![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
390 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Calcium ion homeostasis of blood is controlled by _______ feedback. |
negative |
|
|
Select the characteristic of a female pelvis. Angle of pubic arch more than 90 degrees; Pelvic bones heavier and thicker; Ischial spines shorter and closer together; Sacrum shorter and more curved |
Angle of pubic arch more than 90 degrees |
|
|
In nerve cells, vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release neurotransmitter molecules into the Extracellular fluid. What type of transport is this? |
Exocytosis |
|
|
Function of Muscle cells |
Move body parts |
|
|
Function of nerve cells |
Control body functions |
|
|
Function of epithelial cells |
Cover and line body organs |
|
|
Function of fat cells |
Store nutrients |
|
|
Function of white blood cells |
Fights disease |
|
|
Which of the choices is a general characteristic of all epithelial tissues? Defined by Extracellular matrix; avascular; contractile; conductive; multilayered |
Avascular |
|
|
Which statement best characterizes connective tissue? It has one surface exposed to the exterior of the body or to the interior of a hollow structure; it is always arranged in a single layer of cells; it is found connecting the brain to the spinal cord; it is usually composed of a large amount of Extracellular matter; it consists of cells arranged in many layers |
it is usually composed of a large amount of Extracellular matter |
|
|
What type of epithelial tissue usually forms membranes where filtration, or exchange of substances by diffusion, occurs? |
Simple squamous |
|
|
Function of ribosomes |
Synthesizes proteins |
|
|
Function of flagella |
Propels entire cells |
|
|
Function of cilia |
Move fluids across the cell surface |
|
|
Function of rough endoplasmic reticulum |
Modifies and transports proteins |
|
|
Function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
Forms lipids and detoxifies drugs |
|
|
Adjacent plasma membranes fuse together tightly, like a zipper, in what? |
Tight junctions |
|
|
Select the connective tissue types that are well vascularized, meaning they have a rich blood supply Cartilage tissue; dense connective tissue; adipose tissue; bone tissue; areolar connective tissue |
adipose tissue; bone tissue; areolar connective tissue |
|
|
The process whereby mRNA is made from the DNA in the nucleus is called _________; the process whereby information on mRNA is "decoded" at the ribosomes in the cytoplasm is called __________ |
Transcription; translation |
|
|
Which is the correct sequence of the following events of protein synthesis? 1. tRNA recognizes a complementary mRNA codon calling for its amino acid by binding via its anticodon to the codon. 2. Released tRNA reenters the cytoplasmic pool. 3. mRNA attaches to the ribosome, and translation begins. 4 mRNA is made on the DNA template. 5. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA, a new amino acid is added to the growing peptide chain. |
4-3-1-5-2 |
|
|
One job of the Golgi apparatus is to package __________ for export from the cell. |
proteins |
|
|
During which period of the cell life cycle does DNA replication occur? |
Interphase |
|
|
What does the term cancer refer to? |
Malignant neoplasm |
|
|
Of the different types of muscle tissue, only __________ both is involuntary AND contains intercalated discs. |
Cardiac muscle |
|
|
Microvilli and cell junctions are specializations associated with what cell structure? |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
Movement of oxygen molecules from their area of high concentration outside the cell to low concentration inside the cell |
Simple diffusion |
|
|
Movement of glucose molecules down their concentration gradient through a protein carrier |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
Movement of sodium ions against their concentration gradient using ATP |
Active transport |
|
|
Exocytosis of hormones out of a cell |
Vesicular transport |
|
|
In an area where an epithelium is subjected to considerable wear and tear, you would expect to find __________. |
stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Which of the following cell organelles have double membranes and function to supply most of the ATP used by the cell? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
Which of the following represents active transport? |
Sodium-potassium pump |
|
|
In __________, the chromosomes are aligned at the center of the spindle, midway between the centrioles, so that a straight line of chromosomes is visible. |
metaphase |
|
|
Cells in a __________ solution will burst (lyse) as water rushes into the cell in an attempt to reach osmotic balance. |
hypotonic |
|
|
The __________ scattered in the lipid bilayer are responsible for most of the specialized functions of the plasma membrane. |
proteins |
|
|
The movement of water across the plasma membrane is specifically called __________. |
osmosis |
|
|
Select the characteristics of adipose tissue. Connects bones to bones; Stores energy; Insulates the body; Provides cushioning to some organs; forms the stroma of some organs; It protects the body from extremes of heat and cold. |
Stores energy; Insulates the body; Provides cushioning to some organs; It protects the body from extremes of heat and cold. |
|
|
Assign the terms that describe the overall function of each primary tissue type.Covering; Support; Movement; Control |
Epithelial; Connective; Muscle; Nervous |
|
|
Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function are called _______. |
Tissues |
|
|
Most connective tissue types are well vascularized, meaning they have a rich blood supply. Which of the following connective tissues represent(s) an EXCEPTION? |
Tendons and ligaments |
|
|
Solution A has triple the salt content of a normal red blood cell that is floating in solution. The solution is _______ and the cell will _______. |
hypertonic; shrink or crenate |
|
|
The tendency of water to move down its own concentration gradient is a characteristic of the process called _______. |
Osmosis |
|
|
cellular transport?Small nonpolar molecules can be transported directly across the phospholipid bilayer.; Molecules move from high to low concentration due to their own kinetic energy.; Water can be directly transported across the phospholipid bilayer.; Active transport requires chemical energy in the form of ATP. |
Water can be directly transported across the phospholipid bilayer. |
|
|
Passage of materials across the plasma membrane from a region of high concentration to one of lower concentration is termed _______. |
Diffusion |
|
|
A(n) _______ is the smallest living unit. |
Cell |
|
|
Cells build the majority of their components from _______. |
Proteins |
|
|
The essential nutrient _______ comprises over 60% of any living organism's cells. |
Water |
|
|
Specialized cellular structures called _______ carry out necessary tasks to support life. |
Organelles |
|
|
The job of the Golgi apparatus is to package _______ for export from the cell. |
Proteins |
|
|
The main reason cells go through mitosis is to _______ and _______. |
grow, repair |
|
|
A gene segment of DNA contains the blueprint for building every _______ in the body. |
Protein |
|
|
The four major tissue types are _______, _______, _______, and _______. |
epithelial, muscular, nervous, connective |
|
|
is the lining and covering tissue of the body; forms the glands in the body; hallmarks: cells close together forming sheets; cell junctions include desmosomes and tight junctions; sheets with basal and apical surfaces; avascular; functions include protection, absorption, secretion |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
the most abundant and widely distributed tissue type ;hallmarks: abundant non-living extracellular matrix; variations in blood supply; includes cartilage, bone, and blood |
Connective tissue |
|
|
function is contraction; moves the body, moves blood, moves urine, and moves food |
Muscle tissue |
|
|
forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves; has cell populations of neurons and neuroglia; an internal communication system using nerve impulses |
Nervous tissue |
|
|
The four elements that make up the bulk of living matter and therefore the cell and our bodies are _____, _____, _____, and _____. |
Carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen |
|
|
the unit of structure and function of all living things |
Cell |
|
|
the study of cells |
Cytology |
|
|
“little organ”; a specialized structure in a cell; they have names, structure, and carry out specific functions |
Organelles |
|
|
an English scientist; gave us the word “cell” |
