![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
who first introduced biochemistry |
German Chemist Carl Neuberg, 1903 |
|
|
|
Biochemistry means |
Chemistry of Living beings/ Chemical basis of life |
|
|
|
biochemistry deals with |
the study of biochemical reactions and processes |
|
|
|
Branches of biochemistry |
Medical Clinical bacterial Plant animal industrial |
|
|
|
studies the chemical basis of human body |
medical biochemistry |
|
|
|
studies clinical diseases or pathological conditions |
clinical biochemistry |
|
|
|
studies microbes |
bacterial biochemistry |
|
|
|
studies plants |
plant biochemistry |
|
|
|
studies animals |
animal biochemistry |
|
|
|
studies industrial products involved with microorganisms |
industrial biochemistry |
|
|
|
smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions |
cell |
|
|
|
all living things are made up what? |
cells |
|
|
|
cells come from pre existing cells through |
cell division |
|
|
|
types of cells |
prokaryotic eukaryotic |
|
|
|
this cell do not have structures surrounded by membranes |
prokaryotic |
|
|
|
this cell only has fe internal structure |
prokaryotic |
|
|
|
one-celled organism |
prokaryotic |
|
|
|
this cell has no nucleus |
prokaryotic |
|
|
|
this cell contains organelles surrounded by membranes |
eukaryotic |
|
|
|
most living organisms are composed of this cell |
eukaryotic |
|
|
|
a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell |
organelles |
|
|
|
surrounded by cell membrane and cell wall |
organelles |
|
|
|
outer membrane of the cell; controls movement in and out of the cell; double layer |
cell membrane |
|
|
|
found in plant cells and bacteria; supports and protects cells |
cell wall |
|
|
|
directs all cell activities; separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane; contains dna |
nucleus |
|
|
|
surrounds nucleus; 2 layers; allows material to enter and leave the nucleus |
nuclear membrane |
|
|
|
located in the nuclear; made of dna; contain instructions for traits and characteristics |
chromosomes |
|
|
|
located inside the nucleus; contains rna to build proteins |
nucleolus |
|
|
|
a gel-like mixture; surrounded by cell membrane; contains hereditary material such as genetic information |
cytoplasm |
|
|
|
moves materials around in the cell; has 2 types- smooth and rough |
endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
|
a type of ER that lacks ribosomes |
smooth |
|
|
|
a type of ER that has ribosomes embedded on the surface |
rough |
|
|
|
there are thousands pf this in the cell; make proteins; floating throughout the cell |
ribosomes |
|
|
|
produces energy through chemical reactions; controls water level and other materials; recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates |
Mitochondria |
|
|
|
digestive plant for proteins, fats, and carbohydrates; transports undigested materials to cell membrane |
lysosomes |
|
|
|
membrane bound sacs for storage, digestion, and waste removal; contains water solution; help plants maintain shape |
vacuoles |
|
|
|
found in plant cells; green chlorophyll; site for photosynthesis |
chloroplast |
|
|
|
this is produced by living organisms |
biomolecules |
|
|
|
made up of compound carbon |
biomolecules |
|
|
|
building blocks of life |
biomolecules |
|
|
|
what are the 4 biomolecules |
carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids |
|
|
|
monomer of carbohydrates |
simple sugar |
|
|
|
monomers of lipids |
glycerol and fatty acids |
|
|
|
monomer of proteins |
amino acids |
|
|
|
monomer of nucleic acid |
nucleotide |
|
|
