![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
429 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are special senses? |
Any sense that has a specific organ(s) dedicated to their function |
|
|
What are out six senses? |
Touch Smell Taste Hearing Balance Sight |
|
|
Touch technical term |
Tactile |
|
|
Smell technical term |
Olfactory |
|
|
Tastes technical term |
Gustatory |
|
|
Hearing technical term |
Auditory |
|
|
Balance technical term |
Vestibular |
|
|
Sight technical term |
Vision |
|
|
Tactile receptors |
Thermoreceptors Nociceptos Chemoreceptors Mechanoreceptors |
|
|
Thermoreceptors |
Sense temperature |
|
|
Nociceptors |
-Fast and slow pain -senses referred pain |
|
|
What is referred pain? |
Superficial pain Ex: the heart does not have pain receptors, but other areas of the body (left arm and neck) feel pain when you are havinga heart attack |
|
|
Chemoreceptors |
Detect dissolved substances pH and O2 |
|
|
Mechanoreceptors |
Tactile receptors 2 types: baroreceptors and proprioceptors |
|
|
Baroreceptors of carotid/aortic sinus |
Sense blood pressure |
|
|
Baroreceptors of the lungs |
Sense lung stretching |
|
|
Baroreceptors of the digestive tract |
Sense volume of tract segment |
|
|
Baroreceptors of the colon |
Sense fecal matter in colon |
|
|
Baroreceptors of bladder wall |
Sense volume of urinary bladder |
|
|
Baroreceptors general purpose |
innervate viscera and senses stretch |
|
|
Whats in the olfactory epithelium |
Olfactory neurons Supporting cells Basal epithelial cells |
|
|
What does the olfactory epithelium cover? |
Cribiform plate and superior nasal conchae |
|
|
Where is the lamina propria located and whats in it |
-located deep in the olfactory epithelium -contains olfactory glands (that make mucus), blood vessels, nerves |
|
|
How does smell or olfaction work? |
1. breath in air and nasal conchae make airflow turbulent (air spins around) 2. Compounds in the air come in contact with olfactory mucus 3. Compounds diffuse in the mucus and stimulates olfactory neurons |
|
|
What are olfactory sensory neurons |
Highly modified nerve cells that project beyond epithelium into nasal cavity |
|
|
How many olfactory sensory neurons does your nose have? |
10-20 million per 5 cm^2 of the nose |
|
|
Where do the olfactory sensory neurons cilia extend into and what do they do |
-they extend into the mucus (20 cilia per fiber) -and sense the odor molecules |
|
|
What happens when an odor molecule binds to the cilia of the olfactory sensory neuron cilia? |
Receptor membrane depolarizes and action potential sent to brain |
|
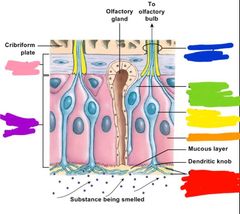
|
Red: olfactory cilia Orange: supportive cells Yellow: olfactory sensory neurons Green: developing olfactory sensory neurons Blue: olfactory nerve fibers Purple: olfactory epithelium Pink: lamina propria |
|
|
How many neurons make up the olfactory pathway? |
2 |
|
|
What does the olfactory pathway bypass? |
The thalamus |
|
|
Describe the olfactory pathway |
-1st order neurons go from olfactory epithelium to olfactory bulb -2nd order neurons go from olfactory blub directly to cerebral cortex |
|
|
Why do smells trigger memories/emotional responses? |
Because second order neurons distribute olfactory info to the limbic system and hypothalamus |
|
|
How many primary smells on there? |
-50ish -Some of these smells can be detect by as few as four molecules coming into contact with the olfactory mucus |
|
|
A Senstive smell means that |
-Info to brain is fired very quickly -less molecules are needed to trigger depolarization |
|
|
What type of neurons are the only ones that regenerate? |
-olfactory neurons -but sensitivity and number decline with age |
|
|
What does the sense gustation do? |
Send info about food and liquid to brain |
|
|
What are the receptors associated with gustation? |
Gustatory epithelial cells |
|
|
Where are gustatory epithelial cells found? |
Taste buds, which line both the: Tongues surface Adjacent to the pharynx/larynx |
|
|
How often do the gustatory epithelial cells get replaced? |
Every 10-12 days |
|
|
What do the gustatory epithelial cells do? |
Sense taste and this stimulation sends action potentials to gustatory cortex for interpretation |
|
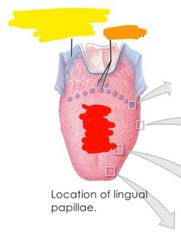
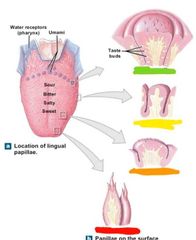
Label where different tastes are sensed |
Red: sour, bitter, sweet, salty Orange: umami Yellow: water (not on tongue but pharynx |
|
|
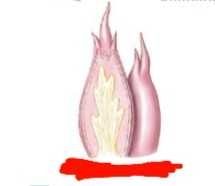
What are lingual papillae |
Epithelial projections 4 types |
|
|
What are the 4 types of lingual papillae |
1. Filiform 2. Fungiform 3. Vallate 4. Foliate |
|
|
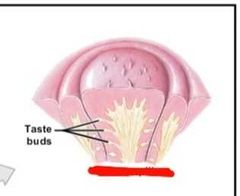
How many cells make up taste buds? |
40-100 |
|
|
What cells make up a taste bud grouping? |
-taste receptors -epithelial cells -basal (stem) cells |
|
|
What do basal cells in taste buds do? |
Divide into transitional cells which them mature to become gustatory epithelial cells |
|
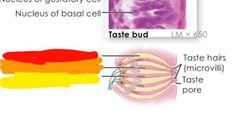
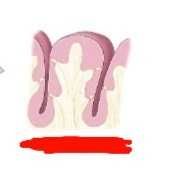
What am I and name my parts |
Taste bud Red: transitional cell Orange: gustatory epithelial cell Yellow: basal epithelial cell |
|
|
Once basal epithelial cella mature into gustatory epithial cells what happens? |
Taste receptors extend microvilli (taste hairs) that run through taste pores and sample surrounding fluid |
|
|
Explain the gustatory pathway |
1. Dissolved chemicals come into contact with taste hairs 2. Taste hairs stimulate gustatory cell 3. Impulses from gustatory cell stimulation get sent through the facial nerve (CN VII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), and vagus nerve (CN X) 4. 1st order synapse: occurs at medulla oblongota (cranial nerves listed) 5. 2nd order synapse: occurs at thalamus (medial lemniscus) 6. Then goes to final destination gustatory cortex |
|
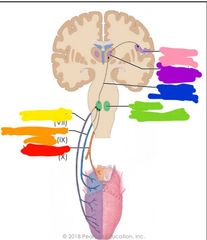