Robert Hooke |
|
|
German biologists who stated that all living things are composed of cells |
Theodore Schwann and Mattias Schleiden |
|
|
a German doctor; determined that cells come from pre-existing cells |
Rudolf Virchow |
|
|
fluid mosaic model is currently accepted theoretical model of plasma membrane structure |
Singer & Nicholson |
|
|
Together, the statements that all living organisms are made of cells and that cells come from pre-existing cells form the what? |
Cell Theory of Biology. |
|
|
The _____ electron microscope (SEM) gives a detailed surface view of the specimen and produces a three-dimensional image. |
Scanning |
|
|
The _____ electron microscope (TEM) is used to study internal structure of cells. |
Transmission |
|
|
Cells have three major regions: _____, _____, and _____ _____ |
Nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane |
|
|
the cellular material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane. |
Cytoplasm |
|
|
the fluid component (mainly water) with dissolved substances |
Cytosol |
|
|
are chemical substances like melanin and glycogen |
Inclusions |
|
|
“little organs;” have specialized structure and specialized functions |
Organelles |
|
|
protein “threads” that support and give shape to cell and provide for movement |
Cytoskeleton |
|
|
Separates cell contents from extracellular environment |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
Functions as the regulatory center for all cell activity |
Nucleus |
|
|
a highly regulated membrane barrier that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm |
Nuclear envelope |
|
|
Involved in the production of ribosomes |
Nucleolus |
|
|
Tubular system involved in processing proteins |
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
Site of protein synthesis |
Ribosomes |
|
|
Ups of cell |
Golgi apparatus |
|
|
Produces ATP using glucose and oxygen |
Mitochondria |
|
|
Digest old organelles |
Lysosomes |
|
|
Detoxifies and neutralizes poisons |
Peroxisome |
|
|
Barrel-like structures especially active during cell division |
Centrioles |
|
|
Membrane projections that increase surface for absorbtion and where are they found? |
Microvilli; found in digestive system (are abundant in epithelial cells that line the small intestine; are supported by protein threads called microfilaments) |
|
|
Membrane projections that "sweep" materials across the cell surface and where are they found? |
Cilia; found in respiratory system (also found on cells lining oviducts of female Reproductive System; are supported by protein threads called microtubules) |
|
|
Membrane projection allowing a cell to "swim" and where are they found? |
Flagella; they are found in reproductive system (only one flagellated cell in the body…sperm; its flagellum is called a “tail;” a flagellum is supported by protein threads called microtubules) |
|
|
The cell’s _____ is a network of various string-like proteins that give shape and support to the cell. The elements that form the cytoskeleton are…from smallest to largest…_____, _____ filaments, and _____. |
Cytoskeleton; microfilaments (actin filaments), intermediate filaments, and microtubules. |
|
|
When a cell is not dividing (is in that part of its life cycle called interphase), DNA is wrapped around proteins…like string around spools…to form a loose network of threads called _____. When a cell is dividing, DNA forms dense, rod-like bodies called _____. |
Chromatin; chromosomes |
|
|
The plasma membrane is a bilayer of _____ molecules arranged with the “tails” of the molecules forming the center of the membrane. _____ molecules are the “machines” with various functions. _____ molecules stabilize the membrane. |
Phospholipid, Protein, and Cholesterol |
|
|
The plasma membrane is described as a __________barrier which means that it allows some substances to pass through it while excluding others. Semi-permeable means the same thing. |
selectively permeable |
|
|
Give some functions for membrane proteins. |
Proteins can function as: enzymes, channels (or pores like aquaporins), receptors, carriers, in cell recognition (like glycoproteins), in attachment |
|
|
The three main types of cell membrane junctions are __________, _____, and __________. |
tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions |
|
|
are impermeable junctions(are like zippers); prevent substances from passing between cells |
Tight Junctions |
|
|
are anchoring junctions(are like snaps); prevent cells from being pulled apart when they are stressed |
Desmosomes |
|
|
are communicating junctions; substances can pass directly from one cell to another through channels |
Gap Junctions |
|
|
Substances move across the plasma membrane in two ways, by _____transport or by _____transport. _____transport does not require any energy input from the cell. _____transport requires __________(ATP). |
Active, Passive, passive, Active, Adenosine Triphosphate |
|
|
Two examples of passive transport processes are _____and _____._____is important for every cell of the body. However, _____occurs across _____walls. |
Diffusion, Filtration, Diffusion, Filtration, Capillary |
|
|
Diffusion is the process by which substances move away from an area of _____concentration to an area of _____concentration. We say that substances move down their _____gradient. This is due to the kinetic energy of the substances themselves. |
High, Low, Concentration |
|
|
the unassisted diffusion of solutes through the membrane; small fats, oxygen, carbon dioxide |
simple diffusion |
|
|
substance diffusing needs some “help” from a carrier protein which undergoes a shape change; glucose |
carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion |
|
|
substance diffusing needs some “help” by moving through a protein channel; mostly ions |
channel-mediated facilitated diffusion |
|
|
diffusion of water through a membrane from a hypotonic solution (less solute but more water) to a hypertonic solution (more solute but less water); because water is a small molecule, it can slowly diffuse through spaces in the lipid bilayer; it diffuses more quickly through channels called aquaporins. |
osmosis |
|
|
Tonicity is a measure of the solution's ability to change the volume and shape of cells by altering their water content. A cell in an _____solution does _____change shape because there is no concentration gradient and therefore no osmosis. A cell in a _____solution will lose water and _____. A cell in a _____solution will gain water. Hypotonic means less solute(and more water)in the solution than inside the cell. Hypertonic means more solute(and less water)in the solution than inside the cell. |
Isotonic, Not, Hypertonic, Crenate, Hypotonic |
|
|
In filtration, water and solutes are "pushed" through a membrane or capillary wall by _____pressure or blood pressure. In filtration, the gradient is a ________ gradient. Whatever is small enough to fit through the intercellular clefts or fenestrations, moves through. Think about the lab demo which used water, kitty litter, and a coffee filter. |
Hydrostatic; pressure |
|
|
The two most important active transport processes are _____transport and _____transport. |
Active, Vesicular |
|
|
Active transport is also called __________.Substances are moving "uphill" or against a gradient. It is similar to facilitated diffusion in that a __________is required. The carrier protein is called a __________. An example of a "pump" is the sodium-potassium pump which is especially active in muscle and nerve cells.It pumps sodium from inside of the cell to outside of the cell where it is in higher concentration. It also pumps potassium from outside of the cell to the inside of the cell where it is in higher concentration. We will be talking more about this particular pump. |
Solute Pumping, Carrier Protein, Solute Pump |
|
|
Vesicular transport involves moving substances into and out of cells in bulk via bubble-like membrane-bound organelles called vesicles. These vesicles are like cargo carriers. The two types of vesicular transport are _____and _____. |
Endocytosis and Excocytosis |
|
|
In endocytosis, cells "drink" and cells "eat." _____, which is cell drinking,is a routine activity of most cells. Extracellular fluid is taken into the cell when the plasma membrane invaginates and forms a vesicle. _____, which is cell eating, is a specialty of white blood cells called phagocytes.It is a protective mechanism. Phagocytes form flowing extensions called _____which flow around something large, like a virus or bacterium. As the pseudopods engulf the bacterium, a vesicle is formed.Once a vesicle is formed by these two methods, it fuses with an organelle called a _____and the contents are digested. |