|
atoms of water |
H2O |
|
|
|
the atoms of water are held together by a |
polar covalent bond |
|
|
|
shape of the water molecule |
bent (mickey mouse) |
|
|
|
7 properties of water |
polarity capillary action surface tension heat capacity heat of vaporization density universal solvent |
|
|
|
positive and negative charged ions |
polarity |
|
|
|
the ability of water to flow upward against the force of gravity due to cohesion and adhesion |
capillary action |
|
|
|
cohesion |
sticking together of two like molecules |
|
|
|
adhesion |
sticking together of two unlike molecules |
|
|
|
a measure of the force necessary to stretch or break the surface of a liquid |
surface tension |
|
|
|
amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost before it actually changes temperature |
specific heat |
|
|
|
the cooling of a surface occurs when the liquid evaporates |
heat of vaporization |
|
|
|
measure of how compact the atoms or molecules are within a substance or how much mass there is in a given space |
density |
|
|
|
water is solvent |
universal solvent |
|
|
|
dissolves particles |
solvent |
|
|
|
gets dissolved |
solute |
|
|
|
are macromolecules composed of amino acids linked together through peptide bonds |
proteins |
|
|
|
one of the 20 a-amino acids normally found in proteins |
standard amino acids |
|
|
|
an organic compound that contains both amino (-NH2) group and a carboxyl (-COOH) group |
amino acid |
|
|
|
an amino acid in which the amino group and the carboxyl group are attached to the alpha carbon atom |
alpha amino acid |
|
|
|
structure of amino acid |
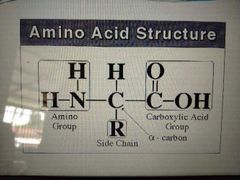
|
|
|
|
the same for all amino acids |
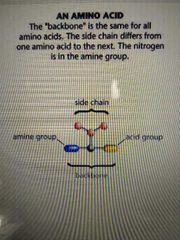
back bone |
|
|
|
2 groups present in amino acids in the same molecules |
carboxyl and amino group |
|
|
|
amino acids found in proteins |
alpha amino acids |
|
|
|
always found on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl group |
amino group |
|
|
|
also called side chains which make each AA unique and distinctive |
R groups |
|
|
|
grouped as non polar hydrophobic polar neutral basic and acidic |
AAs |
|
|
|
glycine alanine valine leucine isoleucine |
aliphatic |
|
|
|
proline |
cyclic |
|
|
|
phenylalanine tyrosine tryptophan |
aromatic |
|
|
|
serine threonine tyrosine |
hydroxyl containing |
|
|
|
cysteine methionine |
sulfur-containing |
|
|
|
histidine lysine arginine |
basic |
|
|
|
aspartic acid glutamic acid asparagine glutamine |
acidic and their amides |
|
|
|
classification of amino acids according to the side-chain polarity |
nonpolar amino acid polar neutral amino acid |
|
|
|
contains one amino group and one carboxyl group and non-polar side chain hydrophobic 9 nonpolar amino acids |
nonpolar amino acid |
|
|
|
contains one amino group one carboxyl group and a side chain that is polar but neutral six amino acids |
polar neutral amino acid |
|
|
|
R groups are nonpolar hydrophobic-aliphatic or aromatic groups r groups are and charged aasar in soluble in h2o |
nonpolar and hydrophobic aas |
|
|
|
R groups are polar: -OH, -SH, -NH2 R groups are highly reactive AAs are soluble in h2o that is hydrophilic |
polar and uncharged aas |
|
|
|
this one amino group and to carboxyl groups the second carboxyl group being part of the side chain (2AA) the side-chain bears a negative charge |
polar acidic amino acid |
|
|
|
contains two amino groups and one carboxyl group the second amino group being part of the side chain (3AA) the side-chain bears a positive charge |
polar basic amino acid |
|
|
|
Basic AAs |