What pathway am i |
Gustatory pathway Red: vagus nerve Orange: glossopharyngeal nerve Yellow: facial nerve Green: medulla Blue: medial lemniscus Purple: thalamus Pink: gustatory cortex |
|
|
What does umami sense? |
The amino acid glutamate |
|
|
Red: filiform papillae Orange: fungiform papillae Yellow: foliate papillae Green: valiate papillae |
|
|
Valiate papillae |
|
|
Foliate papillae |
|

|
Fungiform papillae |
|
|
Filiform papillae |
|
|
Regions of the ear |
External Middle Internal |
|
|
What is the purpose of the ear? |
Hearing and balance |
|
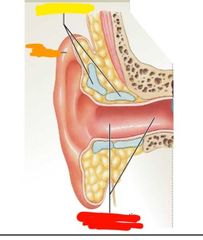
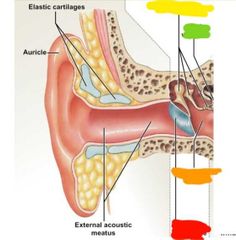
What region of the ear am I |
External Red: external acoustic meatus Orange: auricle Yellow: elastic cartilage |
|
|
What does the tympanic membrane divide? |
External and middle ear |
|
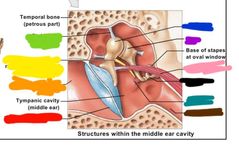
What region of the ear am I |
Middle ear Red: tympanic membrane Orange: tympanic cavity Yellow: auditory ossicles Green: oval window |
|
|
Name the auditory ossicles |
Malus Incus Stapes |
|
|
Infections of the tympanic membrane... |
-puss can cause the membrane to rupture, causes by short canals mainly in kids (treated my tubes) -or by dilation of blood vessels (causes maleus to get stuck on tympanic membrane) |
|
|
What do the auditory ossicles do? |
Convey sound to inner ear |
|
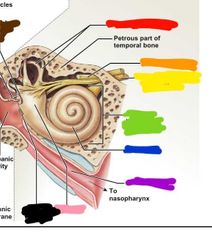
|
Red: tympanic membrane Orange: external acoustic meatus Yellow: CN VII green: stabilizing ligament Blue: malleus Purple: incus Pink: tensor tympan Black: stapes Teal: stapedius Brown: auditory tube |
|
What region of the ear am I |
Inner ear Red: semicircular canal Orange: facial nerve Yellow: vestibulocochlear nerve Green: bony labyrinth Blue: cochlea Purple: auditory canal Pink: vestibule Black: round window Brown: oval window |
|
|
How does hearing work |
-Sound comes into ear and vibrates the tympanic membrane -tympanic membrane vibrates the malleus -malleus vibrates the the incus -incus vibrates the stapes -stapes vibrates the oval window -oval window sends vibrations to the cochlea |
|
|
What do the synovial joints in the middle ear do? |
They vibrate along with the ossicles and amplify the vibration...the reason we can hear whispers |
|
|
What are stabalizing muscles in the ear and what do they do? |
-stapedius and tensor tympan -contract to modulate vibrations to prevent hearinf damage and sensory over load |
|
|
What happens in the inner ear? |
-nerves for sound innervate here picking up auditory signals to be sent to brain |
|
|
What is the cochlea? Where is it locate? What does it do? |
-membranous labyrith and bony labyrinth -found in the inner ear -receives signals from the stapes (vibrations) and turns them into neural signals |
|
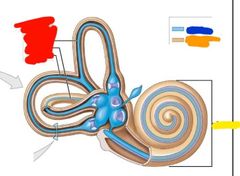
|
Red: semicircular ducts Yellow: cochlea Blue: membranous labyrinth Orange: bony labyrinth |
|
|
Perilymph |
Fluid between the labyrinths of the cochlea |
|
|
Endolymph |
Fluid in the membranous labyrinth of the cochlea |
|
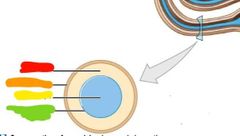
|
Red: perilymph Orange: bony labyrinth Yellow: endolymph Green: membranous labyrinth |
|
|
Pathway of the stapes sending signals to the cochlea |
Stapes 》oval window 》perilymph 》 cochlear duct 》hair cells 》spiral ganglion 》nerve stimulation |
|
|
Hair cells are found where? |
In the cochlear duct |
|
|
What are the primary sensory cells of the inner ear? |
Hair cells |
|
|
What surrounds the hair cell projections? |
Ampulla |
|
|
Where do ampulla extend? |
The endolymph at the ends of the semicircular canals |
|
|
What happens to the hair cells send sensory info? |
They deform |
|
|
How many nerves are in the auditory pathway? |
4 |
|
|
Describe the auditory pathway |
1. hair cells get stimulated 2. Sensory neuron activation in spinal ganglion 3. Sensory info goes to cochlear nerve 4. Sensory info then passed to vestibulocochlear nerve 5. Info ascendes to pons 6. unconscious motor response can happen, like turning head when someone yells) 7. Info goes to thalamus 8. Finally sent to auditory cortex |
|
|
Where does the 1st order neuron of the auditory pathway go |
From cochlea to pons |
|
|
Where does the 2nd order neuron of the auditory pathway go |
From The pons to unconscious motot response area |
|
|
Where does the 3rd order neuron of the auditory pathway go? |
From the unconscious motor area to the thalamus |
|
|
Where does the 4th order neuron of the auditory pathway go? |
From the thalamus to the auditory cortex |
|
|
Where does equilibrium take place? |
The semicircular canals? |
|
|
What do the semicircular canals respond to |
Rotational movement of the head |
|
|
What are the 3 planes of the semicircular duct |
Anterior Posterior Lateral |
|
|
What are the 3 planes of the semicircular ducts continuous with? |
Utricle |
|
|
What are ampulla and where are they? |
Sensory receptors at the base of the canals |
|
|
What is the crista ampullaris |
Receptor region with clusters of hair cells on the gel cap |
|
|
What are otoliths |
Calcium carbonate crystals |
|
|
Where ar otoliths |
They sit on the gelatinous layer that forms the otolithic membrane |
|
|
What do otoliths do? |
Indicate position of the head based on movement |
|
|
Describe otoliths when the head is up right |
-they sit on top of otolithic membrane and push hair cells straight down indicating out head is straight |
|
|
Describe otoliths when the head is tilted |
-the otoliths tilt with gravity, chaning position on the otolithic membrane and distorting hair cells in a different direction which stimulates macular receptors |
|
|
What 3 planes of movement do the semicircular canals respond to? |
•Anterior-posterior (nodding yes)-anterior •horizontal (shaking head no)-lateral •coronal (tilting)- posterior |
|
|
Accessory structures of the eye |
Eyebrows Eyelids Conjunctiva Lacrimal apparatus Extrinsic eye muscles |