Pinocytosis, Phagocytosis, Pseudopods, Lysosome |
|
|
In _____-_____ endocytosis, a specific substance binds with receptor proteins on the plasma membrane.An example of a specific substance would be _____-cholesterol. |
receptor-mediated, LDL |
|
|
_____ results in secretion which is the release of materials from a cell. Because of this, the vesicles are called _____ vesicles. The substance released is also called a secretion. Specific substances that are secreted include digestive enzymes, hormones, mucus, and neurotransmitters. Secretory vesicles form from Golgi, fuse with the plasma membrane, and release their contents into extracellular fluid. |
Exocytosis, secretory |
|
|
The two kinds of cell division are mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis is covered in this chapter. _____is responsible for growth, normal cell replacement, and repair._____has only one function,the formation of sex cells or _____.It is covered in Chapter 16 on the Reproductive System and also in lab. |
Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes |
|
|
Meiosis in males is called _____. It is the production of male gametes or _____. It occurs in the male gonad or _____. Meiosis in females is called _____. Oogenesis is the production of female gametes or _____. It occurs in the female gonad or _____. |
spermatogenesis, sperm, testis, oogenesis, ova, ovary |
|
|
Our body cells, or somatic cells, are diploid cells produced by mitosis. Sex cells (or gametes) are haploid cells produced by meiosis. Diploid,which is represented by the symbol _____, means having _____sets of chromosomes. One set of 23 comes from the mother in the ovum, and one set of 23 comes from the father in the sperm cell. During _____, the male and female gametes join to give the first cell of the new individual (the _____) a total of _____chromosomes. Every cell in the body has the same 46 chromosomes. Man's diploid or 2N number is _____. Haploid, which is represented by the symbol _____,means having 1 set of chromosomes. Man's haploid number or N number is _____. |
2N, 2, fertilization, zygote, 46, 46, N, 23 |
|
|
For both of mitosis and meiosis, the process starts with a _____cell and one replication of DNA molecules. In _____, the diploid cell divides onetime producing two daughter cells that are identical genetically to each other and to the mother cell. In _____, there are two divisions resulting in four _____gametes that differ genetically from one another. |
diploid, mitosis, meiosis, haploid |
|
|
The cell life cycle has two parts: _____and __________. The longer part is _____. If a cell is going to divide, DNA replication occurs during interphase. Cell division consists of _____, division of the nucleus, which is followed by division of the cytoplasm or _____. |
interphase, cell division, interphase, mitosis, cytokenisis |
|
|
the 2 identical parts of a duplicated chromosome attached at the centromere; when they separate during anaphase are called chromosomes. |
Chromatids |
|
|
region where chromatids attach to one another. |
Centromere |
|
|
structure composed of microtubules; provides for attachment and movement of chromosomes |
Mitotic Spindle |
|
|
What are the 4 stages of mitosis? (Play Me A Tune) |
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
|
what is the division of cytoplasm called? |
Cytokenisis |
|

|
Interphase |
|

|
Prophase |
|

|
Metaphase |
|

|
Anaphase |
|

|
Telophase |
|

|
Cytokinesis |
|
|
A _____is a mass of cells resulting from abnormal cell division. _____neoplasms are cancerous, and benign are not. They differ with respect to encapsulation and in the ability to metastasize. |
Neoplasm, Malignant |
|
|
A _____is a cancer causing agent, like a chemical or UV radiation. Carcinogens cause _____, or permanent changes,in genes which are formed from DNA. If you change the DNA of genes, you change the function. Genes that are mutated are those which control normal cell division. Cancer is the result of cell division "gone wild." The process by which cancer develops usually involves the accumulation of mutations over time (years of smoking, lots of exposure to UV radiation). |
Carcinogen, Mutations |
|
|
Proteins are made when the cell is in the part of its life cycle called _____.Protein Synthesis involves two phases: _____, when complementary mRNA is made using the information in the DNA gene and _____, when the information is translated from nucleic acids into proteins. Transcription occurs in the _____; translation occurs in the _____. |
interphase, transcription, translation, nucleus, cytoplasm |
|
|
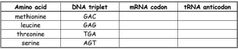
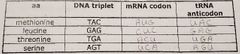
the sequence of base triplets in DNA is copied into a complementary sequence of codons in mRNA. |
transcription |
|
|
the nucleotide sequence in an mRNA molecule specifies the amino acid sequence of a protein or polypeptide; ribosomesin the cytoplasm are the "work benches" for this process. |
translation |
|
|
a piece of the DNA molecule that has the instructions for making one protein. |
gene |
|
|
a set of 3 sequential nucleotides in DNA that "spells" the name of a specific amino acid molecule. |
triplet |
|
|
a set of 3 sequential nucleotides complementary to a DNA triplet; found in mRNA. |
codon |
|
|
a set of 3 sequential nucleotides complementary to the mRNA codon; found on tRNA |
anticodon |
|
|
a single nucleotide strand; carries "message" from DNA to ribosome |
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
|
|
forms ribosomes |
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
|
|
carries an amino acid from the cytoplasm to the ribosome. |
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
|
|
for DNA, A pairs with T and C pairs with G; for RNA, A pairs with U and C pairs with G. |
complementary base pairing |
|
|
What is the first step of DNA forming a protein? |
A portion of the DNA helix uncoils |
|
|
What is the second step of DNA forming a protein? |
The nucleotide strands separate |
|
|
What is the third step of DNA forming a protein? |
an mRNA molecule is synthesized from the active strand |
|
|
What is the fourth step of DNA forming a protein? |
mRNA migrates from the nucleus to the ribosome |
|
|
What is the fifth step of DNA forming a protein? |
tRNA carries an amino acid to the ribosome and binds its anticodon to the codon |
|
|
What is the sixth step of DNA forming a protein? |
amino acids join by peptide bonds |
|
|
What is the seventh step of DNA forming a protein? |
tRNA molecules released to the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
|
|
A _____is a group of similar cells specialized to perform a specific function. _____is the study of tissues |
tissue. Histology |
|
|
The 4 major tissue types are: _____, _____, _____, and _____. _____tissue is the most abundant, the most widely distributed, and the most variable in appearance. |
epithelium, connective, muscle, and nervous. Connective |
|
|
_____tissues cover the body and some organs, they line the cavities of hollow organs and body cavities, and they form glands. Epithelium is given two names according to (1) __________(squamous, columnar, cuboidal)and also according to (2) the number of cell _____present (simple or stratified) |
epithelial, cell shape, layers |
|
|
Choose the characteristics for epithelium vascular/avascular; cells loosely or closely packed; little or a lot of intercellular material; basement membrane present or not present; regenerates or does not regenerate; cells have or have not specialized cell junctions |
avascular, closely packed, little, present, regenerates, has. |
|
|
The unattached surface of the sheet of cells is called the _____surface. It is exposed to the body's exterior, a body cavity, or the lumen of an organ. The attached surface is the _____surface. The __________is a thin, extracellular layer which holds the epithelium in place. |
apical, basal, basement membrane |
|
|
_____cells are cells that function as unicellular mucus-secreting glands. They are associated with simple columnar epithelium, which lines the digestive tract from the _____to the _____, and also pseudo stratified ciliated columnar epithelium, which lines most of the _____tract. |
goblet, stomach, anus, respiratory |
|
|
is the lining and covering tissue of the body; forms the glands in the body; hallmarks: cells close together forming sheets; cell junctions include desmosomes and tight junctions; sheets with basal and apical surfaces; avascular; functions include protection, absorption, secretion |
epithelium |
|
|
the most abundant and widely distributed tissue type; hallmarks: abundant non-living extracellular matrix; variations in blood supply; includes cartilage, bone, and blood |
