![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
Aurochs, horses, and rhinoceroses
Chauvet Cave, Vallon-Pont-d'Arc, France
c. 30,000-28,000 BCE or c. 15,000-13,000 BCE
|
|
|
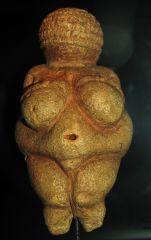
Nude woman (Venus of Willendorf)
Willendorf, Austria
c. 28,000-25,000 BCE
Limestone |
|

|
Palette of King Narmer
Hierakonpolis, Egypt (Predynastic)
c. 3000-2920 BCE
Slate |
|

|
Khafre enthroned
c. 2520-2494 BCE (4th Dynasty)
Diorite |
|

|
Akhenaten
c. 1353-1335 BCE (18th Dynasty)
Sandstone |
|

|
Figurine of a woman
Syros (Cyclades), Greece
c. 2600-2300 BCE
Marble |
|

|
Palace at Knossos, Crete
c. 1700-1370 BCE |
|

|
Landscape with swallows (Spring Fresco)
Akrotiri, Thera (Cyclades)
c. 1650-25 BCE
Fresco |
|

|
Harvesters Vase
Hagia Triada, Crete
c. 1500 BCE
Steatite, originally with gold leaf
|
|

|
Palace and citadel at Tiryns, Greece
c. 1400-1200 BCE |
|

|
Warrior Vase
Mycenae, Greece
c. 1200 BCE
Ceramic |
|

|
Temple of Aphaia
Aegina, Greece
c. 500-490 BCE
Transitional/Early Classical |
|

|
Dying warrior, from west pediment
Temple of Aphaia, Aegina, Greece
c. 490 BCE
Transitional |
|

|
Dying warrior, from east pediment
Temple of Aphaia, Aegina, Greece
c. 480 BCE
Early Classical |
|

|
Iktinos and Kallikrates
Parthenon, Athens
447-38 BCE
High Classical |
|

|
Achilles and Ajax playing a dice game
Exekias
Athenian black-figure amphora
c. 540-30 BCE |
|

|
Three revelers
Euthymides
Red-figure amphora
c. 510 BCE |
|

|
Battle of Issus
Philoxenos of Eritrea
c. 310 BCE
Mosaic |
|

|
"New York" kouros
c. 600 BCE
Marble |
|

|
Seated boxer
c. 100-500 BCE
Bronze |
|

|
Kroisos, kouros from Anavysos, Greece
The "Anavysos" kouros
c. 530 BCE
Marble |
|

|
Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)
Polykleitos
Roman marble copy of bronze original c. 450-40 BCE |
|

|
Apoxyomenos (Scraper)
Lysippos
Roman marble copy of bronze original c. 330 BCE |
|

|
Old market woman
Roman copy of marble original of c. 150-100 BCE |
|

|
Laocoön and his sons
Athanadoros, Hagesandros, and Polydoros of Rhodes
Early 1st century CE
Marble |
|

|
Model of a typical Etruscan temple of 6th century BCE, as described by Roman author Vitruvius |
|

|
Apulu (Apollo of Veii), from roof
Portonaccio temple, Veii, Italy
c. 510-500 BCE
Painted terracotta |
|

|
Interior, Tomb of the Leopards
Monterozzi necropolis, Tarquinia, Italy
c. 480 BCE |
|

|
Temple of Portunus (Temple of Fortuna Virilis)
Rome, Italy
c. 75 BCE |
|

|
Pantheon
Rome, Italy
118-25 CE |
|

|
First Style wall painting in the Samnite House
Herculaneum, Italy
Late 2nd century BCE |
|

|
Gardenscape, Second Style wall paintings, Villa of Livia
Primaporta, Italy
c. 30-20 BCE
Fresco |
|

|
Detail of a Third Style wall painting, Villa of Agrippa Postumus
Boscotrecase, Italy
c. 10 BCE
Fresco |
|

|
Ara Pacis Augustae (Altar of Augustan Peace)
Rome, Italy
c. 13-9 BCE |
|

|
Arch of Titus
Rome, Italy
After 81 CE |
|

|
Column of Trajan, Forum of Trajan
Rome, Italy
Dedicated 112 CE |
|

|
Portrait of a Roman general, from Sanctuary of Hercules
Tivoli, Italy
c. 75-50 BCE
Marble |
|