|
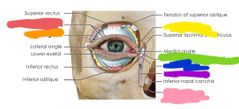
|
Red: lacrimal gland ducts Orange: lacrimal gland Yellow: lacrimal punctum Green: inferior lacrimal canaliculus Blue: lacrimal sac Purple: nasolacrimal ducts Pink: opening of nasolacrimal duct |
|
|
How crying works |
-tears are made in lacrimal gland - tears travel through lacrimal gland ducts -tears go into eye -tears over flow when your nasolacrimal duct cant keep up with tear production |
|
|
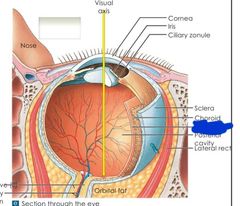
What are the 3 layers of the eye |
Fibrous Vascular Retina |
|
|
Fibrous layer of the eye |
-outer most layer -made of sclera and cornea |
|
|
Vascular layer of the eye |
-houses blood vessels and instrinsic muscles of the eye |
|
|
Retina layer of the eye |
-contains visual receptors and neurons (neural layer) -also pigment layer |
|
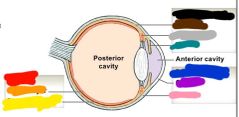
|
Red: retina layer Orange: neural layer Yellow: pigmeny layer Blue: fibrous layer Purple: cornea Pink: sclera Black: vascular layer Brown: choroid Grey: ciliary body Teal: iris |
|
|
What do the cornea and sclera do to light ? |
Bens light and focuses it on retina |
|
|
Functions of the sclera and cornea |
-bens and focuses light -provides shape of eye -sclera attaches to eye muscles |
|
|
Description of sclera |
Opaque and posterior Continuous with cornea |
|
|
Description of the cornea |
Clear and anterior Continuous with sclera |
|
|
What does the cornea cover |
Iris Pupil Anterior chamber |
|
|
Cornea function |
Refracts light 2/3 of eyes optical power Focuses |
|
|
What does the curve of the cornea do? |
Adjusts to focus on objects |
|
|
What are the regions of the vascular layer |
Choroid Ciliary body Iris |
|
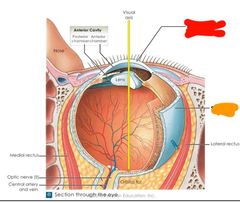
|
Red: cornea Orange: sclera |
|
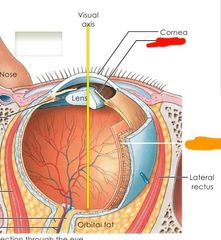
|
Red: iris Orange: choroid |
|
|
What is the choroid and what does it do? |
-membrane below the sclera -contains the blood vessel supply to all layers of the eye -supplies nutrients to retina, cornea, and lens |
|
|
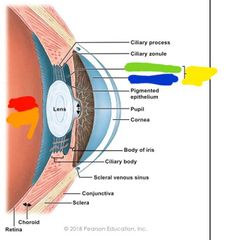
What is the cillary body and what does it do? |
-thickening ring of tissue surrounding lens -secretes and reabsorbs aqueous humor to lubricate eye |
|
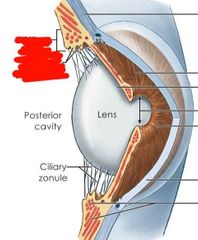
|
Cilliary body and processes |
|
|
What is the iris and its function |
-colored part of eye -melanocytes= color...blue is less brown is more -muscle that changes size of pupil |
|
|
What is the spincter pupillae? |
Part of the iris that constricts pupil |
|
|
Whats the dilator pupillae |
Part of the iris that dilates the pupil |
|
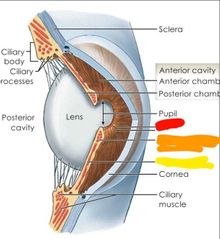
|
Red: iris Orange: sphincter pupillae Yellow: dilator pupillae |
|
|
What is the retina |
-2 layer membrane |
|
|
What are the 2 layers of the retina? |
The pigment layer and neural layer |
|
|
What is the pigment layer of the retina |
Outer layer that absorbs light and prevents it from scattering |
|
|
What is the neural layer of the retina |
-Layer containing photoreceptors that transduce light energy -Rods and cones |
|
|
Retina |
|
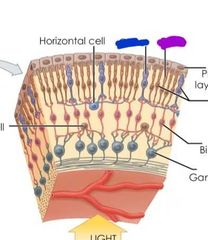
|
Blue: cone Purple: rod |
|
|
What are the 2 photo receptors in the neural layer of the retina? |
Rods and cones |
|
|
What do rods do? |
-respond to dim light -see blue/grey tones -deals with peripheral vision and motion detection |
|
|
What do cones do? |
-respond to bright light -color vision |
|
|
Where are cones found and concentrated? |
Found: macula lutea Concentrated: in fovea centralis |
|
|
Where are ganglion cell axons found? |
-Running along inner surface of retina -leaves the eye as optic nerve |
|
|
What is the optic disc |
-site where optic nerve leaves eye -has no photoreceptors -blind spot |
|
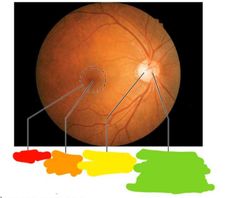
|
Red: macula Orange: fovea centralis Yellow: optic disc Green: center of optic disc where central retinal artery and vein leave |
|
|
What are thw 2 cavities of the eye |
Anterior cavity and posterior cavity |
|
|
What chambers make up the anterior cavity of the eye |
Posterior and anterior chamber |
|
|
What chamber makes up the posterior cavity |
Virteous chamber |
|
|
What fills the anterior and posterior cavities |
Aqueous humor |
|
|
Purpose of aqueous humor in eye |
-fluid eye cushion - transport waste and nutrients |
|
|
What is in the posterior cavity |
Lens |
|
|
Whats the purpose of the posterior cavity? |
-change shape to focua image -spherical=focus close -flattened=focus distant |
|
|
What covers the posterior cavity |
Dense fibrous capsule |
|
|
Red: posterio cavity Orange: vitreous chamber Yellow: anterior cavity Green: posterior chamber Blue: anterior chamber |
|
|
Cataracts |
Clouding of the lense of the eye |
|
|
What makes up the vitreous chamber |
Vitreous body and humor |
|
|
What is the vitreous chamber and whats its purpose |
-gelatinous mass -maintains eye shape -supports posterior lens -supports retina by pressing layers together |
|
|
Visual pathway |
-sensory info partial decussation at optic chiasm occurs -lateral half stays and does not cross **this is so we get a composite image from both eyes **binocular vision -optic chiasm to optic tract -optic tract to lateral geniculate nucleus which relys info to: midbrain, hypothalamus, pineal gland -finally from there to the visual cortex via projection fibers |
|
|
How does visceral pain manifest? |
Superficially in regions innervated by the same spinal nerves |
|
|
What 2 taste sensations are not subjective? |
Umami and water |
|
|
The retina contains 2 kinds of photoreceptors. The _ detect motion while the _ respond to bright light and distinguish between red, green, and yellow |
Rods Cones |
|
|
What is blood? |
-Non-newtonian fluid -connective tissue that circulates through cardio vascular system |
|
|
What does blood do? |
-Distributes nutrients, O2, amd hormones throughout the human body -removes waste from lungs ans kidneys -transports immune cells |
