![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
8 Muscles divided into 3 layers |
SUPERFICIAL LAYER: Pronator Teres, Flexor Carpi Radialis, Palmaris Longus, Flexor Carpi Ulnaris (exception ulnar nerve) INTERME. LAYER: Flexor Digitorum Superficialiis DEEP LAYER: Flexor Digitorum Profundus (1/2 ulnar), Flexor pollicis longus, Pronator Quadratus **ALL innervated by median N except 1.5 |
|
|
Flexor Layers (Origin) Superficial and intermediate layers |
Arise by a "common flexor tendon" from the medial epicondyle of the humerus |
|
|
Deep Flexor Layers (origin) |
None arise from humerus. They arise from radius or ulna. |
|
|
Arteries of the Forearm |
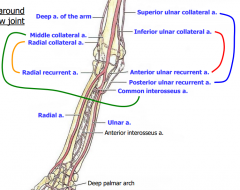
Brachial---> Radial and Ulnar A. Radial A----> radial recurrent artery (to elbow), past the wrist continues as deep palmar Arch. Ulnar A---> Ulnar Recurrent arteries (to elbow), common interosseous artery---> Anterior interosseous A, and posterior interosseous A*, past the wrist its superficial palmar Arch All A of forearm in anterior compartment (*Exc |
|
|
Anastomoses around elbow joint |
|
|
|
Radial N of the forearm |
Passes anterior to lateral epicondule of humerus splits into deep radial n: passes into posterior compartment and become posterior interosseous n. Superficial radial n: to skin of lateral forearm and dorsum of hand. |
|
|
Median N of forearm |
Crosses cubital fossa medial to brachial A. Anterior interosseous branch supplies deeper muscles Descends forearm sandwhiched between FDS and FDP Travels through carpal tunnel of wrist into hand. |
|
|
Ulnar N of forearm |
Passes posterior to medial epicondyle of humerus Travels down medial forearm medial to Ulnar A. Crosses wrist superficial to flexor retinaculum. |
|
|
Flecor Retinaculum |
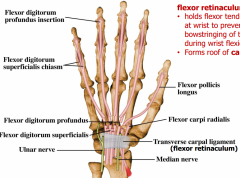
Holds flexor tendons in place at wrist to prevent bowstringing of tendons during wrist flexion Forms roof of carpal tunnel. |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel |
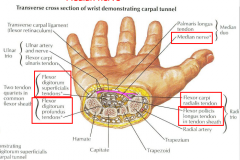
carpal tunnel has tendons of: Flexor Carpi radialis Flexor Digitorum superficialis Flexor pollicis longs Flexor Digit prof Median Nerve. |
|
|
Hand of Benediction |
Paralysis of Median N at elbow, Cannot flex 2nd and 3rd digits, cannot flex thumb at proximal interphalangeal join, can weakly flex 4th and 5th digits (medial part of FDP innervated by ulnar nerve) |
|
|
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome |
Compression of median n occurs if an lesion reduces the side of the carpal tunnel Cause tingling (parasthesia) loss of sensation (anesthesia) or diminshed sensation (hypoesthesia) in lateral 3.5 fingers Can eventually result in atrophy of thenar muscles. |
|
|
Cutaneous Innervation of the Hand |
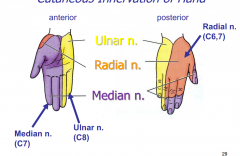
Median nerve: anterior lateral side Ulnar nerve: anterior and posterior medial side Radial nerve: posterior lateral side |