connective tissue |
|
|
function is contraction; moves the body, moves blood, moves urine, and moves food |
muscle tissue |
|
|
forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves; has cell populations of neurons and neuroglia; an internal communication system using nerve impulses |
nervous tissue |
|
|
There are two types of glands, _____glands and _____glands. _____glands secrete their products into ducts that empty onto a surface or intothe lumen of a hollow organ. Examples include sweat glands and salivary glands._____glands("ductless glands") secrete _____directly into interstitial fluid without flowing through a duct. The pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands are examples of endocrine glands. |
exocrine, endocrine, exocrine, endocrine, hormones |
|
|
The two components of connective tissue are: widely spaced _____, the living component,and lots of extracellular _____,the non-living component. Matrix is usually secreted by the cells. It consists of two components, _____substance and _____.Ground substance contains water and organic molecules like proteins and polysaccharides. There are three kinds of fibers found in the matrix. (1) _____fibers are very strong and flexible fibers(like ropes). (2) _____fibers stretch and recoil. (3) _____fibers,which are formed from thin collagen fibers,form branching networks. |
cells, matrix, ground, fibers, collagen, elastic, reticular |
|
|
large connective tissue cells which function in secreting the fibers and ground substance of the extracellular matrix |
fibroblasts |
|
|
similar to fibroblasts, are found in reticular connective tissue |
reticular cells |
|
|
fat cells; are found in adipose tissue; are specialized for storage of triglycerides |
adipocytes |
|
|
produce the matrix in cartilage |
chondroblasts |
|
|
once the matrix is produced, chondroblasts become mature ________ |
chondrocytes |
|
|
mature bone cells |
osteocytes |
|
|
red blood cells |
erythrocytes |
|
|
white blood cells |
leukocytes |
|
|
Dense connective tissue has more fibers than loose and fewer cells. In dense _____connective tissue the fibers run in the _____direction; in dense _____the fibers run in _____directions. |
regular, same, irregular, random |
|
|
what is the most widely distributed connective tissue in the body? |
areolar connective |
|
|
There are three types of cartilage: _____cartilage, _____, and _____cartilage. _____cartilage is the most abundant cartilage in the body._____is the strongest cartilage. |
hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic, hyaline, fibrocartilage |
|
|
The two types of osseous tissue are (1) _____bone and(2) _____bone. |
compact, spongy |
|
|
Blood is also called _____tissue. Blood has a liquid matrix called _____. The three types of formed elements suspended in the plasma are _____, _____, and _____. |
vascular, plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets. |
|
|
The function of muscle is _____, a unique characteristic that sets it apart from any other body tissue. Skeletal muscle cells and smooth muscle cells are elongated, and for this reason they are called muscle _____. Smooth muscle is also called _____muscle because it is located in the walls of hollow _____(= viscera). |
contraction, fibers, visceral, organs |
|
|
where is the location of skeletal muscle? shape of the cell? nucleus number? striated or non-striated? branched or unbranched? voluntary or involuntary? speed of contraction? ability to stay contracted? |
attatched to bone, cylinder, multinucleate, striated, unbranched, voluntary, fastest, least |
|
|
where is the location of smooth muscle or visceral muscle? shape of the cell? nucleus number? striated or non-striated? branched or unbranched? voluntary or involuntary? speed of contraction? ability to stay contracted? |
walls of hollow internal organs, fusiform, uninucleate, no striations, unbranched, involuntary, slowest, greatest. |
|
|
where is the location of cardiac muscle? shape of the cell? nucleus number? striated or non-striated? branched or unbranched? voluntary or involuntary? speed of contraction? ability to stay contracted? |
walls of the heart, usually uninucleate, striated, branching with intercalated discs, involuntary, intermediate, intermediate |
|
|
Nervous tissue forms the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. There are two kinds of cell populations. _____, or nerve cells, transmit messages (nerve impulses) from one part of the body to another. The cytoplasm of the cell is drawn out into processes called axons and dendrites. All neurons have one_____. An axon carries information away from the cell body. The number of dendrites may vary. _____carry information toward the cell body. _____is the ability to respond to stimuli and initiate a nerve impulse._____is the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands._____are support cells. |
neurons, axon, dendrites, irritability, conductivity, neuroglia |
|
|
_____is the replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells. Epithelial tissues and bone regenerate._____involves repair by dense connective tissue or the formation of scar tissue. Cardiac muscle and nervous tissue are replaced by scar tissue. |
Regeneration. Fibrosis |
|
|
Which of these is associated with a skin allergy? Impetigo, psoriasis, cold sores, contact dermatitis |
Contact dermatitis |
|
|
Select all of the true statements regarding the pigment melanin. Melanin ranges in color from yellow to brown to black.; Melanin protects the nuclei of keratinocytes from ultraviolet (UV) radiation.; Freckles and moles appear where melanin concentrates in one spot.; Melanin production increases in the absence of sunlight exposure.; Star-shaped epidermal dendritic cells produce melanin. |
Melanin ranges in color from yellow to brown to black.; Melanin protects the nuclei of keratinocytes from ultraviolet (UV) radiation.; Freckles and moles appear where melanin concentrates in one spot. |
|
|
A mucous membrane __________. |
lines the digestive and respiratory tracts |
|
|
A needle would pierce the skin of the forearm in which order?(1) stratum basale; (2) stratum granulosum; (3) stratum spinosum; (4) stratum corneum; (5) stratum lucidum |
4-2-3-1 |
|
|
Lamellar corpuscles __________. |
are deep pressure-sensitive receptors |
|
|
Burns are assessed by the rule of __________. |
nines |
|
|
Which type of membrane lines body cavities that open to the exterior? |
Mucous membrane |
|
|
The __________ is the avascular, keratinized layer of skin. |
epidermis |
|
|
Most numerous cells of the epidermis |
Keratinocytes |
|
|
Produce the pigment melanin |
Melanocytes |
|
|
Sensitive to touch |
Merkel cells |
|
|
Help fight infection |
Epidermal dendritic cells |
|
|
The type of tissue that makes up the bulk of the dermis is __________. |
dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
Select all of the functions of skin. Protects internal body structures; Regulates body temperature; Excretes waste products; Synthesizes vitamin C; Stores calcium |
Protects internal body structures; Regulates body temperature; Excretes waste products |
|
|
The epidermis is predominately composed of __________ tissue. |
epithelial |
|
|
Select all of the true statements regarding the significance of alterations in skin color. Jaundice usually signifies a liver disorder in which excess bile pigments are deposited in body tissues.; Bruises reveal sites where blood has escaped from the circulation and formed hematomas.; Blanching (or pallor) may indicate embarrassment, fever, inflammation, or hypertension.; Erythema may indicate anemia and low blood pressure. |
Jaundice usually signifies a liver disorder in which excess bile pigments are deposited in body tissues.; Bruises reveal sites where blood has escaped from the circulation and formed hematomas. |
|
|
Select all of the characteristics of malignant melanoma. Irregular border; Asymmetry; Uniform color; Diameter smaller than a pencil eraser |
Irregular border; Asymmetry |
|
|
Select the terms that relate to hair. Follicle;Bulb; Sheath; Free edge; Lunule |
Follicle; Bulb; Sheath |
|
|
Mitosis occurs in which layer of the epidermis? |
Stratum basale |
|
|
All epithelial membranes have a layer of __________ that underlies an epithelial layer. |
connective tissue |
|
|
Sunburn without blistering represents which type of burn? |
First-degree burn |
|
|
One important role of the skin is to produce __________, which is essential for normal calcium absorption. |
vitamin D |
|
|
Which glands produce the oily secretion called sebum? |
Sebaceous glands |
|
|