|
|
Blood volume of woman |
4-5 liters |
|
|
Blood volume of men |
5-6 liters |
|
|
Hypovolemic |
Low blood volume |
|
|
Hypervolemic |
High blood volume |
|
|
Normovolemic |
Normal blood volume |
|
|
Blood pH |
7.35-7.45 |
|
|
Blood temp |
37 °C (98.6°F) |
|
|
What is blood made of? |
Formed elements and plasma |
|
|
What is plasma |
Liquid matrix containing dissolved proteins |
|
|
What is serum? |
Plasma minus the clotting factors |
|
|
What are formed elements |
Blood cells and cell fragements dissolved into plasma |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
Transport O2 and CO2 |
|
|
What do white blood cells do? |
Immune response |
|
|
What do platelets do? |
Aid in blood clotting |
|
|
What are the main proteins in plasma? |
Albumin Globulin Fibrinogen Lipoproteina |
|
|
What solutes are in plasma |
Proteins Organic nutrients Electrolytes Respiratory gasses |
|
|
What percent of plasma is water |
92% |
|
|
What percent of plasma is proteins? |
7% |
|
|
What percent of other solutes (not water or proteins) is plasma? |
1% |
|
|
What is albumin and what does it do |
-protein in plasma -transports lipids and steroid hormones |
|
|
What is globulin and what are the types and their function? |
-plasma protein -2 types: -immunoglobulins=antibodies -transport globulins |
|
|
What organic nutrients are in plasma |
Glucose Carbohydrates Amino acids |
|
|
Electrolytes in plasma |
Sodium Potassium Calcium Chloride Bicarbonate |
|
|
Respiratory gasses in plasma |
Oxygen and carbon dioxide |
|
|
What is hematocrit? |
The percent of the blood that is formed elements |
|
|
What is the normal hematocrit range for men |
40-54 |
|
|
What is the normal hematocrit range for women |
37-47 |
|
|
What do high hematocrit levels indicate |
-low plasma levels -sleep apnea -dehydration -COPD -capillary leakage -drugs |
|
|
What can low hemotocrit levels indicate |
-anemia -leukemia |
|
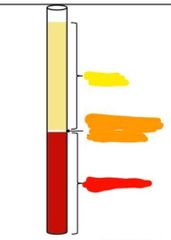
|
Yellow: plasma Orange: white blood cells and platelets Red: red blood cells |
|
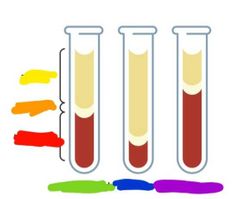
|
Yellow: plasma Orange: buffer coat Red: hematocrit Green: normal blood Blue: anemia Purple: polycythemia |
|
|
What are erythrocytes |
Red blood cells |
|
|
What are leukocytes? |
White blood cells |
|
|
What are the 2 divisions of leukocytes |
Granular leukocytes Agranular leukocytes |
|
|
What are thrombocytes |
Platelets |
|
|
What percent of formed elements is red blood cells? |
99.9% |
|
|
What percent of formed elements is white blood cells |
<0.1% |
|
|
What percent of formed elements are platelets |
<0.1% |
|
|
What are the types of granular leukocytes |
Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils |
|
|
What are the types of agranular leukocytes |
Lymphocytes Monocytes |
|
|
What percent of formed elements are in blood |
37-54% |
|
|
What is the shape of red bloos cells (erythrocytes) |
Biconcave discs (for stacking) |
|
|
Why are erthrocytes anucleate and have no organelles? |
Because organelles would use oxygen and red blood cells need to transport as much oxygen as possible. |
|
|
What are erythrocytes full of? |
Hemoglobin (95% of red blood cell) |
|
|
What is the life span of a red blood cell |
120 days |
|
|
How long does it take for a red blood cell to circulate through the entire body? |
30 seconds |
|
|
What are stacked erythrocytes called |
Rouleaus |
|
|
Why do red blood cells stack? |
To contort and squeeze through capillaries |
|
|
What is oxyhemoglobin |
Hemoglobin bound to oxygen |
|
|
What is deoxyhemoglobin |
Hemoglobin after oxygen has diffused into tissue -reduced form |
|
|
What color is oxygenated blood? |
Bright red |
|
|
What color is deoxygenated blood |
Deep red / purple |
|
|
Blood type depends on what? |
Antigens on the surface of red blood cells -A blood has A antigens -O blood has no antigens |
|
|
What is anemia |
-When there is a decrease in red blood cells or hemoglobin in blood -most common blood disorder |
|
|
Symptoms of anemia |
Weakness Fatigue Poor concentration Dyspnea (shortness of breath) |
|
|
What causes anemia |
-impaired red blood cell production -increased red blood cell distribution -blood loss/fluid overload |
|
|
What is sickle cell anemia |
-Inherited blood disorder where hemoglobin becomes stiff and curved once it give it O2 up -this shape change causes red blood cells to get trapped in capillaries |
|
|
What do white blood cells do |
-defend body from invasion of pathogens and removes waste/damaged cells -attracted to chemical signals of inflammation/infection |
|
|
What is the life span of white blood cells? |
A few days |
|
|
What are neutrophil and what do they do |
-type of glanular white blood cells -they consume bacteria via phagocytosis -makes up 60-70% of white blood cells |
|
|
Where are lymphocytes located? |
The lymphatic tissue |
|
|
What do lymphocytes do and what are the 3 types |
-adaptive immune response -3 types: B cells, T cells, natural killer cells |
|
|
What type of white blood cell is the B cell and what does it do? |
-its a type of lymphocytes -produces antibodies |
|
|
What type of white blood cell is the T cell and what does it do |
-lymphocyte -targets viruses, fungi, cancer cells, and transplanted cells |
|
|
What type of cells are natural killer cells and what do they do |
-lymphocyte -attack and destroy foreign microbes |
|
|
What do eosinophils do |
-a white blood cell that destroys parasites and combat the effects of histamine -controls allergies and asthma |
|
|
What do basophils do? |
-white blood cells that control allergic reactions -releases histamine |
|
|
What do monocytes do? |
-white blood cells that develop into macrophages and remove debris after infection |
|
|
How to categorize leukrocytes |
By lobes and grandules |
|
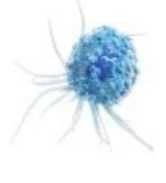
|
Monocyte |
|
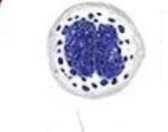
