![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thiamine Coenzyme
|
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
|
|
|
B2 - Coenzyme
|
FAD/FADH2;
FMNFMNH2 |
|
|
Xanthine oxidase
|
In liver, MAO deactivates tyramine (toxic amine). MAO inhibitors treat depression and PD. Avoid cheese, beer, wine (high in tyramine).
|
|
|
Thiamine: a/k/a
|
B1
|
|
|
Riboflavin
|
B2
|
|
|
Nicotinic Acid / Niacin aka
|
B3
|
|
|
Pantothenic Acid
|
B5
|
|
|
Pyridoxine
|
B6
|
|
|
Thiamine- name the Coenzyme
|
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
|
|
|
Riboflavin - name the Coenzyme
|
FAD/FADH2; FMA/FMNH2
|
|
|
Nicotinic Acid / Niacin- name the Coenzyme
|
NAD+/NADH; NADP+/NADPH
|
|
|
Pantothenic Acid - name the Coenzyme
|
Coenzyme A (CoASH)
|
|
|
Pyridoxine - name the Coenzyme
|
Prydoxal-5'- phosphate (PLP)
|
|
|
Thiamine- name the Reaction Type
|
Decarboxylation, Aldehyde transfer
|
|
|
Riboflavin -
name the reaction type |
Oxidation/Reduction
|
|
|
Nicotinic Acid / Niacin- name the Reaction Type
|
Oxidatn/Reductn
|
|
|
Pantothenic Acid - name the Reaction Type
|
Acyl transfer
|
|
|
Pyridoxine - name the Reaction Type
|
Removal & replacement of groups from the a-carbon of a.a.'s.
Amino acid: racemases, decarboxylation, transamination |
|
|
Thiamine- name some Example reactions
|
--Pyruvate DH, --?-ketoglutarate DH, pyrruvate DC
|
|
|
Riboflavin - name some Example reactions
|
Succinate DH, Monoamine Oxidase, Xanthine Oxidase
|
|
|
Nicotinic Acid / Niacin- name some Example reactions
|
Alcohol metabolism; Lactate DH
|
|
|
Pantothenic Acid - name some Example reactions
|
Transfer of acetyl (2-carbon or more) acyl groups like:
Acetyl CoA; Succinyl CoA |
|
|
Pyridoxine - name some Example reactions
|
Alanine racemase, Histidine DC, Alanine, a-ketoglutarate transaminase
|
|
|
Krebs mnemonic - compounds
|
Citrate
Is (isocitrate) a (a-ketoglutarate) sour (succinyl-CoA) substance (succinate) for (fumarate) most (malate) organizisms (oxaloacetate) |
|
|
Amadori rearrangement product
|
R-CO--CH2-NH-Protein
glycosylated protein via shiff base reaction |
|
|
Glycolysis mnemonic
|
Goodness (Glucose)
Gracious, (Glucose-6-P) Father (Fructose-6-P) Franklin (Fructose-1,6-diP) Did (Dihydroxyacetone-P) Go (Glyceraldehyde-P) By (1,3-Biphosphoglycerate) Picking (3-phosphoglycerate) Pumpkins (2-phosphoglycerate) (to "2") PrEPare (Phosphoenolpyruvate [PEP]) Pies (Pyruvate) |
|
|
Glycolysis enzyme mnemonic
|
Hungry - HX/GK
Peter - ph-iso Pan - phosphofructokinase And - aldolase The - triosephosiso Growling - G3P de-H Pink - PG kinase Panther - PG mutase Eat - enolase Pies - pyruvate kinase |
|
|
Aldolase cleaves glucose where?
|

in the middle, plucks h from
|
|
|
Importance of lactate for continuation of glycolysis
|
converts NADH back to NAD+ needed for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase reaction
|
|
|
Energy reactions in Krebs (4+1)
|
reduce a lot of coenzymes that have to be reoxidzed to continue;
isocitrate deHy gives NADH a-Ketogluatarate deH gives NADH succinate deH gives FADH malate deH gives NADH (also get subs-lvl phos with succ-CoA synthetase) |
|
|
Reactions that need FAD
|
Succinate deH
|
|
|
Reactions that need NAD+
|
iso-cit deH; a-ketoglu deH; malate deH; glyceraldehyde-3-phos deH;
|
|
|
Reactions that need NADH
|
Lactate dehydrogenase to form lactate
when yeast convert pyruvate to ethanol |
|
|
Reactions that need ATP
|
HX/GK; phosphofructo-kinase;
|
|
|
Reactions that need ADP
|
pyruvate kinase, pholphoglycerate kinase
|
|
|
Aldolase reacts where?
|
pulls the H off the OH at Carbon 4; C3-4 bond breaks and forms alkene at C3-2 but last step ketone forms at C2
|
|
|
Reactions where Pi is added
|
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate deH (to 1,3-BPG)
|
|
|
G3P deH mech
|
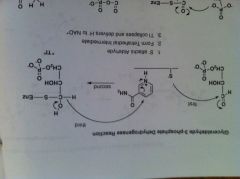
|
|
|
Differentiate FAD/FMN and NAD+
|
FAD/FMN bind tight to enzymes (covalent) while NAD+ binds loose
FAD/FMN can transfer 1e- or 2; NAD+ is 2e- shift (hydride); FADH2/FMNH2 are readily oxidized in air |
|
|
Cysteine protease intemediate
|
acyl
|
|
|
Cystiene protease residues in active site
|
CYS, HIS
|