|
Portrait of Vespasian
c. 75-79 CE
Marble |
|

|
Colossal head of Constantine, from the Basilica Nova
Rome, Italy
c. 315-30 CE
Marble |
|

|
Painted portrait of Septimius Severus and his family
Egypt
c. 200 CE
Tempera on wood |
|

|
Portrait of Augustus as general
Primaporta, Italy
Early 1st century CE copy of a bronze original of c. 20 BCE
Marble |
|

|
Equestrian statue of Marcus Aurelius
Rome, Italy
c. 175 CE
Bronze |
|

|
Apotheosis of Antoninus Pius, pedestal of the Column of Antoninus Pius
Rome, Italy
c. 161 CE
Marble |
|

|
Decursio, pedestal of the Column of Antoninus Pius
Rome, Italy
c. 161 CE
Marble |
|

|
Interior, Santa Sabina
Rome, Italy
c. 422-432 |
|

|
Miracle of the Loaves and Fishes
Sant'Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna, Italy
c. 504
Mosaic, nave wall |
|

|
Sarcophagus with philosopher, orant, and Old and New Testament scenes (Santa Maria Antiqua sarcophagus)
c. 270
Marble |
|

|
Sarcophagus of Junius Bassus, from the Vatican cemetery
Rome, Italy
c. 359
Marble |
|
|
Paleolithic |
Of, relating to, or denoting the early phase of the Stone Age, lasting about 2.5 million years, when primitive stone implements were used |
|
|
Neolithic Revolution |
About 10,000 BCE, humans began to cultivate crops and domesticate certain animals. This was a change from the system of hunting and gathering that had sustained humans from earliest times. As a result, permanent settlements were established. |
|
|
Neolithic |
Of, relating to, or denoting the later part of the Stone Age, when ground or polished stone weapons and implements prevailed. |
|
|
Post and lintel |
A system with a lintel (header) as the horizontal member over a building void supported at its ends by two vertical posts.
i.e. Stonehenge |
|
|
Twisted perspective |
A convention of representation in which part of a figure is shown in profile and another part of the same figure is shown frontally. |
|
|
Stele |
A stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected as a monument, often for funerary or commemorative purposes. |
|
|
Clerestory |
The level between the two green roofs, reinforced here by flying buttress. |
|
|
Register |
A vertical level in a work that consists of several levels, especially where the levels are clearly separated by lines. Comparable to a row/line in modern texts. |
|
|
Hypostyle |
In architecture, a hall with a roof that is supported by columns. |
|
|
Hierarchy of scale |
A technique in which the artist uses unnatural proportion or scale to depict the relative importance of figures in the artwork. |
|
|
Conceptual representation |
Art in which the ideas involved in the work take precedence over traditional aesthetic and material concerns. |
|
|
Amarna period |
Era of Egyptian history toward latter half of 18th Dynasty. Dramatic change of Egypt's polytheistic religion into one where a sun-god Aten was worshipped over all other gods. |
|
|
Capital |
In the Classical styles, the architectural member that most readily distinguishes the order. Two simple forms are a square wooden block called an abacus, placed on the top of a post, and an oblong block called a billet, set with its greatest dimensions parallel to the beam above. |
|
|
Doric order |
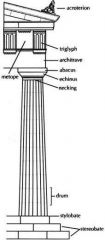
Columns stand directly on flat pavement without a base; vertical shafts topped by a smooth capital.
|
|
|
Ionic order |
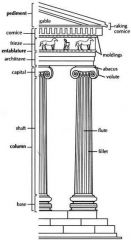
Columns normally stand on a base which separates shaft of column from platform; cap is usually ornamental.
|
|
|
Corinthian order |
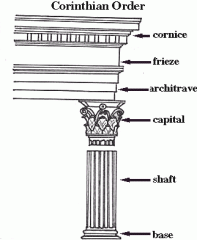
Most ornate of the orders, with slender columns and elaborate capitals decorated with leaves and scrolls.
|
|
|
Cella/naos |
Inner chamber of a temple in classical architecture. |
|
|
Pronaos |
Greek for "before a temple"; a porch leading to the entrance of the building |
|
|
Opisthodomos |
Either the rear room of an ancient Greek temple or the inner shrine |
|
|
Peripteral |
Having a single row of pillars on all sides in the style of the temples of ancient Greece. |
|
|
Dipteral |
Having a double row of pillars on all sides. |
|
|
Triglyph |
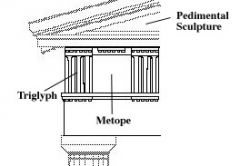
The vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze, so called because of the angular channels in them, two perfect and one divided.
|
|
|
Metope |
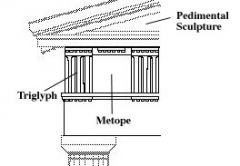
A rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze
|
|
|
Stylobate |
The top step of the crepidoma, the stepped platform on which colonnades of temple columns are placed (the floor of the temple) |
|
|
Peristyle |