As cells progress from the deeper portion of the epidermis toward the surface, __________. |
they become flatter and die |
|
|
Sebaceous glands are usually associated with __________. |
hair follicles |
|
|
As humans age, the skin's elasticity declines, and skin gets __________. |
Thinner |
|
|
Hair, nails, and the outer layer of the skin are made mostly of a tough protein called __________. |
Keratin |
|
|
What type of membrane surrounds each of the lungs? |
Serous |
|
|
Glands usually associated with the skin of the genitals and the axillary region, and which secrete fatty acids and proteins, are called _______. |
apocrine glands |
|
|
Pacinian corpuscles _______. |
are deep pressure-sensitive receptors |
|
|
Which of the following statements regarding the significance of alterations in skin color is FALSE?Blanching (or pallor) may signify anemia, low blood pressure, allergy, or impaired blood flow into an area.; Bruises reveal sites where blood has escaped from the circulation and produces hematomas.; None of the above statements is false.; Jaundice usually signifies a liver disorder in which excess bile pigments are deposited in body tissues.; Erythema may indicate embarrassment, fever, inflammation, or hypertension. |
Blanching (or pallor) may signify anemia, low blood pressure, allergy, or impaired blood flow into an area. |
|
|
The structure that contracts to cause "goose bumps" is the _______. |
arrector pili muscle |
|
|
The type of tissue making up the bulk of the dermis is _______. |
dense (irregular) connective tissue |
|
|
Two types of glands found in the skin are the _______ and _______ glands. |
sudoriferous; sebaceous |
|
|
You can cut your hair without feeling pain because _______. |
the shaft of the hair consists of dead cells |
|
|
All epithelial membranes have a layer of _______ underneath them. |
Connective tissue |
|
|
The layer of the skin that is made of stratified squamous epithelium is called the _______. |
Epidermis |
|
|
The thick proximal nail fold is commonly called the _______. |
Cuticle |
|
|
What kind of membranes line body cavities and, except for the dorsal body cavity and joint capsules, do not open to the outside of the body? |
Serous |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of malignant melanoma?Asymmetry; Varied color; Border irregularity; Smooth border; Diameter larger than a pencil eraser |
Smooth border |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of skin?It plays an important role in regulating heat loss from the body.; It protects the whole body from mechanical damage.; It insulates and cushions the body.; It produces vitamin C in the presence of sunlight.; It manufactures several proteins important to immunity and synthesizes vitamin D in the presence of sunlight. |
It produces vitamin C in the presence of sunlight. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding melanin?Melanin is produced by special cells called melanocytes.; Melanin ranges in color from yellow to brown to black.; The stratum basale cells phagocytize the melanin produced by the melanocytes and it accumulates within them.; Freckles and moles are seen where melanin is concentrated in one spot.; More melanin is produced when the skin is not exposed to sunlight. |
More melanin is produced when the skin is not exposed to sunlight. |
|
|
This type of membrane lines body cavities that are open to the exterior. |
mucous |
|
|
Sebaceous glands produce oils whereas the _______ glands produce sweat. |
sudoriferous |
|
|
One important role of the skin is to produce ______ _______, which is essential for healthy cell functioning. |
Vitamin D |
|
|
The _______ is the avascular, keratinized layer of skin. |
Epidermis |
|
|
The terms sheath, bulb, and follicle all relate to which of the following? |
Hair |
|
|
Most minor skin afflictions are attributed to infection or _______. |
Allergies |
|
|
Medications and stress can affect hair graying and loss; however, _______ factors play more of a key role. |
genetic |
|
|
Body membranes are classified according to ______ makeup and _______ in the body. |
tissue; location |
|
|
The three epithelial membranes are: Your skin or __________ membrane, ______ membranes (or mucosae) and ______ membranes (or serosae). |
cutaneous; mucous; serous |
|
|
The two tissue components of an epithelial membrane are an __________ tissue layer and an underlying __________ tissue layer. So, these membranes are actually simple organs. |
epithelial; connective |
|
|
stratified squamous epithelium + dense irregular connective tissue; a relatively dry membrane; is an external membrane that covers our body |
Cutaneous membrane |
|
|
epithelium (varies but examples are stratified squamous/simple columnar/pseudostratified ciliated columnar) + areolar connective tissue; connective tissue layer is called the lamina propria; are wet membranes and are usually associated with mucus; line body cavities that open directly to the exterior of the body like the digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts |
Mucous membrane |
|
|
simple squamous epithelium + areolar connective; occur in pairs, the parietal layer and the visceral layer; two layers are separated by a serous cavity with serous fluid; line body cavities that do not open directly to the exterior of the body (found in the thoracic and abdominal cavities of the ventral body cavity) |
Serous membrane |
|
|
The serous membranes lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs are the parietal and visceral _______, and the cavity is the _________ cavity. The serous membrane for the heart is the ____________, and the cavity is the ___________ cavity. The serous membrane for the abdominal cavity is the , and the cavity is the _______ cavity. |
pleurae; pleural; pericardium; pericardial; peritoneum; peritoneal |
|
|
A major function for the _________ __________ is protection. It is the body’s first line of defense against disease causing organisms. |
cutaneous membrane |
|
|
_______ __________, along with the skin, form the body’s first line of defense against disease causing organisms. Mucus prevents cavities from drying out. Mucus in the respiratory system traps debris in the air we inhale. It helps to lubricate food as it moves through the digestive tract. The epithelium lining the digestive tract functions in the secretion of enzymes and also in the absorption of small food molecules. |
Mucous membranes |
|
|
_______ reduces friction during movement of organs |
Serous fluid |
|
|
________ membranes line the articular capsules of synovial (or freely movable) joints. Serous membranes also line ______ and ______ sheaths. LIKE serous membranes, they line cavities that do not open to the exterior of the body. Synovial membranes are composed only of _______ connective tissue. Therefore, these are not epithelial membranes. They are connective tissue membranes. Synovial membranes secrete ________ fluid. FUNCTION: Synovial fluid reduces friction between moving parts. |
Synovial; bursae; tendon; areolar; synovial |
|
|
The largest organ of the body is the ______. It plus its appendages, ______ glands and ______ glands and _____ and ______ make up the __________ System |
skin; sweat; oil; hair; nails; Integumentary |
|
|
Give five functions for the skin |
Protects, regulates body temperature, excretes, gives information about external environment, synthesizes vitamin D |
|
|
The skin protects _________ (as an intact barrier against invading microbes), the skin protects _____ (with the production of melanin and oil and sweat), and the skin protects ________ (with phagocytes) |
physically; chemically; biologically |
|
|
Modified _________ molecules in skin cells are converted to vitamin D in the presence of sunlight. Synthesis is completed in the kidneys to produce calcitriol, an active form of vitamin D. Vitamin D is necessary for the absorption of dietary ________ from the gastrointestinal tract into the blood. |
cholesterol; calcium |
|
|
The skin is composed of two tissue layers. The superficial layer of the skin is called the _______. It is composed of _________ _________ epithelium. Deep to the epidermis is the ___. It is composed mainly of _____ ______ _____ tissue. Deep to the dermis is the subcutaneous layer or _________. It is an area of connective tissue, both ______ and _____ connective, that anchors the skin to structures below. |
epidermis; stratified squamous; dermis; dense irregular connective; hypodermis; adipose; areolar |
|
|