|
Basophil |
|
|
Eosinophil |
|
|
-lymphocytes B cells T cells Natural killer cells |
|

|
Lymphocyte |
|

|
Neutrophil |
|
|
Red: neutrophil Orange: lymphocyte Yellow: monocyte Green: natural killer cells Blue: T cell Purple: B cell Pink: basophil Black: eosinophil |
|
|
Describe a neutrophil |
2-5 lobes and pale granules |
|
|
Describe basophils |
Highly granulated and purple/blue in color |
|
|
Describe eosinophils |
2 lobes and red granules |
|
|
Describe lymphocytes |
Smallest white blood cells Large nucleus No granulas (agranular) |
|
|
Describe monocytes |
-largest white blood cells -large oval nucleus -no granules (agranules) |
|
|
What percent of white blood cells are lymphocytes |
20-25% |
|
|
What percent of white blood cells are monocytes |
3-8% |
|
|
What percent of white blood cells are basophil |
0.5-1% |
|
|
What percent of white blood cells are neutrophils |
60-70% |
|
|
What percent of white blood cells are eosinophils |
2-4% |
|
|
What are platelets |
Cell fragments from megakaryocytes |
|
|
Whats the purpse of thrombocytes(platelets) |
-initiate and control clotting by releasing enzymes -clump together to form platelet plug at injuries |
|
|
What do platelets contain and whats the purpose |
-Actin and myosin -the actin and myosin shorten during clotting and this pulls the cut together |
|
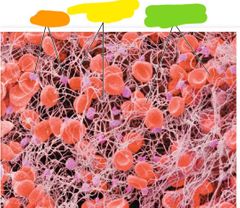
|
Orange: platelets Yellow: fibrin fiber network Green: red blood cells in fibrin strands |
|
|
What is thrombosis |
Blood clotting |
|
|
What does thrombosis do |
-prevents excessive bleeding |
|
|
What is an embolus |
When a blood clot forms on the inside of a vessel and doesnt dissolve |
|
|
What does the formation of a platelet plug active? |
Clotting factors (13) |
|
|
What is ischemic stroke |
-Blockage in artery that sends blood to the brain -very fast -most common type of stroke |
|
|
What does an ischemic stroke do to the brain |
-Reduces blood flow and oxygen to brain -results in brain damage |
|
|
What is the heart at its most basic level? |
A pump |
|
|
How many loops is the circulatory system? |
2 Pulmonary circuit Systemic circuit |
|
|
What does the pulmonary circuit do? |
Carries CO2 rich blood from heart to lungs and O2 rich blood from lungs back to heart |
|
|
What structures are part of the pulmonary circuit? |
Pulmonary arteries Capillaries in lungs Pulmonary veins Right atrium Right ventricle |
|
|
What does the systemic circuit do? |
Transports O2 rich blood from the heart to the body and CO2 rich blood from the body to the heart |
|
|
Structures of the systemic circuit |
Capillaries in head and neck Systemic arteries Left atrium Left ventricle Capillaries in abdominal organs Systemic veins Capillaries in upper limbs, lower limbs, and trunk |
|
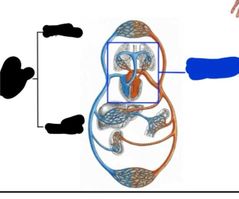
|
Blue: pulmonary circuit Black: systemic circuit (upper and lower) |
|
|
What sac surrounds the heart |
Parietal pericardium |
|
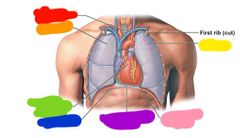
|
Red: trachea Orange: right lung Yellow: left lung Green: base of the heart Blue: diaphragm Purple: parietal pericardium Pink: apex of heart |
|
|
Where is the hearts position in the chest? |
-Lies between intercostal spaces 2-5 -2/3 of heart is left of the midsternal line |
|
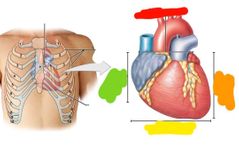
|
Red: superior border Orange: left border Yellow: inferior border Green: right border |
|
|
The pericardium is made of what type of layers? |
Fibrous layers |
|
|
The pericardium is make up of how many serous layers |
2 Serous pericardium layers -parietal layer outer most -visceral layer inner most |
|
|
Whats another name for the visceral serous paricardium? |
Epicardium |
|
|
Whats inbetween the parietal and visceral layer of the paricardium and whats its purpose? |
-Pericardial cavity full of serous fluid -reduces friction during contraction |
|
|
Layers of the heart wall |
Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium Pericardial cavity |
|
|
What is the epicardium |
-visceral layer of serous pericardium -membrane that covers the heart |
|
|
What is the myocardium |
Thick muscular layer of the heart |
|
|
What is the endocardium |
Smooth inner lining of the heart |
|
|
How much fluid does the pericardial cavity contain normally |
5-30 ml |
|
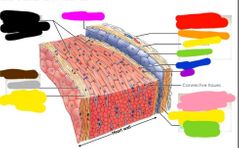
|
Red: parietal layer of serous pericardium Orange: dense fibrous layer Yellow: areolar tissue Green: mesothelium Blue: artery Purple: vein Pink: visceral layer of serous pericardium Hot pink: pericardial cavity Black: myocardium (cardiac muscle tissue) Brown: endocardium Grey: endothelium
|
|
|
What is pericarditis |
-swelling and irritation of the pericardium |
|
|
Symptoms of pericarditis |
Chest pain Shortness of breath Fatigue |
|
|
How long does pericarditis last |
3-5 weeks |
|
|
What can cause pericarditis? |
Viral infection Or unknown cause (idiopathic) |
|
|
What is pericardial effusion? |
Buildup of fluid in the pericardium |
|
|
What does pericardial effusion cause |
-pressure and compression of heart (cardiac tamponade) -prevents proper heart beat |
|
|
What is cardiac tamponade |
-compression of the heart caused by pericardial effusion (fluid buildup) |
|
|
Symptoms of pericardial effusion |
Low blood pressure Distension of jugular vein Quiet heart sounds |
|
|
How to treat pericardial effusion |
Drain fluid Can be a medical emergency |
|
|
What join cardiomyocytes together |
Intercalated discs |
|
|
What are the purpose intercalated discs |
To join cardiomyocytes together to support synchronization of contraction |
|
|
What are within intercalated discs? |
Gap junctions |
|
|
What do the gap juctions in the intercalated discs do? |
Links the cytoplasms of all the muscle cells of the heart |
|
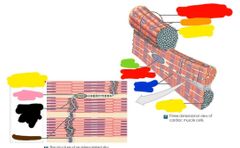
|
Red: cardiac muscle cell Orange: mitochondria Yellow: intercalated disc Green: nucleus Blue: bundles of myofibrils Pink: Gap junctions es Black: z linesBrown: desmosomes Brown: desmosomes |
