![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy |
is the science of body structures and the relationships among them |
|
|
Physiology |
is the science of body functions |
|
|
What are the body's six levels of structural organization? |
1. chemical 2. cellular 3. tissue 4. organ 5. system 6. organismal |
|
|
Atoms |
the smallest units of matter that participate in chemical reactions |
|
|
Molecules |
two or more atoms joined together |
|
|
Cells |
the basically structural and functional units of an organism that are composed of chemicals |
|
|
What composes the chemical level? |
Atoms and molecules |
|
|
What are the four basic types of tissues? And what does each do? |
1. Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs and cavities and forms glands 2. Connective tissues connects, supports and protects body organs while distributing blood vessels to other tissues 3. Muscular tissue contracts to make body parts move and generates heat 4. Nervous tissue carries information from one part of the body to another through nerve impulses |
|
|
Organs |
structures that are composed of two or more different types if tissues; they have specific functions and usually have recognizable shapes |
|
|
System |
consists of related organs with a common function |
|
|
Organism |
any living individual |
|
|
What are the 11 systems of the human body? |
1. Integumentary system 2. Skeletal system 3. Muscular system 4. Nervous system 5. Endocrine system 6. Cardiovascular system 7. Lymphatic system 8. Respiratory system 9. Digestive system 10. Urinary system 11. Reproductive system |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the integumentary system. |
Components: skin and associated structures such as hair, fingernails and toenails, sweat glands and oil glands Functions: protects body; helps regulate body temperature; eliminates some wastes; makes vitamins D; detects sensations such as touch, pain, warmth and cold |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the skeletal system. |
Components: bones and joints of the body and their associated cartilages Functions: support and protect the body; provide surface area for muscle attachments; aids body movements; houses cells that produce blood cells; stores minerals and lipids (fats) |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the muscular system. |
Components: skeletal muscle tissue Functions: participate in body movements such as walking; maintains posture; produces heat |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the nervous system. |
Components: brain, spinal cord and nerves and special sense organs such as eyes and ears Functions: generates action potentials (nerve impulses) to regulate body activities; detects changes in body's internal and external environments, interprets changes and responds by causing muscle contractions or glandular secretions |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the endocrine system. |
Components: hormone producing glands and hormone producing cells in several other organs Functions: regulates body activities by releasing hormones |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the cardiovascular system. |
Components: blood, heart and blood vessels Functions: heart pumps blood through blood vessels; blood carries oxygen and nutrients to cells and carbon dioxide and waste away from the cells and helps regulates acid-base balance, temperature, and water content of body fluids; blood components help defend against disease and repaid damaged blood vessels |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the lymphatic system. |
Components: lymphatic fluid and vessels Functions: returns proteins and fluid to blood; carries lipids from gastrointestinal tract to blood; contains sites of maturation and proliferation of B cells and T cells that protect against disease-causing microbes |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the respiratory system. |
Components: lungs and air passageway Functions: transfers oxygen from inhaled air to blood and carbon dioxide from blood to exhaled air; helps regulate acid-base balance of body fluids; air flowing our of lungs through vocal cords produces sounds |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the digestive system. |
Components: organs of the gastrointestinal tract Functions: achieves physical and chemical breakdown of food; absorbs nutrients; eliminates solid wastes |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the urinary system. |
Components: kidneys, uterers, urinary bladder, and urethra Functions: produces, stores and eliminates urine; eliminates waste and regulates volume and chemical composition of blood; helps maintain the acid-base balance of blood; maintains body's mineral balance; helps regulate production of red blood cells |
|
|
Describe the components and major functions of the reproductive system. |
Components: gonads and associated organs Functions: gonads produce gametes (sperm and oocytes) that unit to form a new organism; gonads also release hormones that regulate reproduction and other body processes; qssociated organs transport and store gametes; mammary glands produce milk |
|
|
What are the 6 most important life processes of the human body? |
1. Metabolism 2. Responsiveness 3. Movement 4. Growth 5. Differentiation 6. Reproduction |
|
|
Metabolism |
the sum of all chemical processes that occur in the body |
|
|
Catabolism |
the breakdown of complex chemical substances into similar components |
|
|
Anabolism |
the building up of complex chemical substances from small, simpler components |
|
|
Responsiveness |
the body's ability to detect and respond to changes |
|
|
Movement |
includes motion of the whole body, individual organs, single cells and even tiny structures inside cells |
|
|
Growth |
an increase in body size that results from an increase in the size of existing cells, an increase in the number of cells or both |
|
|
Differentiation |
the development of a cell from an unspecialized to a specialized state |
|
|
Reproduction |
refers to either 1) the formation of new fells for tissue growth, repair, or replacement, or 2) the production of a new individual |
|
|
Homeostasis |
is the condition of equilibrium (balance) in the body's internal environment due to the constant interaction of the body's many regulatory processes |
|
|
Intracellular fluid (ICF) |
fluid within cells |
|
|
Extracellular fluid (ECF) |
fluid outside body cells |
|
|
Interstitial fluid |
ECF that fills the narrow spaces between cells of tissues |
|
|
Feedback system |
isn't cycle of events in which the status of a body condition is monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitored, reevaluated and so on |
|
|
Controlled condition |
any monitored variable ie blood pressure, body temperature |
|
|
Stimulus |
any disruption that changed a controlled condition |
|
|
What are the three basic components of a feedback system? |
1. Receptor 2. Control Center 3. Effector |
|
|
What is a receptor (feedback system)? |
A body structures that monitors changes in a controlled condition and send input to a control center. Ie certain nerve endings in the skin sense temperature and can detect changes, such as a dramatic drop in temperature |
|
|
What is a control center (feedback system)? |
Sets the range of values within which a controlled condition should be maintained, evaluates the input it relieves from receptors, and generates output commands when they are needed. Ie. The brain acts as the control center receiving nerve impulses from the skin receptors (temperature change) and generates nerve impulses as outputs. |
|
|
What is an effector (feedback system)? |
A body structure that receives output from the control center and produces a response or effect that changes the controlled condition. Ie when your body temperature drops sharply, your brain (control center) sends nerve impulses (output) to your skeletal muscles (effectors). The result is shivering, which generates heat and raises your body temperature. |
|
|
What does a negative feedback system do? |
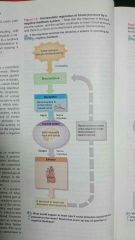
Reverses a change in a controlled condition. |
|
|
What does a positive feedback system do? |

Tends to strengthen of reinforce a change in one if the body's controlled conditions.