The epidermis is composed of up to five layers. “Thin” skin has ____ layers, and “thick” skin has ____. They are, from deep to superficial: stratum ______, stratum _____, stratum _____, stratum _____, and stratum _____. Stratum _____ is present only in “thick” skin which is located on fingertips, palms, and soles of the feet. Most of the epidermis consists of stratum _____. These dead cells are completely filled with the protein, _____. This layer helps to make the skin a protective structure. Most of the dust in your house consists of cells from this layer which have been shed from your body! Excessive shedding of this layer is called _____. |
four; five; basale; spinosum; granulosum; lucidum; corneum; lucidum; corneum; keratin; dandruff |
|
|
Most cells in the epidermis are _________. Keratinocytes produce _____, a tough, fibrous protein. Keratinocyte stem cells in stratum _______ undergo continuous _____ cell division to produce new epidermal skin cells. Because of this, the layer is also called stratum __________. Stratum basale is a well-nourished layer that depends on diffusion of nutrients and oxygen from blood vessels in the dermis. |
keratinocytes; keratin; basale; mitotic; germinativum |
|
|
Melanocytes, located in stratum ______, produce the pigment, ______. The amount and kind of melanin produced results in different skin colors. Exposure to sunlight increases melanin production and gives the skin a tanned appearance. Within limits, melanin protects the DNA of keratinocytes from UV radiation in sunlight. |
basale; melanin |
|
|
Other cells found in the epidermis are __________ cells also called Langerhans cells. They are important in alerting the immune system to foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. Cells that function in detecting touch are tactile or _______ cells. |
dendritic; Merkel |
|
|
The dermis consists of connective tissue. It has two regions. The superficial ______ layer of _______ tissue, and the deep _______ layer of ______ ______ connective tissue. The papillary layer has finger-like projections called dermal ______. These indent the epidermis and form ridges and patterns that are unique. They form our _________. Both collagen and elastic fibers are found throughout the dermis. _______ fibers make skin strong and ________ fibers make it stretchy…when we are young! |
papillary; areolar; reticular; dense irregular; papillae; fingerprints; Collagen; elastic |
|
|
_________ glands are commonly called oil glands. They are found all over the skin except on the palms and soles of the feet. They are usually connected to hair follicles. Sebaceous glands secrete oil or sebum. _____ lubricates and defends against certain bacteria. |
Sebaceous; Sebum |
|
|
___________ glands are commonly called sweat glands. They secrete sweat or perspiration. Sweat is mainly water plus salt, ammonia, urea, uric acid, and lactic acid. _____ sweat glands are found all over the body. Their main function is to help regulate body temperature through evaporation. They also function in eliminating small amounts of wastes and in inhibiting the growth of some bacteria. ______ sweat glands are located primarily in the axilla and groin. Their secretion is sweat plus lipids and proteins. When this secretion is utilized by bacteria, an odor is produced. |
Sudoriferous; Eccrine; Apocrine |
|
|
The part of the hair that projects above the surface of the skin is the ____; the part below the surface of the skin is the ____. The root is enclosed in the hair follicle which produces the hair. The follicle is formed from an inner layer of _________ tissue that forms the hair; it is covered by an outer layer of ________ tissue. The connective tissue supplies blood vessels to stratum basale in a nipple-like hair ______. Stratum basale cells at the bottom of the follicle divide mitotically resulting in growth of a hair. Muscle connects the hair follicle to the dermis. It is _________ muscle called the ________ _______ muscle. When it contracts, the hair is pulled upright, producing goosebumps |
shaft; root; epithelial; connective; papilla; smooth; arrector pili |
|
|
The seriousness of a burn is determined, in part, by both the _____ and the _______ of the burned area. |
depth; extent |
|
|
Burns are classified according to how deep they go. In ____ degree burns, only the epidermis is damaged. In _____ degree burns, the epidermis and the upper dermis are damaged. First and second degree burns are called _____-thickness burns. |
first; second; partial |
|
|
_____ degree burns destroy the entire thickness of the skin and often extends into the subcutaneous layer. ___ degree burns extend into muscle and bone. Both third degree and fourth degree burns are called _____-thickness burns. |
Third; Fourth; full |
|
|
How much of body surface that is burned is called the extent of burns. The _____ __ _____ is used to estimate surface area of a burn. The greater the surface area that is burned, the greater the volume of ____ that is lost and must be replaced. |
rule of nines; fluid |
|
|
The two life-threatening consequences of a severe burn are ____ and _____. The immediate concern is _______ because burned skin is sterile for about 24 hours. |
dehydration; infection; dehydration |
|
|
The most important risk factor for skin cancer is overexposure to ______. The three kinds of skin cancer are _______ _____ carcinoma, ______ ______ carcinoma, and _________. |
sunlight; squamous cell; basal cell; melanoma |
|
|
________ _____ ________ involves cells of stratum basale, and it is the least malignant and most common skin cancer. ________ ______, a cancer of melanocytes, is the deadliest. |
Basal cell carcinoma; Malignant melanoma |
|
|
The ABCDE rule for recognizing melanoma is: |
A = asymmetry; B = border irregularity; C = color; D = diameter; E = evolution |
|
|
Why are tattoos considered to be permanent? |
Pigment is deposited into the dermis which is never shed. |
|
|
Inherited inability to produce melanin |
albinism |
|
|
Infection of sebaceous glands |
Acne |
|
|
A fungal infection of the skin of the foot |
Athlete's foot |
|
|
Exposure of sebum in blocked duct to air |
blackhead |
|
|
A separation of dermis and epidermis with fluid accumulation in the space |
Blister |
|
|
Fluid-filled blisters caused by a virus |
Cold sore |
|
|
A bluish color to the skin due to insufficient oxygen |
cyanosis |
|
|
Bedsores caused by prolonged pressure |
decubitus ulcer |
|
|
Red color to skin |
Erythema |
|
|
Accumulations of melanin |
freckles/liver spots/moles |
|
|
Blood clots |
hematomas |
|
|
A highly contagious skin infection caused by bacteria; common in children |
Impetigo |
|
|
An abnormal yellow skin tone which signifies a liver disorder |
Jaundice |
|
|
Overproduction of skin cells; thought to be an autoimmune disorder |
Psoriasis |
|
|
A white cheesy-looking substance, produced by the sebaceous glands, which protects the baby’s skin inside the mother |
vernix caseosa |
|
|
Blockage of sebaceous gland duct by sebum |
Whitehead |
|
|
Mature bone cell |
Osteocyte |
|
|
Bone-building cell |
Osteoblast |
|
|
Bone-destroying cell |
Osteoclast |
|
|
Contains osteons |
Compact bone |
|
|
Contains trabeculae |
Spongey bone |
|
|
Which disease results from the "wear and tear" on joints over many years? |
Osteoarthritis |
|
|
Select all of the characteristic features of cervical vertebrae. Spinous processes often short and divided into two branches; Presence of foramina in transverse processes; Large blocklike bodies; Presence of costal facets |
Spinous processes often short and divided into two branches; Presence of foramina in transverse processes |
|
|
Select the characteristic of a female pelvis. Angle of pubic arch more than 90 degrees; Pelvic bones heavier and thicker; Ischial spines shorter and closer together; Sacrum shorter and more curved |
Angle of pubic arch more than 90 degrees |
|
|
Select all of the fracture types that are particularly common in the elderly. Compression; Comminuted; Greenstick; Spiral; Depressed |
Compression; Comminuted |
|
|
In a ________ fracture, the bone splinters into three or more fragments. The aged are more susceptible to this type of fracture because their bones are more brittle. |
comminuted |
|
|
In a _______ fracture, the bone is crushed. This type of fracture is more common in older people because their bones are more porous. The vertebrae are particularly susceptible to compression fractures. |
compression |
|
|
________ fractures are more prevalent in children, whose bones are more flexible. These are partial fractures in which one side of the bone breaks while the other side bends. |
Greenstick |
|
|
_____ fractures are common in sports injuries. Excessive twisting forces result in a ragged break along the long axis of the bone. |
Spiral |
|
|
In a ______ fracture, the broken part of the bone is pressed inward. These breaks are typical of skull fractures. |