|
|
Function of right and left atrium? |
Receive blood returning from the heart |
|
|
Function of the right and left ventricle |
Discharges blood into vessels to leave the heart |
|
|
Function of arteries |
Take blood away from the heart |
|
|
Function of veins |
Brings blood to the heart |
|
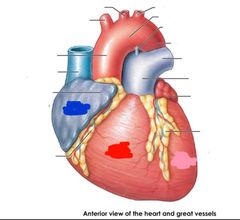
|
Blue: right atrium Red: right ventricle Pink: left ventricle |
|
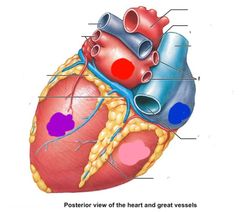
|
Red: left atrium Blue: right atrium Purple: left ventricle Pink: right ventricle |
|
|
Route blood takes going to heart to lung |
-deoxygenated blood comes in from the superior and inferior vena cava -goes to the auricle of the right atrium -pumped into the right ventricle -right ventricle pumps to the pulmonary trunk/left pulmonary artery -pumped to lungs |
|
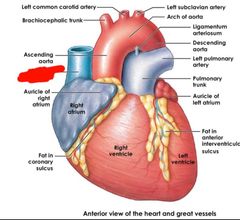
|
Superior vena cava |
|
|
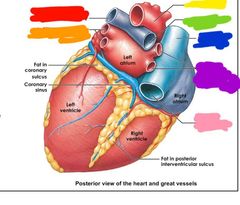
Red: superior vena cava Orange: inferior vena cava |
|
|
Superior vena cava and inferioe vena cava come together and enter where? |
The right atrium |
|
|
What is the Auricle of the right atrium |
Pocket or pouch that sits on the right atrium |
|
|
What does the auricle of the right atrium do? |
Pumps blood into the right ventricle |
|
|
Route blood takes coming back from lungs to heart |
-blood comes back from the lungs and enters left atrium -pumped into left ventricle -then pumped out aorta |
|
|
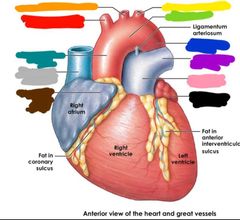
Red: brachiocephalic trunk Orange: left common carotid artery Yellow: left subclavian artery Green: arch of aorta Blue: descending aorta Purple: left pulmonary artery Pink: polmonary trunk Black: auricle of the left atrium Brown: auricle of the right atrium Grey: superior vena cava Teal: ascending aorta |
|
|
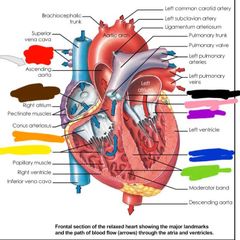
Red: right pulmonary arteries Brown: opening of the coronary sinus Orange: tricusip valve Yellow: chordae tendineae Green: trabeculae Blue: interventricular septum Purple: mitral valve Pink: aortic valve Black: interatrial septum |
|
|
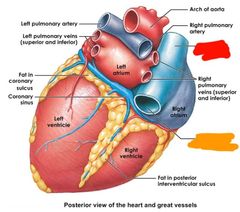
Red: left pulmonary artery Orange: left pulmonary veins (superior and inferior) Yellow: arch of aorta Green: right pulmonary artery Blue: superior vena cava Purple: right pulmonary vein (superior and inferior) Pink: inferior vena cava |
|
|
What is heart failure? |
-What the heart doesnt pump blood as well as it should -blood will back up and fluid will fill the lungs |
|
|
How to improve heart failure |
Lose weight/exercise Reduce salt Manage stress VAD |
|
|
Symptoms of heart disease |
Shortness of breath Fatigue Weakness Swelling of extremities Rapid or irregular heart beat Cough or wheezing Rapid weight gain (fluid) Chest pain |
|
|
Whats an ICD |
-Implantable cardioverter defibrillator -implanted in heart -regulates heart beat -and administers shock if needed |
|
|
Function of superior/inferior vena cava |
Returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart |
|
|
Function of the pulmonary trunk |
Delivers unoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs |
|
|
Funtion of the aorta |
Delivers blood to the body |
|
|
Where does oxygenated blood enter the heart? |
-The 4 pulmonary veins -Right and left pulmonary veins (each has 2) |
|
|
Coronary arteries arise from where? |
The aorta |
|
|
What does the coronary sinus do |
-Pools blood to flow into right atrium again -3rd opening in right atrium |
|
|
6 Arteries of the heart |
-coronary arteries (R/L) -circumflex arteries -marginal artery -anterior/postetior interventricular arteries |
|
|
4 veins of the heart |
Great cardiac vein Middle cardiac vein Small cardiac vein |
|
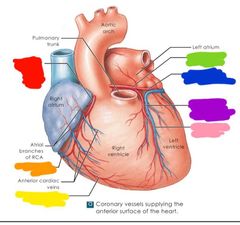
|
Red: right coronary artery Orange: small cardiac vein Yellow: marginal branch (RCA) green: left coronary artery Blue: circumflex branch of LCA Purple: anterior interventricular branch of LCA Pink: great cardiac vein |
|
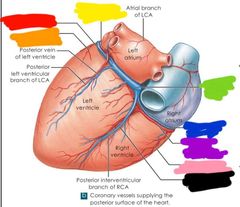
|
Red: great cardiac vein Orange: marginal branch of LCA Yellow: circumflex branch of LCA Green: coronary sinus Blue: small cardiac vein Purple: right coronary artery Pink: right marginal branch of RCA Black: middle cardiac vein |
|
|
What is a heart attack |
-Blood flow to the heart is blocked -blockage usually fat, cholesteral, etc build up (forms plaque in coronary arteries) |
|
|
NSTEMI |
Partial blockage of the heart |
|
|
STEMI |
Complete heart blockage |
|
|
Heart attack risk factors |
men over 45 women over 55 tobacco High blood pressure High cholesterol/triglyceride levels Obesity Diabetes Family history Drugs Stress |
|
|
Signs of heart attack in men |
Chest pain Shortness of breath Discomfort/tingling in arms, back, neck, shoulder, jaw |
|
|
Signs of heart attack in women |
Sudden dizziness Heartburn Cold sweat Unsually tired Nausea or vomiting |
|
|
When ventricles are relaxed |
Av valves are open Semilunad valves are closed Chordae tendineae are loose Papillary muscles are relaxed |
|
|
When ventricles are contracting |
Av valves are closed Semilunar valves are open Chordae tendineae are right Papillary muscles are contracted |
|
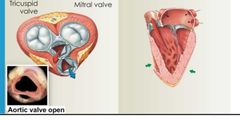
|
Contracting ventricles |
|
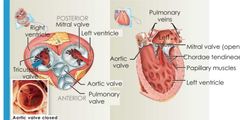
|
Relaxed ventricles |
|
|
What is a cardiac cycle |
-One complete sequence of filling and pumping blood -heart beat cycle |
|
|
1st step of the cardiac cycle |
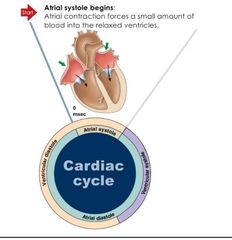
|
|
|
2nd step of cardiac cycle |
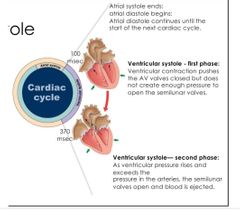
Ventricular systole (2 phases) |
|
|
3rd step of cardiac cycle |
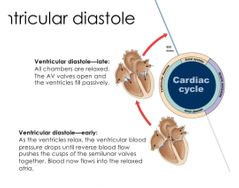
Ventricular diastole |
|
|
Componants of conducting system |
Sinoatrial (SA) node Atrioventricular (AV) node Purkinje fibers |
|
|
Sinoartrial (SA) node |
Pacemaker cells initiate the electrical impulse that results in a heartbeat |