|
|
|
|
Acidic AAs |

|
|
|
|
examples of acidic amino acids |

|
|
|
|
examples of basic amino acids I |

|
|
|
|
examples of basic amino acids II |

|
|
|
|
no of essential amino acids |
10 |
|
|
|
no of nonessential amino acids |
10 |
|
|

|
essential amino acids |
|
|

|
nonessential amino acids |
|
|

|
complete protein |
|
|

|
incomplete protein |
|
|
|
non-superimposed molecules mirror image four different group bounded to the alpha carbon |
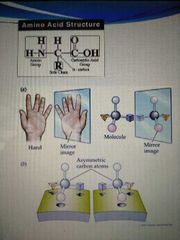
chirality |
|
|
|
except for glycine all amino acids have |
chiral carbon atom, have optical isomers |
|
|
|
the amino acids found in proteins are all |
levorotatory or L forms |
|
|
|
have a tendency to lose protons H+ producing a negatively charged species |
carboxyl groups |
|
|
|
have a tendency to accept protons H+ juicing positively charged species |
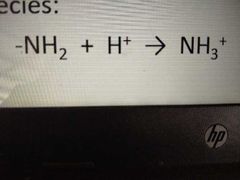
amino groups |
|
|
|
capability of behaving as both an acid and a base since they have both a proton donor group and a proton acceptor group |
amphoteric |
|
|
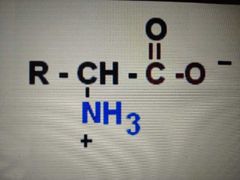
dipolar ion form |
zwitterion |
|
|
|
a molecule that has a positive charge on one atom and a negative charge on another atom but which has no net charge |
zwitterion |
|
|
|
in this solution, the zwitterion accepts a proton to form a positively charged ion |
acidic solution |
|
|
|
in this solution the NH3 of the zwitterion loses a proton and a negatively charged species is formed |
basic solution |
|
|
|
three different amino acid in a solution |
zwitterion negative ion and a positive ion |
|
|
|
is the ph at which an amino acid solution has no net charge because an equal number of positive and negative charges are present |
isoelectric point |
|
|
|
is the process of separating charged electrode associated with an electric field |
electrophoresis |
|
|
|
unbranched chain of amino acid |
peptide |
|
|
|
how is a peptide classified |
by the number of amino acids present in the chain |
|
|
|
a type of peptide that contains two amino acids |
dipeptide |
|
|
|
a type of peptide that contains three amino acid |
tripeptide |
|
|
|
a type of peptide that has 10 to 20 amino acids |
oligopeptide |
|
|
|
a type of peptide that has more than 20 amino acids and is a long on branched chain of amino acids each joined to the next by a peptide bond |
polypeptide |
|
|
|
it is a covalent bond formed between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of its next amino acid with the elimination of one h2o molecule |
peptide bond |
|
|
|
is formed and lost when two amino acids combine |
amide and water molecule |
|
|
|
working molecule of the cell |
protein |
|
|
|
function of protein |
building of new cells maintenance of existing cells replacement of old cells |
|
|
|
function of protein
regulation of |
metabolic processes |
|
|
|
function of protein catalysis of |
biochemical reactions |
|
|
|
function of protein transportation of |
oxygen (hemoglobin) in blood and in the muscle (myoglobin) |
|
|
|
classification of proteins according to shape |
globular - ball fibrous - rod |
|
|
|
biochemical catalyst called enzymes |
catalytic protein |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
antibodies, central to functioning of the body's immune system |
defense protein |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
hemoglobin |
transport proteins |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
transmit signals insulin |
messenger proteins |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
collagen |
structural proteins |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
bind small molecules for future use myoglobin |
storage proteins |
classification of proteins based on function |
|
|
important in the early stages of lie from embryo to infant casein in milk |
nutrient proteins |
|
|
|
composed of only amino acid unit and on hydrolysis yield only amino acids |
simple protein |
classification of proteins according to composition |
|
|
contain another type of molecule or compound attached to the amino acid unit and on hydrolysis yield amino acids and that other molecule |
conjugated proteins |
classification of proteins according to composition |
|

|
secondary |
level of structure of protein |
|

refers to the complex conformations that result from the extensive bending and folding of protein chains that characterizes globular proteins |
tertiary |
level of structure of protein |
|
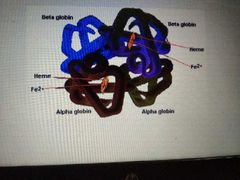
occurs when 2 or more protein units combine to form a more complex unit |
quaternary |
level of structure of protein |
|
|
denatured proteins tend to |

|
|
|
|
protein packaging plant; move materials out of the cell |
golgi bodies |
|

