![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are ear molds used for? |
|
|
|
What encompasses a successful fitting? |
|
|
|
important factors for EMIs |
|
|
|
what can alter the quality of EMI? |
air bubble? helix? concha bowl? tragus? |
|
|
What are some possible fit issues due to jaw movement? |
it can change the canal shape and create less of a seal for earmold |
|
|
Where do you want to make a mark on impression for direction microphones? |
where their eyes are |
|
|
contraindications for EMI |
|
|
|
What are precautions for enlarged auditory canal? |
the end of their canal is longer than the front, can't pull impression out |
|
|
Why was there only one frequency response curve back in the day? |
they couldn't individualize them like today so they just used one that fit the most patients (SNHL in high frequencies) |
|
|
Where is the natural ear canal resonance? |
2.7 kHz |
|
|
What happens when you have insertion loss? |
occlusion of natural open ear thus reducing signal transmission |
|
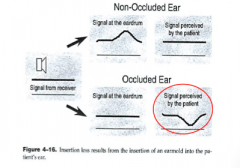
|
reduction in high frequencies not low frequencies because it is reducing the effectiveness of the pinna and external ear |
|
|
What contributes to localization and naturally enhancing incoming sound? |
external ear |
|
|
What causes the natural enhancement of 10-20 dB at the TM? |
resonance characteristics |
|
|
How do you know front to back localization? |
pinna shapes frequency information to give that localization |
|
|
What does the pinna do? |
disturbs the sound field around the EAM allowing the brain to extract information (IID/ITD) for directional processing
alters spectral characteristics |
|
|
What does the concha do? |
influences direction of sound sources
contributes to directional hearing |
|
|
What are the implications for hearing aid fittings? |
stlye? (BTE vs ITE vs CIC) |
|
|
What are earmolds used for? |
|
|
|
Deciding on EM is a balance between... |
audiological information, patient characteristics, and patient wants/needs |
|
|
Upon deciding on EM, look at... |
|
|
|
EM materials |
|
|
|
What has reduced reliance on silicone material for severe to profound losses? |
feedback suppression |
|
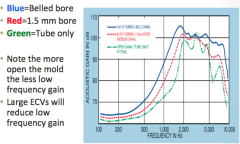
|
blue = more response in HF
green = less response to low and high frequency |
|
|
prior to digital signal processing, acoustics of amplification werre heavily influenced by |
use of EM acoustics |
|
|
examples of difficult losses, pre-digital |
reverse slope cookie bite high frequency only |
|
|
tubing length |
longer tubing shifts mid frequency peak to lower frequency and shorter tubing shifts peak to higher frequency |
|
|
tubing diameter |
tubing internal diameter can affect frequency response
smaller internal tubing diameter = reduced high frequency gain |
|
|
sound bore length |
longer bore length reduces high frequency responses
shorter bore length increases high frequency responses |
|
|
sound bore diameter |
wider diameter increases high frequency response (horns)
narrower diameter decrease high frequency response (reverse horns) |
|
|
Why would you use a sound bore? |
it is a natural HF technique opposed to just turning up HF gain (good for extended bandwidth) |
|
|
what is the traditional amplification bandwidth? |
5-6 kHz |
|
|
increasing diameter of libby horn increases... |
high frequency output |
|
|
venting option |
|
|
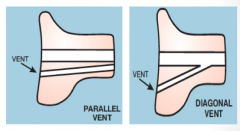
|
venting |
|
|
consequences of large vent |
reduces low frequency response |
|
|
consequences of diagonal venting |
can adversely affect high frequency response |
|
|
dampers/filtering |
filtering or damping affects the mid frequency region of the frequency response
effects will vary based on placement of the filter |
|
|
prior to feedback management, what was used to control feedback? |
dampers and filters because it reduced peaks in frequency response |
|
|
As you move damper close to where sound exits, what happens? |
you reduce peakiness of sound output |
|
|
venting improves sound quality but reduces... |
occlusion |
|
|
vents reduce loss of amplification at __ kHz and below |
1 kHz |
|
|
How do open fits affect directionality? |
the natural and processed sounds are entering the ear |
|
|
How do you account for limited fitting range? |
offer a high power receiver |
|
|
directional mice are directional to HF sounds with open fits |
... |
|
|
How do you account for directional rolloff? |
add them back in if you need gain in that region (base boost) |