|
|
Atrioventricular (AV) nodes |
Slows the electrical impulse when it arrives from the intermodal pathways |
|
|
Purkinje fibers |
Convey the impulses very rapidly to the contract cells of the ventricular myocardium |
|
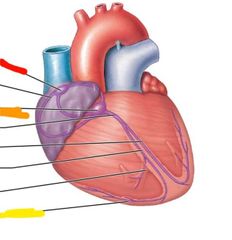
|
Red: sinoatrial node Orange: atrioventricular node Yellow: purkinje fibers |
|
|
What does the SA node do? |
Activates impulse that does heart contraction |
|
|
What does AV node do? |
Delays the spread of electrical activity |
|
|
What do the purkinjie fibers do |
Spread electrical impulse along heart |
|
|
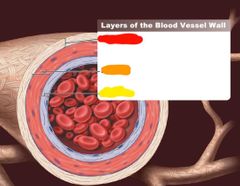
What layers make up blood vessel and artery walls |
Adventitia Middle media Inner intima |
|
|
Outer layer of arteries and veins |
Adventitia |
|
|
Middle layer of arteries and veins |
Media |
|
|
Inner layer of arteries and veins |
Intima |
|
|
Red: adventitia Orange: media Yellow: intima |
|
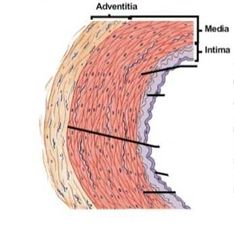
Vein or artery |
Artery |
|
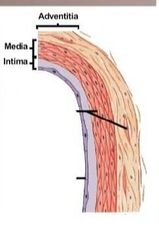
Vein or artery |
Vein |
|
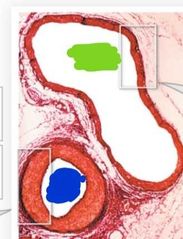
Which is a vein and which is an artery |
Green: vein Blue: artery |
|
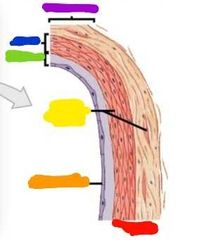
|
Red: vein Orange: endothelium Yellow: smooth muscle Green: intima Blue: media Purple: adventitia |
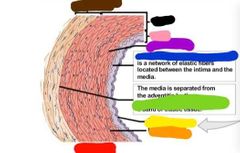
|
|
Red: artery Orange: elastic fibera Yellow: endothelium Green: external elastic membrane Blue: initial elastic membrane Purple: smooth muscle Pink: intima Black: media Brown: adventitia |
|
|
What is the adventitia? |
Thick connective tissie sheath around vessels |
|
|
What is the adventitia made of |
Collagen fibers and elastic fiber bands |
|
|
What does the adventitia do |
-Stabilizes the vessel structure and anchors blood vessels to tissues |
|
|
What is the media |
-Circularly arranged smooth muscle supported by elastic tissue **middle layer of vessels |
|
|
What is the intima |
Endothelial lining -areolar tissue, elastic fibers, and scattered smooth muscle ***inner most layer of vessels |
|
|
Tunica externa |
Adventitia |
|
|
Tunica media |
Media |
|
|
Tunica intima |
Intima |
|
|
Where arteries and veins found |
Side by side in a sheath of connective tissue |
|
|
Artery walls are ... |
-thick -have more smooth muscle and elastic fibers |
|
|
Vein walls are... |
-Thin -not as much smooth muscle or elastic fibers |
|
|
Why are artery walls thicker? |
To resist pressure |
|
|
Vein lumen... |
Are squished looking |
|
|
Artert lumen |
-round and small -will constrict when artery walls contract |
|
|
Do veins or arteries have valves? |
Veins |
|
|
Why do veins have valves? |
To prevent back flow |
|
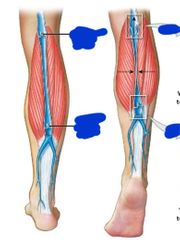
What are we? |
Valves in veins |
|
|
What layer gives vessels their vascular tone |
Media |
|
|
High vascular tone of a vessel means... |
The vessel is contracted (smaller lumen) |
|
|
Low vascular tone of a vessel means |
That the vessel is dilated (larger lumen) |
|
|
Lumen |
Center of the vessels |
|
|
Whats up with the endothelium in an artery? |
-it cant contract so it folds when constricted (making the artery look pleated) |
|
|
Why do u get kankles when u sit for to long? |
Contracting muscles helps operate the valves of veins in your legs helping blood get pumped back up |
|
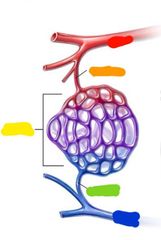
Blood vessel order of opperation |
Blood goes from... Red: artery Arteriole Capillaries Venule Blue: vein |
|
|
Capillary networks or beds |
Increases oxygen diffusion |
|
|
Medium sized veins... |
-few muscle cells -diameters range feom 2-10 mm -has thick adventitia |
|
|
Which 2 veins are your large veins? |
Superior and inferior vena cava |
|
|
What are capillaries and what do they do? |
-They are the thinnest smallest vessels -they are the site of nutrients/gas transfer |
|
|
Types of capillaries |
Continuous Fenstrated Sinusoids |
|
|
Where are Continuous capillaries |
In all tissues except epithelia and cartilage |
|
|
Where are fenestrated capillaries located? |
Epithelia and cartilage |
|
|
Where are sinusoid capillaries and what do they do? |
-premits free exchange of water and solutes |
|
|
What are sinusoid capillaries |
-look like fenestrated, but flat and irregular, and has gaps |
|
|
What diffuses across epithelial cells in capillaries |
Lipid soluble materials Gases Water |
|
|
What diffuses through gaps in capillaries |
Water Small solutes Large products in sinusoid capillaries |
|
|
What diffuses througg pores in fenestrated capillaries |
Water and solutes |
|
|
What type of blood vessel is most prominant in the body |
Venous blood vessels |
|
|
Pulmonary circuit (loop) pathway |
-from right ventricle -to Pulmonary circuit artery -to the lungs -to the pulmonary circuit veins -back to the heart(left atrium and then lefr ventricle |
|
|
Atria are connected to what? |
Veins and theu receive blood |
|
|
Ventricles are connected to what? |
Ateries that expell blood |
|
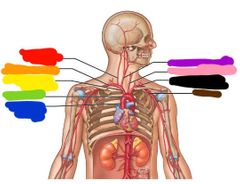
|
Red: vertebral Orange: right subclavian Yellow: brachiocephalic trunk Green: aortic arch Blue: ascending aorta Purple: right common carotid Pink: left common carotid Black: left subclavian Brown: axillary |
|
|
What do subclavian arteries supply |
Extend over lungs to supply upper body |
|
|
What does the thyrocervical branch supply |
Muscles and tissues of neck, shoulders, and back |
|
|
Internal thoracic arteries supply what |
Pericardium and anterior chest wall |
|
|
Vertebral arteries supply |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
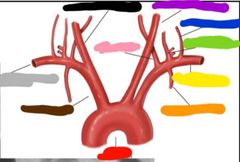
|
Red: aortic arch Orange: internal thoracic artery Yellow: left suclavian artery Green: thyrocervical trunk Blue: costocervical arteries Purple: left common cartoid artery Pink: vertebral artery Black: right common artery Grey: right subclavian artery Brown: innominate artery |
|
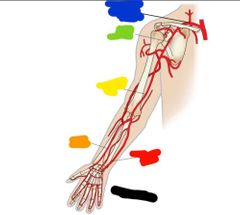
