![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is compartment syndrome?
|
This is a surgical emergency where the legs swells with fluid, thanks to the compartmentalization of the leg, leading to pressures high enough to cut off circulation and can lead to amputations.
|
|
|
What is a fasciotomy?
|
This is a procedure used to help Compartment Syndrome patients with high pressure and swelling in the legs, (surgically opening the fascial compartment) decompresses the injury site, and allows tissue perfusion
|
|
|
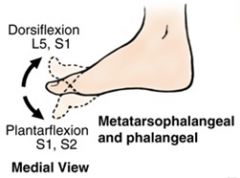
What appears as elevations during the 4th week of development?
|
upper limb buds
|
|
|
What appears during the 5th week of development, growing laterally from the L2-S2 segments (metameres)?
|
Lower limb buds
|
|
|
The center of gravity is located ___ to the S2 vertebra?
|
anterior
|
|
|
Only minor postural adjustments by the ____ ___ __ _____ and the ____ ____ of the ankle are necessary to maintain the relaxed standing posture because of the arrangement of the ligaments of the hip and knee, the bony architecture, and the line of gravity in relationship to the joint axis of motion.
|
extensors of the back;
plantar flexors |
|
|
the rotational axis of the knee and ankle lie ____ to the vertical line of the center of gravity.
|
posterior
|
|
|
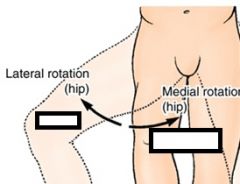
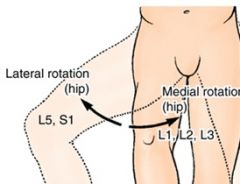
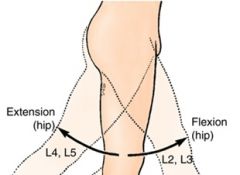
What are two functions of the muscles groups surrounding the hip?
|
move the femur AND
stabilize the pelvis and trunk |
|

|

|
|
|
Fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh and is continuous with the ____ ____ of the leg.
|
crural fascia
|
|
|
The fascia lata is continuous with the ____ ligament
|
inguinal
|
|
|
The inguinal ligament is the aponeurosis at the inferior end of the ____ _____ _____ ____. It attaches to the ASIS and the pubic tubercle.
|
external abdominal oblique muscle
|
|
|
Where are the superficial veins of the leg located?
|
the subcutaneous tissue (superficial fascia)
|
|
|
Deep veins accompany the arteries and are deep to what?
|
the deep fascia (fascia lata & crural fascia)
|
|
|
The great saphenous vein of the lower limb ascends ____ to the medial malleolus.
|
anterior
|
|
|
Union of what two veins create the great saphenous vein of the lower limb?
|
veins from the dorsal digital vein of the great toe and dorsal venous arch of the foot
|
|
|
Where does the great saphenous vein of the lower limb drain into?
|
the femoral vein
|
|
|
What does the great saphenous vein of the lower limb traverse?
|
the saphenous opening of the fascia lata
|
|
|
which vein does the great saphenous vein of the lower limb anastomose with?
|
the small saphenous vein
|
|
|
True or false: the great saphenous vein of the lower limb has valves.
|
True; unlike the vertebral veins, which do not. this lack of valves in the vertebral column, can allow some cancers to metastasize by retrograde (backwards) flow and form cancers "upstream".
|
|
|
True or false: the femoral vein of the lower limb has valves.
|
True; unlike the vertebral veins, which do not. this lack of valves in the vertebral column, can allow some cancers to metastasize by retrograde (backwards) flow and form cancers "upstream".
|
|
|
What is the function of perforating veins in the leg?
|
connect the great saphenous vein and the deep veins of the leg, the fibular and posterior tibial.
Additionally, these veins are part of the musculovenous pump, not just by muscular contraction. because of high pressure, they keep venous blood flow from heading from deep veins to superficial, and act as a shunt against this flow. |
|
|
True or false: perforating veins of the leg have valves.
|
True.
|
|
|
the superficial lymphatic vessels of the lower limb converge on and accompany the ____ ____ and their tributaries.
|
saphenous veins
|
|
|
the superficial lymphatic vessels of the lower limb accompanying the great saphenous vein end in the _____ _____ ____ ____
|
supercicial inguinal lymph nodes, this then passes to the external iliax lymph nodes, but some map also pass into the deep inguinal lymph nodes.
|
|

