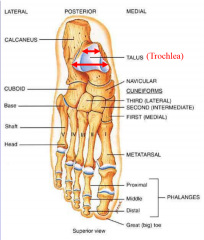
7 tarsal 5 metatarsal 14 phalanges transverse tarsal joint, tarsal-metatarsal joint calcaneus-- heel bone (sustentaculum tali-- bump holds talus), sulcus between them talus on top (subtalar joint) (trochlea articulates with tibia) (head, neck and body) navicular (ship, in front of talus) cuneiforms (3 lateral [center of foot], 2 intermediate, 1 medial) in front of navicular cuboid is lateral to navicular and cuneiform 5 metatarsals (1 is medial, 5 is lateral. 2 is longest) 14 phalanges (3 on every toe, 2 on big toe) proximal middle and distal |
|
|
describe the spring ligament |
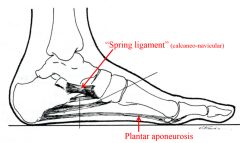
sustains arch of foot along with natural shape of bones plantar aponeurosis also helps |
|
|
describe the action of the talocrural joint |
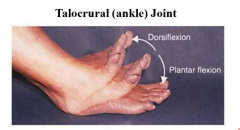
dorsiflexion plantarflexin |
|
|
describe the action of the subtalar joint |
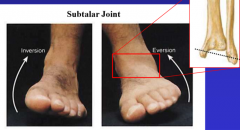
inversion (more- fibula lower) eversion |
|
|
describe the fascia coverings of the ankle |
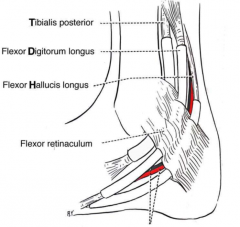
flexor retinaculum covers medial ankle (tom dick harry-- tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum and flexor hallucis longus) extensor retinaculum (sup/inf) covers anterior ankle fibular retinaculum (sup/inf) covers lateral ankle |
|
|
what are the intrinsic muscles of the dorsal foot |
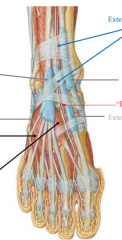
extensor hallucis brevis (calcaneous to extensor hallucis longus tendon) extensor digitorum brevis (calcaneous to extensor digitorum longus tendons) hard to distinguish these muscles |
|
|
what is the fascia on the plantar foot |
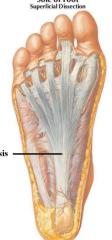
plantar fascia plantar aponeurosis (thickening) tightening when toes are flexed-- maintains arch |
|
|
describe the muscles in the first layer of the plantar foot |
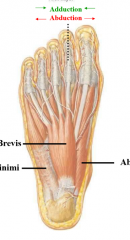
AFA abductor digiti minimi flexor digitorum brevis (flexes toes, off calcaneous to 4 toes) abductor hallucis |
|
|
describe the muscles of the second layer of the plantar foot |
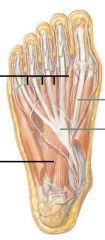
lumbricals (worm) (from flexor digitorum longus to extensor digitorum longus quadratus plantae (heel to flexor digitorum longus tendon) porta pedis |
|
|
describe the muscles of the third layer of the plantar foot |
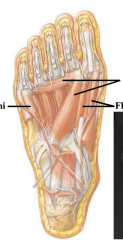
FAF flexor digiti minimi- flexor of outside toe adductor hallucis- transverse and oblique to 2nd toe flexor hallucis brevis- flexor of big toe |
|
|
describe the muscles of the fourth layer of the plantar foot |
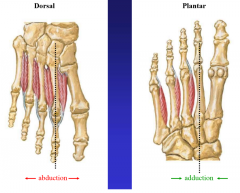
dorsal DAB abduction plantar PAD adduction none on 2nd toe (gets two from abduction) |
|
|
describe the nerves of the plantar foot |
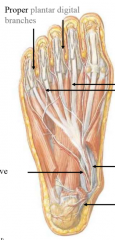
second layer tibial nerve medial plantar-- first lumbrical, flexor hallucis brevis, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor hallucis lateral plantar-- everything else common and then proper |
|
|
describe the nerves of the posterior leg |
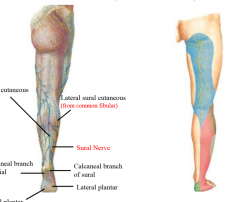
posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh saphenous nerve (medial) sural nerve (calf) |
|
|
describe the nerves of the dorsal foot |
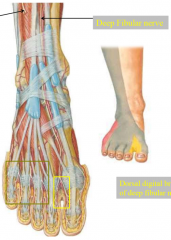
deep fibular nerve-- between 1st and 2nd toe superficial fibular nerve-- everything else |
|
|
describe the blood supply to the dorsal foot |
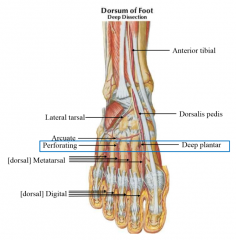
anterior tibial to
dorsalis pedis to deep plantar AND lateral tarsal branch, arcuate (arch) dorsal metatarsal and dorsal digital perforating to plantar surface |
|
|
describe the blood supply to the plantar foot |
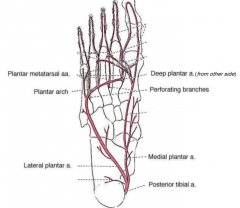
posterior tibial artery to medial plantar AND lateral plantar-- plantar arch to deep plantar from dorsal |
|
|
describe venous drainage |
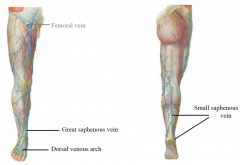
great saphenous vein to femoral small saphenous vein to popliteal vein |
|
|
describe valgus |
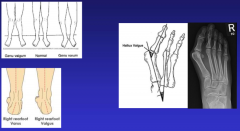
increased inside angle knees, ankles, toes (bunions) |