|
Black: palmar arches Red: ulnar artery Orange: radial artery Yellow: brachial artery Green: axillary artery Blue: subclavian artery |
|
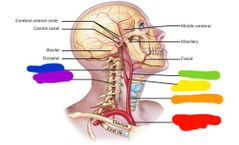
|
Red: brachiocephalic trunk Orange: common carotid Yellow: carotid sinus Green: external carotid Blue: internal carotid Purple: vertebral |
|
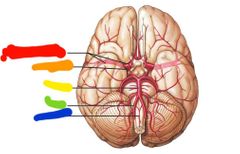
|
Red: internal carotid Orange: middle cerebral Yellow: basilar Green: vertebral Blue: anterior spinal |
|
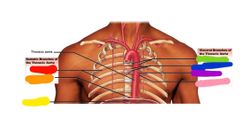
|
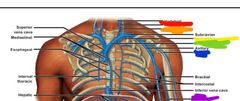
Red: intercostals Orange: superior phrenic Yellow: inferior phrenic Green: bronchial Blue: esophageal Purple: mediastinal Pink: pericardial |
|
|
Branches of the thoracic aorta |
Visceral and parietal |
|
|
The visceral branch of the thoracic arota contains |
Bronchial Esophageal Mediastinal Pericardial |
|
|
Parietal branches of the thoracic aorta |
Intercostal Superior phernic |
|
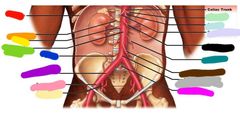
|
Red: celiac trunk Orange: descending aorta Yellow: diaphragm Green: renal Blue: superior mesentaric Purple: gonadal Pink: inferior mesenteric Black: common iliac Browb: internal iliac |
|
|
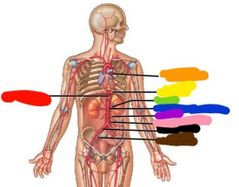
Paired abdominal arteries |
Inferior phrenica Adrenals Renals Gonadala Lumbars |
|
|
Red: diaphragm Orange: adrenal Yellow: renal Green: abdominal aorta Blue: lumbar Purple: right common iliac Pink: external iliac Lit yellow: internal iliac Lit green: left gastric Lit blue: splenic Lit purple: common hepatic Black: superior mesenteric Teal: gonadal Brown: inferior mesenteric Grey: terminal segment of aorta Hot pink: median sacral |
|
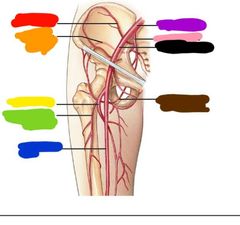
|
Red: iliolumbar Orange: superior gluteal Yellow: deep femoral Green: lateral femoral circumflex Blue: femoral Purple: common iliac Pink: internal iliac Black: external iliac Brown: medial femoral circumflex |
|
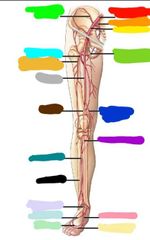
|
***Going from red down and around foot and up Common iliac Internal iliac External iliac Medial femoral circumflex Descending genicular Posterior tibial Medial plantar Plantar arch Dorsal arch Lateral plantar Doraal pedis Fibular Anterio tibial Popliteal Femoral Lateral femoral circumflex Deep femoral Iliolumbar |
|
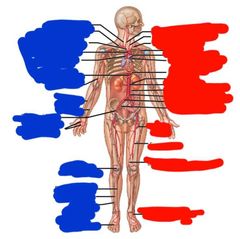
Blue side (right side) top to bottom arteries: |
Blue side (right side) top to bottom: Vertebral Right subclavian Brachiocephalic trunk Aortic arch Ascending aorta Celiac trunk Brachial Radial ulnar External iliac Palmar arches Popliteal Posterior tibial Anterior tibial Fibular Plantar arch |
|
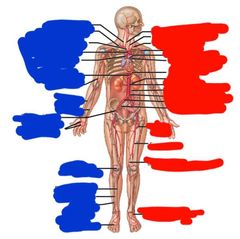
Red side (left side) top to bottom arteries: |
Red side (left side) top to bottom: Right common carotid Left common carotid Left subclavian Axillary Pulmonary trunk Descending aorta Diaphragm Renal Superior mesenteric Gonadal Inferior mesenteric Common iliac Internal iliac Deep femoral Descending genicular Dorsalis pedis |
|
|
What is the only organ that empties directly into the vena cava |
Liver |
|
|
Where do all other visceral organs drain through |
Hepatic portal system |
|
|
Pathway to and from the hepatic portal system |
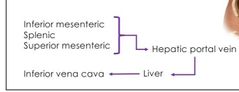
-from Inferior mesenteric, splenic, superior mesenteric -to hepatic portal vein -to liver -to inferior vena cava |
|
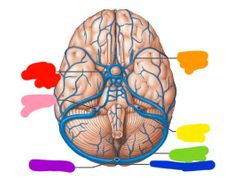
|
Red: cavernous sinus Orange: middle cerebral Yellow: sigmoid sinus Green: transverse sinus Blue: confluence of sinuses Purple: occipital sinus Pink: internal jugular |
|
|
Red: superior sagittal sinus Orange: inferior sagittal sinus Yellow: straight sinus Green: petrosal sinus Blue: right transverse sinus Purple: occipital sinus Pink: sigmoid sinus Black: cavernous sinus |
|
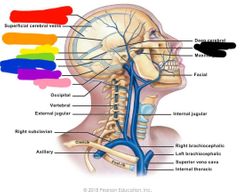
|
Red: internal jugular Orange: external jugular Yellow: highest intercostal Green: brachiocephalic Blue: cephalic Purple: basillic |
|
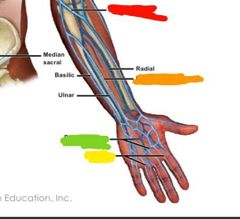
|
Red: median cubital Orange: median antebrachial Yellow: digital Green: palmar venous arches |
|
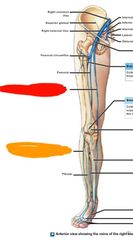
|
Red: greater saphenous Orange: small saphenous |
|
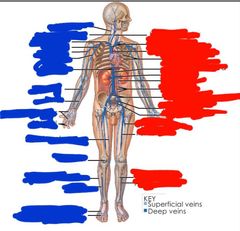
Blue side (right) top to bottom: |
Blue side (right) top to bottom: Vertebral External jugular Subclavian Axillary Cephalic Brachial Hepatic Radial Ulnar Palmar venous arches Digital Great saphenous Popliteal Small saphenous Fibular Dorsal venous arch Plantar venous arch |
|
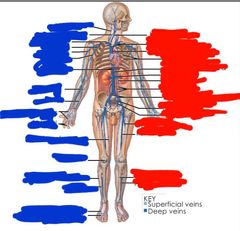
Red side (left side) top to bottom |
Red side (left side) top to bottom: Internal jugular Brachiocephalic Superior vena cava Intercostal Inferior vena cava Renal Gonadal Lumbar Left and right common iliac External iliac Internal iliac Deep femoral Femoral Posterior tibial Anterior tibial |
|
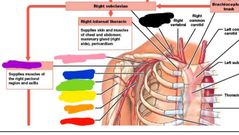
|
Red: deep brachial Orange: subscapular Yellow: posterioe humeral circumflex Green: anterior humeral circumflex Blue: lateral thoracic Purple: axillary Pink: thoracoacromial Black: thyrocervical trunk |
|
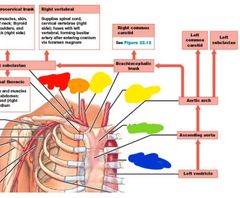
|
Red: thyrocervical trunk Orange: vertebral Yellow: R/L common carotid Green: subclavian Blue: thoracic aorta |
|
|
Muscular arteries have... |
A thicker media greater percentage of smooth muscle |
|
|
What is fibrinogen and what does it do |
-plasma protein -clotting protein |
|
|
Elastic arteries example |
-aorta |
|
|
Elastic arteries media have... |
A high density of elastic fibers and few smooth muscle cells |
|
|
Example of muscular arteries |
Radial and ulnar arteries |
|
|
Arterioles media consist of... |
Scattered smooth muscle that doesnt form a complete layer |
|
|
2 types of capillaries |
Fenestrated and continuous |
|
|
Whats the difference between fenestrated and continuous capillaries? |
Fenestrated capillaries have pores while continuous capillaries dont |