|
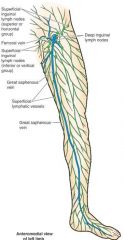
|
|
|
External iliac lymph nodes follow which vein?
|
external iliac vein
|
|
|
Lymph vessel traveling with the lesser saphenous vein drain into ___ ___ ___ in the ___ ___which also collects lymph from the deep lymphatic vessels of the leg.
|
popliteal lymph nodes;
popliteal fossa |
|
|
what is a lymphadenopathy?
|
this term generally indicates swollen lymph nodes, or some issue with a lymph node. When they are enlarged, the entire field of drainage must be examined.
|
|
|
The External iliac artery changes its name to the femoral artery after descending into the thigh and passing deep to what structure?
|
inguinal ligament
|
|
|
Genicular arteries branch from the femoral and the popliteal arteries to supply what structure?
|
the knee
|
|
|
the lumbar plexus is composed of the ___ rami of lumbar spinal nerves
|
anterior
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|
|
|
|
coxa vara and coxa valga refer to what abnormality?
|
Coxa vara and coxa valga refer to a decrease and an increase in the angle of inclination between the head and neck of the femur, and the long shaft of the femur, respectively.
|
|
|
What is Osgood Schlatter disease?
|
This refers to a fracture or injury to the tibia at the epiphyseal plate of the tibial tuberosity, which can cause inflammation and chronic pain in adolescence, especially in young athletes.
|
|
|
What is the dancer's fracture?
|
A fracture of the metatarsals, caused when a dancer loses balance using the demipointe technique, putting the full body weight on the metatarsals.
|
|
|
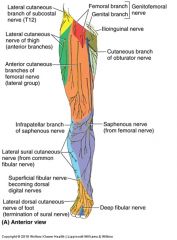
Why might a patient complain of pain or numbness along the medial border of the foot after a saphenous cutdown?
|
the procedure allows access to the saphenous vein just anterior to the medial malleolus, allowing a cannula to be inserted for prolonged administration of fluids, drugs, etc. The saphenous nerve accompanies this vein, and if it were cut it could cause the symptoms described.
|
|
|
Venous stasis (stagnation) is an important cause of ____ formation.
|
thrombus, or blood clot. these can travel to main arteries and can cause death.
|
|
|
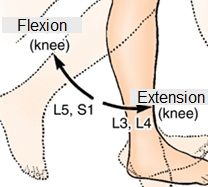
The patellar reflex tests the integrity of what nerves and spinal cord segments?
|
This tests the integrity of the femoral nerve and L2-L4 spinal segments.
|
|
|
Trochanteric bursitis and ischial bursitis is characterized by what?
|
Trochanter bursitis has symptoms of diffuse deep pain in the lateral thigh region, especially during stair climbing or rising from a seated position. there is point tenderness over the greater trochanter, but pain raidates along the iliotibial tract as well.
Ischial bursitis has pain developing from excessive friction between ischial bursae and ischial tuberosities, (ie. from cycyling). These may lead to pressure sores in paraplegics or debiliated persons, since the tuberosities bear the weight when a person is sitting. |
|
|
Tall Californian Navy Medcial Interns Lay Cuties
|
Tarsal bones
"Tall Californian Navy Medcial Interns Lay Cuties": · In order (right foot, superior to inferior, medial to lateral): Talus Calcanous Navicular Medial cuneiform Intermediate cuneiform Lateral cuneifrom Cuboid |

