![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
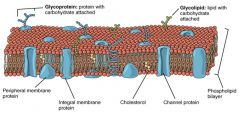
Phospholipid BiLayer |
|
|
|
Plasma Membrane |
- Responsible for what goes in and out of cell. - It is SELECTIVE/SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE. - Regulates movements. |
|
|
Structure of Plasma/Cell Membrane |
1 - Phospholipid BiLayer 2 - Proteins |
|
|
What is a solution? |
Homogeneous Mixture |
|
|
What is a solvent? |
Fluid/H2O in which substance dissolved. |
|
|
What is solute? |
Solid dissolved in liquid/H2O. ie: salt or sugar |
|
|
Passive Transport |
- Movement of substance from high to low concentration -ATP not required -Down gradient/slope |
|
|
Examples of Passive Transport |
Diffusion Osmosis |
|
|
Active Transport |
-Movement of substance from low to high concentration. -ATP required USING CARRIER PROTEIN -Up against gradient/slope |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
ie: In lungs during gas exchange: Intake of O2/Release of CO2. |
|
|
Osmosis |
Diffusion of molecules down their concentration across a selectively permeable membrane
|
|
|
Factors that affect the rate of diffusion through a membrane. |
- Temperature >High Temp = high diffusion rate >Low Temp = low diffusion rate - Size of molecule |
|
|
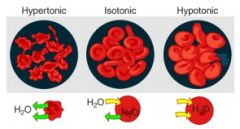
Tonacity - Response of cells to 3 types of solutions: |
|
|
|
Hypotonic |
Distilled Water - Cell swells/Gains H2O - Cell Bursts (LYSIS) |
|
|
Isotonic |
0.9% NaCl - No change in cell - Cell restored to normal |
|
|
Hypertonic |
10% NaCl -Cell shrinks/loses H20 -CRENATION |