depressed |
|
|
True or False Bones are remodeled continually in response to changes in blood calcium ion levels and the pull of gravity and muscles on the skeleton |
True |
|
|
True or false Except for flat bones that form on fibrous membranes, most bones develop using hyaline cartilage structures as their “models.” |
True |
|
|
True or false When blood calcium ion levels drop below homeostatic levels, the parathyroid glands release PTH, a hormone that activates osteoblasts in bones. |
False |
|
|
True or false Growth hormone controls appositional growth, the process by which bones increase in length. |
False |
|
|
Select all of the characteristics of a synovial joint. Articular cartilage covers the ends of adjoining bones.; A fluid-filled joint cavity separates adjoining bones.; The functional classification is synarthrosis.; Examples include symphyses and synchondroses.; Collagen fibers hold the adjoining bones together. |
Articular cartilage covers the ends of adjoining bones.; A fluid-filled joint cavity separates adjoining bones. |
|
|
The true ribs __________. |
attach directly to the sternum by costal cartilages |
|
|
Place the events of bone fracture repair in the correct order.(1) bony callus forms; (2) fibrocartilage callus forms; (3) hematoma forms; (4) bone remodeling occurs |
3-2-1-4 |
|
|
The foramen magnum is a feature of the __________ bone. |
occipital |
|
|
The __________ is an important cranial landmark, as it houses the pituitary gland. |
sella turcica (Turk’s saddle) |
|
|
Which of the following bones belongs to the appendicular skeleton? Clavicle; Frontal bone; Vertebra; Sternum |
Clavicle |
|
|
The sagittal suture is located between the __________ and __________ bones. |
left parietal; right parietal |
|
|
The glenoid cavity is located where the __________. |
Head of the humerus articulates with the scapula |
|
|
The skeleton is organized into two subdivisions: the axial skeleton and the __________ skeleton. |
appendicular |
|
|
The spinal curvatures in the __________ and __________ regions are referred to as primary curvatures because they are present when we are born. |
thoracic; sacral |
|
|
What bone shape is the humerus? |
Long bone |
|
|
What bone shape is the sternum? |
Flat bone |
|
|
What bone shape is a tarsal? |
Short |
|
|
What bone shape is a vertebra? |
Irregular |
|
|
The hard palate (roof of the mouth) is composed of the __________ and __________ bones. |
maxillae; palatine |
|
|
The __________ bones form the lateral portion of the eye orbits, are lateral to the nose, and articulate with the maxillae. |
Zygomatic |
|
|
Tiny canals that connect bone cells to the nutrient supply |
Canaliculi |
|
|
Tiny cavities that contain osteocytes |
Lacunae |
|
|
Concentric rings of bone tissue |
Lamellae |
|
|
contain blood vessels and nerves and run perpendicular to the bone shaft |
Perforating (Volkmann's) canals |
|
|
Run lengthwise through the center of each osteon and parallel to the bone shaft. |
Central (Haversian) canals |
|
|
Select all of the functions of bone. Supports and protects; Allows movement; Stores minerals; Synthesizes vitamin D |
Supports and protects; Allows movement; Stores minerals |
|
|
Which type of joint permits the thumb to move toward the other fingers? |
Saddle joint |
|
|
The coronoid process, olecranon, and trochlear notch are features of the __________. |
Ulna |
|
|
The pectoral girdle is composed of the__________. |
scapula and clavicle |
|
|
Which of the following are paired bones of the cranium? Parietal and temporal; Parietal and maxillary; Frontal and occipital; Frontal and parietal |
Parietal and temporal |
|
|
Name the canals that, in dense bone, are the communication from the outside of the bone to its interior central canals. |
Volkmann's (perforating) canals |
|
|
True or false When blood calcium levels drop below homeostatic levels, the parathyroid glands release PTH, a hormone that activates osteoclasts in bones. |
True |
|
|
True or false The process by which bones increase in diameter is called appositional growth, a process of long-bone growth that is controlled by growth hormone and, during puberty, by the sex hormones. |
True |
|
|
Which of the following is a characteristic of the thoracic vertebrae? The dense process on the axis acts as a pivot for rotation.; Modified atlas and axis; The vertebral artery is found in the transverse foramen.; Presence of facets for ribs; Presence of transverse foramina |
Presence of facets for ribs |
|
|
Which of the following is a characteristic of a synovial joint?Articular cartilage; Joint cavity; diarthrotic; Fibrous articular capsule; All of the above are characteristics of a synovial joint. |
All of the above are characteristics of a synovial joint. |
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a function of bone?Storage; Breakdown of proteins into amino acids; Support; Movement; Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) |
Breakdown of proteins into amino acids |
|
|
In an osteon, bone cells are arranged in concentric circles around longitudinal tubes called _______. |
Haversian canals |
|
|
Which structure is contained within the lacuna of living bone? |
Osteocyte |
|
|
The cell type that is responsible for basic bone formation is the _______. |
Osteoblast |
|
|
The metacarpophalangeal joints are examples of which type of synovial joint, based on shape? |
Condyloid joint |
|
|
Ligaments join _______ to bone at joints. |
Bone |
|
|
Among other functions of bones, they store _______ and _______. |
minerals, fat |
|
|
Blood cell formation called _______ occurs within the marrow of certain bones. |
hematopoiesis |
|
|
The femur is an example of this category of bone. |
Long bone |
|
|
The _______ is an opening in the skull that surrounds the lower part of the brain and allows the spinal cord to connect with the brain. |
foramen magnum |
|
|
_______ involves the accumulation of uric acid in the blood, which is then deposited as needle-shaped crystals in the soft tissues of joints, causing pain. |
Gout |
|
|
Bones have to be physically _______ to remain healthy; this means being active through exercise that keeps the body moving for extended periods of time. |
Stressed |
|
|
Twiddling your thumbs utilizes which type of joint? |
saddle |
|
|
In addition to bones, what other structures are included in the skeletal system? |
joints, cartilages, and ligaments |
|
|
A ________ is dense regular connective tissue that attaches bone to bone. |
ligament |
|
|
A _______ is a cord of dense regular connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone. |
tendon |
|
|
Give five functions of the skeletal system. |
support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell formation |
|
|
Adipose tissue or _____ is stored in the medullary cavities of adult bones. Bone also stores the minerals ______ and ________. |
fat; calcium; phosphorus |
|
|
___________ is formation of blood cells and platelets. This process occurs in the cavities of certain bones like the skull bones, the sternum, and the proximal epiphyses of the femur and humerus where red bone marrow is found. |
Hematopoiesis |
|
|
Like other connective tissues, bone contains an abundant non-living extracellular ______ and widely separated cells. Within the matrix, _______ fibers give bone strength and flexibility. The ________ salts, mainly calcium phosphate, make it hard. |
matrix; collagen; mineral |
|
|
_____________ build bone matrix. They are found on bone surfaces. When they become trapped in the matrix they are building, they become ________. |
Osteoblasts; osteocytes |
|
|
________ are mature bone cells, and they are the main cells in bone tissue. They are involved with daily metabolism. |
Osteocytes |
|
|
________ break down bone matrix. They release acid which breaks down the calcium salts releasing calcium and phosphate ions into the blood. Their lysosomes release enzymes which break down collagen. This is called _____ _________. Like osteoblasts, they are found on bone surfaces. |
Osteoclasts; bone resorption |
|
|
There are two kinds of osseous tissue. _______ bone is dense and looks smooth. It makes up most of total bone mass. ______ bone consists of thin plates of bone and has many spaces like a sponge. Because of this, it is lighter in weight than compact bone. |
Compact; Spongy |
|
|
How many bones are there? |
The adult skeleton is composed of 206 bones. |
|
|
Bones are classified according to shape into four groups. Name the groups and give an example of a bone in each group. |
The four groups according to shape are: long bones, short bones, flat bones, and irregular bones. |
|
|
