![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Eccrine glands are found where? |
Everywhere EXCEPT:
ears and lips!!! external auditory canal, lips, clitoris, labia minora/glans penis |
|
|
Apocrine glands are distributed where? |
Molly's mom needs to bring her eyes and ears to the PTA meeting...
eyelids (Moll's glands) EAC (cerumin glands) PITS TITTS ASS |
|
|
Sebaceous glands are distributed where? |
everywhere but palms and soles |
|
|
Meibomian glands? |
sebaceous glands of tarsal plate
remember Zeis (sebaceous glands on superficial eyelid) goes BOOM (meibomian glands) |
|
|
Montgomery tubercles? |
Sebaceous glands on nipple and areola |
|
|
Tyson's glands? |
sebaceous glands of gland penis/labia minora |
|
|
Fordyce spots? |
sebaceous glands on vermillion border of lips, labia majora, penile shaft |
|
|
Gland of Zeis? |
Sebaceous glands on superficial eyelid
Zeis goes BOOM (mebomian glands on eye) |
|
|
Study showed that 21% of women with LSA also had an autoimmune disease... |
MC thyroid (12%), AA (9%), vitiligo (2%) |
|
|
Antibodies to ECM-1? Loss of function of ECM-1? |
Autoantibodies: LSA
LOF: lipoid proteinosis |
|
|
MC location of LSA? |
85% genital |
|
|
Clinical distinction between LSA and vaginal LP? |
LSA does NOT involve vagina or cervix, vaginal LP does |
|
|
What is delling? |
white-brown follicular plugs, seen in LSA |
|
|
Risk of SCC with LSA? |
In women, slightly increased risk, <5%
In men, 25-50% of penile SCC are preceded by LS |
|
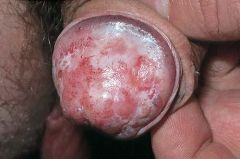
treatment? |
balanitis xerotica obliterans
ultra potent topical steroids |
|
|
What are the 4 types of genital LP? Which is most common in women? |
papules/plaque
hypertrophic
erosive- MC in women
LPP |
|
|
What type of LP is associated with hepatitis C? |
erosive oral LP |
|
|
genital LP has an associated increased risk of what? |
SCC |
|
|
Treatment for LP? |
topical steroids
LP less likely to remit than LSA |
|
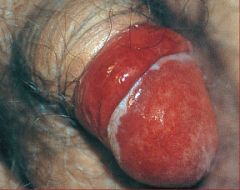
cure? |
Zoon's balanitis, usually seen in uncircumsized men d/t poor hygiene and chronic irritation
erythematous, moist plaques with cayenne pepper speckled appearance and orange hue
circumcision = cure |
|
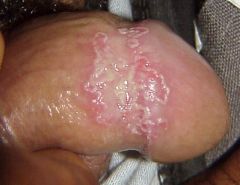
disease? |
Circinate balanitis is the dermatologic manifestation of reactive arthritis |
|
|
Characteristics of reactive arthritis? Derm findings? |
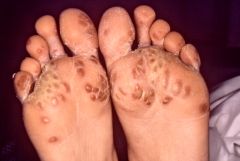
Arthritis, urethritis, conjunctivitis
circinate balanitis- serpiginous dermatitis of penis
keratoderma blenorrhagicum- foot |
|
|
MCC of genital fixed drug eruption? |
bactrim |
|
|
MCC of lip (mouth) fixed drug eruption? |
NSAIDS (pyrazolone derivatives) |
|
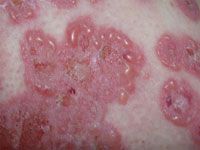
what is this? |
Chronic bullous disease of childhood (linear IgA)
genital involvement is common especially in kids |
|
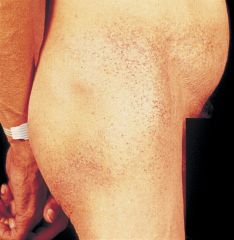
gene defect? |
Angiokeratomas in a bathing suit distribution --> Fabry's disease
XLR
GLA gene (alpha galactosidase A) --> accumulation of glycosphingolipids in vascular endothelial tissue |
|
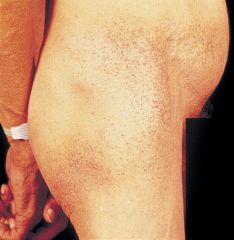
extracutaneous features associated? |
Angiokeratomas in a bathing suit distribution --> Fabry's disease
XLR
GLA gene (alpha galactosidase A) --> accumulation of glycosphingolipids in vascular endothelial tissue
cardiac disease with abnormal EKG and MI, renal disease with maltese cross (lipids in urine), corneal opacities |
|
|
Which genoderm can have verruciform xanthoma-like changes within its epidermal nevi? |
CHILD syndrome (congenital hemidysplasia, ichthyosiform erythroderma and Limb defects
XLD defect in NSDHL gene (cholesterol metabolism)
no CHILD in the NHL |
|
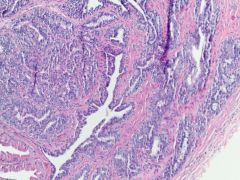
lesion on labia majora? |
hidradenoma papilliferum |
|
|
HPV associated with genital neoplasia? |
HPV 16, 18, 31, 33 |
|
|
What are the 4 types of extramammary paget's? |
1. primary EMPD- arises intraepidermally from Toker cells= apocrine stem cells in skin)
2. extension of underlying adnexal carcinoma
3. a/w underlying adjacent visceral malignancy
4. a/w underlying distant carcinoma |
|
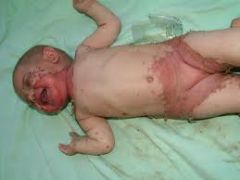
Presentation? |
perioral and genital dermatitis after weaning from breast feeding (breastmilk has adequate and accessible zinc) |
|
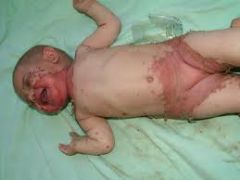
What is the defect? |
SLC39A4
Acrodermatitis enteropathica |
|
|
What is the staining pattern for langerhans cells? |
Cd1a+, S100+, Langerin + |
|
|
Criteria for Bechet's disease? |
recurrent oral ulcers >3 in 1 year, plus any 2 of the following:
recurrent genital ulcers
ocular findings (uveitis, retinal vasculitis)
cutaneous lesions (EN)
positive pathergy test |
|
|
Cause of perianal strep? |
group A B hemolytic strep (pyogenes) |
|
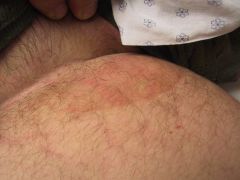
fluoresces with a woods lamp? |
erythrasma
coral red d/t coproporphyrin III
corynebacterium minutissimum |