A columned porch or open colonnade in a building surrounding a court that may contain an internal garden
|
|
|
Continuous frieze |
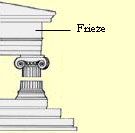
A frieze that goes all the way around the temple
i.e. Parthenon |
|
|
Hypaethral |
Having no roof; open to the sky. |
|
|
Kouros (pl. kouroi) |
A statue of a standing nude youth that did not represent any one individual youth but the idea of youth. Used in Archaic Greece as dedication to the gods in sanctuaries and as a grave monument. Standard kouros stood with his left foot forward, arms at his sides, looking straight ahead. |
|
|
Kore (pl. korai) |
A free-standing ancient Greek sculpture of the Archaic period depicting female figures, always of a young age. Could represent mortals or deities. |
|
|
Amphora |

Container used for the transport and storage of various products, both liquid and dry, but mostly for wine.
|
|
|
Krater |

A large vase used to mix wine and water in Ancient Greece.
|
|
|
Mosaic/tessera(e) |
Mosaic: An image created with individual tiles known as tesserae |
|
|
Votive |
A small candle intended to be burnt as a votive offering in an act of Christian prayer |
|
|
Black-figure |

Figures drawn on the natural clay surface of a vase in glossy black pigment; finishing details incised into the black
|
|
|
Red-figure |

Decoration outlined in black, but background outside filled in with black, leaving figures red. Details painted rather than incised. |
|
|
Contrapposto |
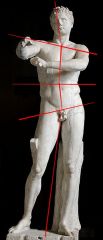
A human figure standing with most of its weight on one foot so that shoulders and arms twist off-axis from hips and legs. |
|
|
Apotheosis |
The elevation of someone to divine status (often seen in Greek and Roman portraiture) |
|
|
Coffer(ing) |

A sunken panel in the shape of a square, rectangle, or octagon in a ceiling. Series of coffers used for decoration. |
|
|
Pax Augusta/Pax Romana |
Long period of relative peace and minimal expansion by military force experienced by the Roman Empire after the end of the Final War of the Roman Republic and before the beginning of the Crisis of the Third Century. |
|
|
Spolia |
Reusing earlier building material or decorative sculpture on new monuments. |
|
|
Veristic/verism |
Extremely or strictly naturalistic. |
|
|
Damnatio memoriae |
"Damnation of memory": Person must not be remembered. A form of dishonor that could be passed by the Roman Senate upon traitors or others who brought discredit to the Roman State (i.e. Nero). |
|
|
Tetrarchy |
Any form of government where power is divided among four individuals, but in modern usage usually refers to the system instituted by Roman Emperor Diocletian in 293. |
|
|
Classicizing |
To imitate a classical style |
|
|
Circumambulation |
The act of moving around a sacred object or idol. |
|
|
Sarcophagus |
A stone coffin, typically adorned with a sculpture or inscription and associated with the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Rome, and Greece. |
|
|
Basilica |
An open public court building, usually located adjacent to the forum of a Roman town. By extension, applies to Christian buildings. |
|
|
Basilican plan |
Features a central nave (body of the church, approach to high altar) and aisles. |
|
|
Catacomb |
An underground cemetery consisting of a subterranean gallery with recesses for tombs, as constructed by the ancient Romans. |
|
|
Orant (orans) |
A figure in art with extended arms or bodily attitude of prayer, usually standing, with the elbows close to the sides of the body and with the hands outstretched sideways, palms up. |