The long, cylindrical, main portion, or shaft, of the bone is the _____. The distal and proximal ends are called the _______. |
diaphysis; epiphyses; |
|
|
The covering over the epiphyses, where the bone forms an articulation, is a thin layer of _____ cartilage called the articular cartilage. The rest of the bone is covered by the ________ which is ______ ________ connective tissue. |
hyaline; periosteum; dense irregular |
|
|
The space within the diaphysis is called either the _______ cavity or the _____ cavity. In adults it contains ______ bone marrow. In infants it contains ____ bone marrow. The lining of the medullary cavity is called the ________. |
medullary; marrow; yellow; red; endosteum |
|
|
In a growing bone, there is a region of ______ cartilage between the epiphysis and diaphysis, that enables the bone to grow in length. This is the growth plate or _______ plate. When a bone stops growing the plate is replaced by bone and is called the ______ _____. |
hyaline; epiphyseal; epiphyseal line |
|
|
The _____ (or Haversian system) is the unit of structure and function in _______ bone. Each osteon consists of a central canal, lamellae, canaliculi, lacunae, and osteocytes. |
osteon; compact |
|
|
In the center of the osteon is a longitudinal channel containing blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves. It is the _____ ____. |
central canal |
|
|
The ______ form concentric rings of matrix between rings of bone cells or osteocytes. The osteocytes “sit” in small spaces between the lamellae called _____. |
lamellae; lacunae |
|
|
Small channels…”cracks” in the matrix…connect the central canal with the lacunae. They are filled with extracellular fluid and form a transportation system for nutrients and cell wastes. These are the ________. |
canaliculi |
|
|
The thin bony plates forming spongy bone are called ________. There are lamellae and osteocytes in lacunae and canaliculi but no _____ _____. |
trabeculae; central canal |
|
|
In newborns, all bone marrow is red. How is this different in an adult? In ____ red bone marrow is found in the _____ bone of flat bones of the skull and pelvis, the ribs, sternum, and proximal epiphyses of the humerus and femur. ______ marrow consists of reticular tissue. ______ bone marrow consists of adipose tissue. Yellow marrow is found in the ______ _______ of adult long bones. |
adults; spongy; Red; Yellow; medullary cavities |
|
|
________ is the formation of bone. There are two types: __________ (within membrane) ________ and _______ (within cartilage) _______. |
Ossification; intramembranous ossification; endochondrial ossification |
|
|
The flat bones of the skull and the mandible are formed by ________ ______. Most of the bones of the body are formed by ________ _______. _________ (or mineralization) is the deposit of calcium salts around collagen fibers. |
intramembranous ossification; endochondrial ossification; Calcification |
|
|
A _______ (“soft spot”) is an area between the cranial bones of an infant’s skull that has not yet ossified. They provide flexibility to the skull as the baby moves through the birth canal. They also permit brain growth during infancy. |
fontanel |
|
|
The ________ ______, or growth plate, is a region of _______ _______ between the diaphysis and epiphysis. It is responsible for the _________ growth of long bones. |
epiphyseal plate; hyaline cartilage; lengthwise |
|
|
As a bone grows, ____ _____ are formed on the Epiphyseal side of the plate, while _____ _______ on the diaphyseal side of the plate are replaced by bone. Initially the plate maintains its thickness as it is pushed away from the ______ _____. However, the rate of building bone (replacing the cartilage on the diaphyseal side) will become faster than new cartilage production on the epiphyseal side. Eventually bone replaces all of the cartilage, and the epiphyseal plate becomes the __________ _______. |
new chondrocytes; old chondrocytes; medullary cavity; epiphyseal line |
|
|
_________ growth is bone growth in thickness or diameter. ___________ deposit bone on the outer surface, and __________ destroy bone on the inner surface enlarging the medullary cavity. |
Appositional; Osteoblasts; osteoclasts |
|
|
During childhood ______ hormone promotes growth at the epiphyseal plate. This hormone is produced by the ______ lobe of the _______ gland. At puberty, the ____ _____ speed up the process. Ultimately, the ____ _____ also shut down growth at the epiphyseal plates. |
growth; anterior; pituitary; sex hormones; sex hormones |
|
|
Two factors that affect bone remodeling are 1) ______ levels in the blood, and 2) the pull of _______ and ________ on the skeleton. Bones become thicker and stronger with ________ mechanical stress, and they tend to lose mass and to atrophy with a ________ in mechanical stress. “Use it or lose it.” |
calcium; gravity; muscles; increased; decrease |
|
|
Calcium ion homeostasis of blood is controlled by _______ feedback. |
negative |
|
|
When blood calcium levels drop, the __________ glands secrete _________ hormone (PTH). PTH stimulates ____________ to break down bone matrix and release calcium into the blood. PTH is a ________ hormone. It increases calcium levels in the blood. |
parathyroid; parathyroid; osteoclasts; hypercalcemic |
|
|
When blood calcium levels rise, the ________ gland secretes the hormone, __________ to decrease ________ activity. It acts antagonistically to PTH. _______ is a __________ hormone. It decreases calcium levels in the blood. |
thyroid; calcitonin; osteoclast; Calcitonin; hypocalcemic |
|
|
A ________ is a break in a bone. In a ________ _______, the broken bone does not penetrate the skin. In a ________ ________, the skin is penetrated. |
fracture; simple fracture; compound fracture |
|
|
In ______ reduction, the fractured ends of a bone are brought into alignment by manual manipulation. In ____ reduction, the fractured ends are brought into alignment by a surgical procedure, and the ends are secured with pins, wires, screws, rods, plates. |
closed; open |
|
|
Why are greenstick fractures more common in children? In children, bones are not fully ______. They have more _______ than inorganic salts. Remember that ________ is a strong and flexible protein. It is like a rope, difficult to break. |
ossified; collagen; collagen |
|
|
Why do bone injuries heal much more rapidly than injuries to cartilage? |
Bone heals more rapidly because bone is highly vascularized, and cartilage is avascular. |
|
|
Briefly describe the stages in the healing of a bone fracture. |
Steps: Formation of a fracture hematoma ->Fibrocartilage callus formation -> Bony callus formation -> Bone remodeling |
|
|
Joints, where two or more bones meet, are also called _________. Joints can be classified in two ways. The ________ classification is based on the amount of movement the joint allows as immovable, slightly immovable, and freely movable. The ________ classification is based on whether there is a cavity between the bones or whether there is some kind of connective tissue attaching the bones together. |
articulations; functional; structural |
|
|
Structurally there are fibrous joints, cartilaginous joints, and synovial joints. Examples of fibrous joints are the _______ of the skull. These are _________ joints. Examples of immovable cartilaginous (hyaline) joints are the joints between _____ 1-7 and the sternum. Examples of slightly movable cartilaginous joints are the fibrocartilage discs between the ______. |
sutures; immovable; ribs; vertebrae |
|
|
________ joints are joints in which the articulating bone ends are separated by a joint cavity containing synovial fluid. Synovial joints are _____ movable joints. All the joints of the limbs are _______ joints. |
Synovial; freely; synovial |
|
|
Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults -> thick misshapen bones of face, hands, feet |
Acromegaly |
|
|
Inflammation of bursae |
Bursitis |
|
|
Hypersecretion of growth hormone in children -> normal body proportions but extremely tall |
Gigantism |
|
|
Deposit of uric acid crystals in the joints |
Gouty arthritis |
|
|
Degeneration of articular cartilage; usually in elderly; “wear-and-tear” arthritis |
Osteoarthritis |
|
|
Bone resorption is faster than bone deposition -> not enough calcium |
Osteoporosis (porous bones) |
|
|
Hyposecretion of growth hormone in children -> normal body proportions but maximum height of 4 feet |
Pituitary dwarfism |
|
|
An autoimmune disease causing inflammation of joints; eventually ends of bones become fused |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
|
|
Calcium salts are not deposited and bones become soft and easily deformed |
Rickets |

