![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What forms the apex of the axilla?
|
The convergence point of the clavicle, superior border of the scapula and the first rib.
|
|
|
The _____________________ is the entrance to the axilla. This is found at the _________ of the axilla.
|
-cervicoaxillary canal
-apex |
|
|
What is thoracic outlet syndrome?
|
When the cervicoaxiallary canal narrows, impinging on the axillay nerve.
|
|
|
The base of the axilla is formed of the
|
axillary fasia, superficial fascia, and skin of the axillary fossa
|
|
|
What makes the anterior wall of the axilla?
|
pectoralis major and minor
|
|
|
What makes the posterior wall of the axilla?
|
scapula, subscapularis muscle, latissimus dorsi, teres major
|
|
|
What makes the lateral wall of the axilla?
|
intertubercular groove between the humerus and long head of the biceps brachii
|
|
|
What makes the medial wall of the axilla?
|
the chest wall and intercostal musclecs covered by the serratus anterior
|
|
|
What nerve innervates the serratus anterior?
|
the long thoracic nerve
|
|
|
What is the action of the serratus anterior?
|
it holds the scapula close to chest wall (protraction) and upwardly rotates the glenoid cavity by pulling the inferior angle of the scapula laterally
|
|
|
You can find the serratus anterior being pierced by what nerves?
|
lateral cutaneous branches of intercostal nerves
|
|
|
Paralysis of which muscle causes winging of the scapula?
|
serratus anterior
|
|
|
How can you test if a patient has paralysis of the serratus anterior?
|
have him push against a wall to see if the scapula wings out
|
|
|
Winging of the scapula is associated with difficulty of what action?
|
abduction of arm above the horizontal
|
|
|
What are the contents of the axilla?
|
1. axillary artery
2. axillary vein 3. brachial plexus 4. axillary lymph nodes |
|
|
Which structures are enclosed in the axillary sheath?
|
1. axillary artery
2. axillary vein 3. brachial plexus |
|
|
Where do you inject anesthetic to perform a nerve block of the brachial plexus?
|
into the axillary sheath
|
|
|
At which point does the subclavian artery become the axillary artery?
|
the lateral border of the first rib
|
|
|
The axillary artery is a continuation of the...
|
subclavian artery
|
|
|
The axillary artery becomes the ____________ at what point?
|
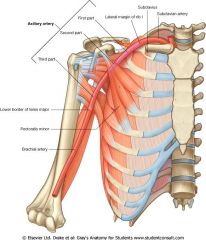
brachial artery at the inferior border of the teres major
|
|
|
The axillary artery is divided into 3 parts by what muscle?
|
pectoralis minor
|
|
|
What are all the branches of the axillary artery? Organize your answer by the three parts.
|

She Tastes Like Sweet Apple Pie
|
|
|
The _____________ artery traverses the quadrangular space with the axillary nerve.
|
posterior humeral circumflex artery
|
|
|
Between the first rib and the subscapular artery, _____________ of the axillary artery can form allowing blood to bypass ______________ in that area.
|
-arterial anastomoses
-vascular stenosis |
|
|
How do you control bleeding from the axillary or brachial artery?
|
compress the subclavian against the 1st rib
|
|
|
The axillary vein is a continuation of what vein? When does this happen?
|
continuation of the basillic vein at the inferior border of the teres major
|
|
|
The axillary vein becomes the ______________ at the lateral border of the first rib.
|
subclavian vein
|
|
|
What major vein drains into the medial part of the axillary vein?
|
cephalic vein
|
|
|
An injury at the point where the axillary vein turns into the subclavian vein is dangerous because...
|
-dangerous bleeding
-air can be sucked into the vein, causing a dangerous air embolism |
|
|
Axillary and subclavian veins are frequently used by doctors to...
|
administer fluids, medications, renal dialysis, etc.
|
|
|
The brachial plexus is formed by the _________ of which nerves?
|
anterior rami of spinal nerves C5 to T1
|
|
|
What are the stages of the brachial plexus?
|
ROWDY TEENS DRINK COLD BEER
R- roots T-trunks D-divisions C-cords B-branches |
|
|
The female breast is supplied by branches of what arteries?
|
-internal thoracic artery
-thoracic aorta -subscapular artery -thoracoacromial trunk |
|
|
What nerves form the superior, middle, and inferior trunks?
|
-Superior: C5 and C6
-Middle: C7 -Inferior: C8 and T1 |
|
|
What forms the lateral cord of the brachial plexus?
|
the anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunks
|
|
|
What forms the medial cord of the brachial plexus?
|
The anterior division of the inferior trunk
|
|
|
What forms the posterior cord of the brachial plexus?
|
The posterior divisions of all three trunks
|
|
|
What does the lateral cord divide into?
|
-musculocutaneous nerve
-lateral root of median nerve |
|
|
What does the posterior cord divide into?
|
-the radial nerve
-the axillary nerve |
|
|
What does the medial cord divide into?
|
-medial root of median nerve
-ulnar nerve |
|
|
Erb's palsy occurs from nerve lesions of the ___________________, usually from a violent increase in the angle between the neck and the shoulder.
|
upper part of the brachial plexus (C5 and C6)
|
|
|
Erb's palsy results in the characteristic ___________________ position
|
waiter's tip (medial rotation of arm, hand pronated)
|
|
|
In Klumpke's paralysis, nerve lesions of the ______________________, usually from jerking the arm when it's in an upward position, result in the characteristic _____________ position.
|
lower part of the brachial plexus (C8 and T1) cause the claw hand
|
|
|
Nerve lesions of the upper part of the brachial plexus cause
|
erb's palsy
|
|
|
Nerve lesions of the lower part of the brachial plexus cause
|
Klumpke's paralysis
|

