![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Port / Starboard Fore / Aft |
Port = Left Starboard = Right Fore = Forward Aft = Back |
|
|
|
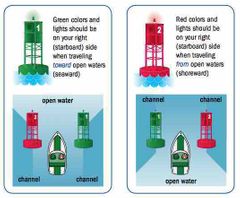
Red Right Returning |
“nun” (triangle top) buoys “can” (square top) buoys |
|
|
|
Boating Right-of-Way head on, crossing paths, overtaking |
Head-on: both vessels give-way starboard Crossing paths: Starboard vessel is stand-on Overtaking: the one overtaking is give-way, can pass either side |
|
|
|
Power vs. Sail Right-of-Way |
Power = give way Sail = stand on Overtaking = whichever one is overtaking |
|
|
|
Aircraft Right-of-Way |
aircraft in distress always has right of way overtaking: must pass slower aircraft on the right and stay well clear landing: lower altitude plane has right of way |
|
|
|
Standard Liquid Weights water oil gas |
Gasoline - 6lbs/gallon Oil - 7.5lbs/gallon Water - 8.35lbs/gallon |
|
|
|
Windlass |

used to hoist anchors and lines |
|
|
|
Fog: Definition Radiation, Ground, Advection, Upslope, Steam |
Definition: when the temperature of air near the ground is cooled to the air’s dew point. Then water vapor in the air condenses and becomes visible in the form of fog. Radiation: clear nights, no wind, valleys. occurs when ground cools rapidly due to terrestrial radiation. Disappears with sun & heat. Ground: radiation fog that’s less than 20ft thick Advection: coastal areas, when a layer of warm, moist air moves over a cold surface. wind is required. does not disappear with sun Upslope: same as advection Steam: cold, dry air moves over warm water. as the water evaporates, it rises and resembles smoke over the water. common on bodies of water in coldest time of year. |
|
|
|
Ship terminology Freeboard, Draft, Forecastle, Fantail, Keel, Lubbers line |
Freeboard: water level to deck Draft: water level to bottom of boat Forecastle: bow half of deck Fantail: stern half of deck Keel: structure line underneath boat running from bow to stern Lubber line: fixed line on a compass pointing towards ships bow |
|
|
|
Air weights |
humid air lighter than dry air warm air lighter than cold (heat rises) |
|
|
|
Dead Reckoning & Terrain Association |
relying solely on your compass for direction & using surrounding terrain to guide you along your way |
|
|
|
“Wing Load” |
ratio of wing surface area to aircraft weight |
|
|
|
Boat Lights |

Port - Red Starboard - Green White - indicates direction Yellow - special |
|
|
|
Autorotation |

a maneuver used by helicopter pilots to make an emergency landing when he has lost engine power during flight |
|
|
|
Compass Deviation / Variation |

deviation: (pink area) the error of a magnetic compass due to local magnetism, dependent on your heading. Variation: difference between true bearing and magnetic bearing |
|
|
|
RIO |
Radar Intercept Officer sits in back seat of F-14 and manages battlefield and mission execution |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CG / CGN |
Carrier, guided-missile (N - nuclear powered) |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CG / CGN |
Carrier, guided-missile (N - nuclear powered) |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CA |
Gun Cruiser |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CG / CGN |
Carrier, guided-missile (N - nuclear powered) |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CA |
Gun Cruiser |
|
|
|
Longitude / Latitude & Prime Meridian |
Latitude across the globe, measured from equator Longitude north to south poles, measured from prime meridian in Greenwich, England. 000 degrees |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CG / CGN |
Carrier, guided-missile (N - nuclear powered) |
|
|
|
Navy Ship Naming CA |
Gun Cruiser |
|
|
|
Longitude / Latitude & Prime Meridian |
Latitude across the globe, measured from equator Longitude north to south poles, measured from prime meridian in Greenwich, England. 000 degrees |
|
|
|
UTC |
Coordinated Universal Time The time in Greenwich, England. Time zones are divided by 15 degree intervals, 360/15 = 24 time zones. |
|
|
|
Airport Beacons Military, civilian, water, heliport. |
military: two quick white flashes alternating with a green flash civilian: flashing white & green water: flashing white & yellow heliport: flashing white yellow green |
|
|
|
VASI |
Visual Approach Slope Indicator 2-bar and 3-bar VASIs. 2-bar installations provide one visual glidepath set at 3 degrees. both red: below glidepath both white: above glidepath |
|
|
|
Pulsating VASI |

steady white = on glidepath |
|
|
|
RCLS |
Runway Centerline Lighting System spaced 50ft intervals on centerline of runway. white until the last 3,000ft of runway, then alternate with red for the next 2,000ft, then red for the last 1,000ft of runway. |
|
|
|
Tides Diurnal, Neap, Ebb, Spring |
Diurnal: one high and one low tide each day Spring: sun & moon in alignment for highest tides Neap: smaller difference between the high and low tides due to opposing gravitational pull by sun/moon Ebb: when the tide falls after high tide |
|
|
|
Space Projects in Order |
1. Mercury 1961 - if humans could survive in space 2. Gemini 1965 - carried two astronauts to space 3. Apollo 1967 - first attempt land on moon Apollo 11 landed on moon in 1969 with Neil Armstrong, Edwin Aldrin Jr, Michael Collins |
|
|
|
John Glenn |
US Marine, 149 combat missions between WWII and Korean war. 5 distinguished flying crosses (heroism during aerial flight) first to fly supersonic across US first american to orbit earth in Project Mercury on the Friendship 7 |
|
|
|
Yuri Gagarin |
Russian cosmonaut, first man in space |
|
|
|
Pioneer 10 |
First american spacecraft to explore the outer solar system. |
|
|
|
Pioneer 10 |
First american spacecraft to explore the outer solar system. |
|
|
|
Ed White |
first American to walk in space |
|
|
|
Atmospheres |

Troposphere - 20,000ft at poles 60,000ft at equator Tropopause - boundary Stratosphere - 120,000ft Ozone Layer - blocks radiation from sun Mesosphere - 300,000ft Thermosphere/Ionosphere/Aurora |
|
|
|
Navy Officer Ranks |
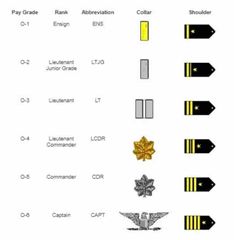
Company grade - Ensign through Captain Flag Officers - Commodores & Admirals |
|
|
|
Transponders |
“Squawk” pilot speak for setting the transponder code 1200 - aircraft is operating under visual flight rules 7500 - hijacking 7600 - loss of radio communication 7700 - emergency 7777 - military flight
|
|
|
|
Bonhomme Richard |
was a sailing frigate (warship) in the Navy during the 1760s. Sunk. |
|
|
|
Boat Names CV |
aircraft carrier |
|
|
|
Boat Names L** |
Amphibious / Landing Craft Carriers |
|
|
|
Boat Names L** |
Amphibious / Landing Craft Carriers |
|
|
|
Boat Names BB, S, A*, M* |
Battleship Submarine A* - Combat Logistics M* - Mine warefare |
|
|
|
Helicopters |
First conflict to see wide use of helicopters was the Korean War |
|
|
|
Sailboats and name of aft-most mast |

Yawl - double mast, mizzen is rear of rudder post Sloop - single mast |
|

