![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Multicellular Organism vs Single |
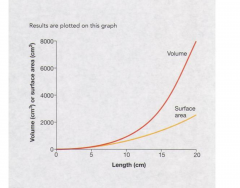
Single celled organisms have all interaction with the outside world carried across the external membrane, there's a limit to the size you can be if you want those functions to be effective. The larger you get the volume goes up as the cube of your radius while SA goes up as the square. (Surface to volume goes down.) Multicellular has a huge increase of SA to increase efficiency of transfer. |
|
|
Tissue |
A collection of cells that work together. Tissues are assembled into organs and organ systems. The cells, all of which have the same genetic info, can become specialized in many different ways to carry out jobs. Epithelia, connective, muscle, and nervous. |
|
|
Epithelial Tissue |
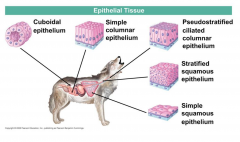
Consists of sheets of cells. Stratified contains complexity and several layers. Squamous means flattened, cuboidal and columnar are different shapes. Contains a basal layer that is non-cellular and made up of cross-linked collagen, gives structure. Linked by tight junctions. Epithelia are specialized for secretion or absorption. |
|
|
Lung |
Contains simple squamous epithelial tissue. Allows for relatively easy diffusion of oxygen.
|
|
|
Esophagus, Anus, Vagina |
Stratified squamous epithelium, used to protect against abrasion. |
|
|
Small Intestine |
Contains simple columnar cells specialized for absorption. |
|
|
Kidney |
Cuboidal cells that form a tubule. |
|
|
Connective Tissue |
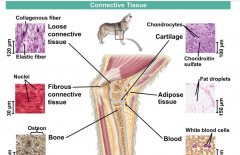
Fairly loosely organized tissue consisting of cells plus cellular matrix. Contains fibroblasts and macrophages. |
|
|
Fibroblasts |
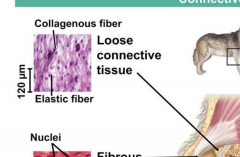
Used to secrete the fibrous proteins like collagen and elastin. Fibrous proteins are loosely arranged and can wander the meshwork fairly easily. Collagen is strong and holds things together. Fibrous is found in tendons (holds muscles to bones) and ligaments (holds joints to bones.)Cartilage is found at the joint and used for cushioning. |
|
|
Macrophages |
Scavenger cells involved in defense. |
|
|
Adipose tissue |
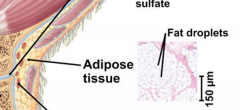
Fat. Consists of cells with a very thin cytoplasm. |
|
|
Bone |
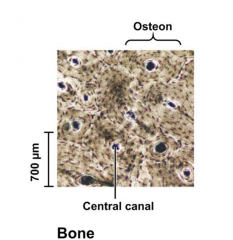
Specialized connective tissue. Bone-forming cells are called osteoblasts that secrete collagen and hydroxyapateite (hardener). |
|
|
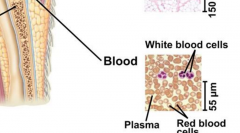
Blood |
Also a connective tissue. Contains red and white blood cells that are suspended in plasma. |
|
|
Muscle Tissue |
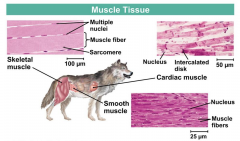
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle |
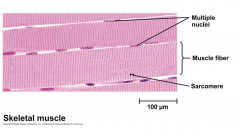
Also called striated (contains cross striations) these are formed through many precursor cells called myoblasts. Can be stimulated and contract. Also called voluntary muscles because they need input from the nervous system. |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle |
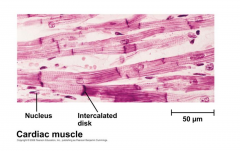
Also striated, but each has a single nucleus and is connected by gap junctions that link with neihbors to produce synchronous contraction. Involuntary (controled by autonomic nervous system.) |
|
|
Smooth Muscle |
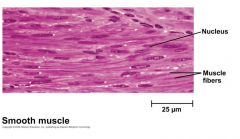
Not striated and also involuntary (controlled by autonomic nervous system.) |
|
|
Nervous Tissue |
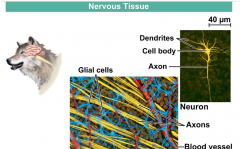
Contains Neurons and glia. Neurons are highly branched cells and their job is to signal other cells. They have a long process called an axon that sends signals to the cell body. |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Mechanisms in the body responsible for maintaining constancy of various parameters like pH and temp. Work by negative feedback. |
|
|
Negative Feedback |
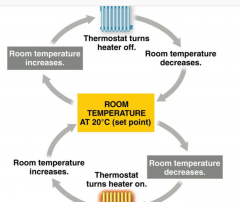
There is a receptor, a detector (detects changes in variable being measured, and a control system (activates a mechanism for reversing change detected.) Negative feedback are important in maintaining internal constancy of organisms. Temp goes down the control center calls for increased metabolism to produce more heat. Temp, blood pressure, breathing, blood osmolarity. |
|
|
Positive Feeback |
If something goes up, the feedback sends even more (instead of calming things down, it increases the action potential.) Action potential and childbirth are examples. |