|
|
|
Disorder |
any abnormality of structure or function |
|
|
Disease |
a more specific term for an illness characterized by a recognizable set of signs and symptoms |
|
|
Describe local disease and systemic disease. |
Local disease affects one part of or a limited region of the body. Systemic disease affects either the entire body or several parts of it. |
|
|
What is epidemiology? |
The science of when, where, and why disease occur and how they are transmitted among individuals. |
|
|
What is pharmacology? |
The science that deals with the effects and uses of drugs in the treatment of disease. |
|
|
Anatomical position |
subject stands erect facing the observer, arms at their sides, palms forward |
|
|
Prone position |
lying face down |
|
|
Supine position |
lying face up |
|
|
What are the five principle regions? |
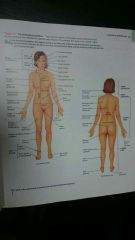
1. Head 2. Neck 3. Trunk 4. Upper limb 5. Lower limb |
|
|
Superior |
Towards the head, or the upper part of the structure. |
|
|
Inferior |
Away from the head, or the lower part of the structure. |
|
|
Anterior |
Near to or at the front of the body. |
|
|
Posterior |
Near to or at the back of the body. |
|
|
Medial |
Near to the midline. |
|
|
Lateral |
Farther from the midline. |
|
|
Intermediate |
Between two structures. |
|
|
Ipsilateral |
On the same side of the body as another structure. |
|
|
Contralateral |
On the opposite side of the body from another structure. |
|
|
Proximal |
Nearer to the attachment of a limb to the trunk; nearer to the origination of a structure. |
|
|
Distal |
Farther from the attachment of a limb to the trunk; farther from the origination of a structure. |
|
|
Superficial |
Towards the surface of a body. |
|
|
Deep |
Away from the surface of a body. |
|
|
Sagittal plane |
is a vertical plane that divides the body or an organ into right and left sides. If the sides are equal, meaning it passes through the midline, it is called a midsagittal place or a median plane. |
|
|
Parasagittal plane |
the division of the body or organ into unequal left and right sides. |
|
|
Frontal or coronal plane |
divides the body or organ into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions. |
|
|
Transverse plane aka cross-sectional or horizontal plane |
divides the body or organ into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) portions. |
|
|
Oblique plane |
passes through the body or organ St an angle between the transverse plane and either a sagittal or frontal plane. |
|
|
Cranial cavity |
Formed by cranial bones and contains brain. |
|
|
Vertebral cavity |
Formed by vertebral column and contains spinal cord and the beginnings of spinal nerves. |
|
|
What is meninges and it's function? |
Meninges is three layers of protective issue that line the cranial cavity and the vertebral cavity. |
|
|
Thoracic cavity |
Chest cavity is former by the ribs, muscles of the chest, sternum and the thoracic portion if the vertebral column (backbone). |
|
|
Pericardial cavity |
A fluid filled space that surrounds the heart. |
|
|
Pleural cavities |
Each surround a lung and contains a small amount of fluid. |
|
|
Mediastinum |
Central portion of thoracic cavity between the lungs; contains heart, thymus, esophagus, trachea, and several large blood vessels. |
|
|
What is the diaphragm? |
A dome shaped muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity. |
|
|
Abdominopelvic cavity |
Divided into two portions - abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity. Abdominal contains the stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small intestine and most of the large intestine. The pelvic contains urinary bladder, portions of large intestine and internal reproductive organs |
|
|
Abdominal cavity |
Superior portion; contains the stomach, spleen, liver, gallbladder, small intestine and most of the large intestine. |
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Inferior portion; contains the urinary bladder, portions of the large intestine, and internal organs of the reproductive system |
|
|
Viscera |
organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities |
|
|
Chemistry |
the science of the structure and interactions of matter |
|
|
Mattet |
anything that occupies space and has mass |
|
|
Mass |
the amount of matter in any object, which does not change |
|
|
What are the four major elements in the human body? |
Oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen |
|
|
Atom |
the smallest unit of matter |
|
|
Nucleus |
the dense central core of an atom |
|
|
What does the nucleus consist of? |
Positively charged protons, uncharged neutrons - tiny negatively changed electrons orbit thr space around the nucleus |
|
|
Atomic number |
number of protons in an atom |
|
|
Mass number |
Number of protons and neutrons in an atom |
|
|
Atomic mass |
Average mass of all stable atoms of a given elements in Dalton's |
|
|
Isotopes |
atoms of an element that have difference numbers of neutrons and therefore different mass numbers |
|
|
Ion |
an atom that has a positive or negative changed because it gas unequal numbers of protons and electrons |
|
|
Ionic bond |
molecular bond formed between atoms with opposite charges |
|
|
Cation |
positively charged ion |
|
|
Anion |
negatively charged ion |
|
|
Covalent bond |
forms when two or more atoms share electrons rather than gaining or losing them |
|
|
Catalyst |
Chemical compounds that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy needed for a reaction to occur |
|
|
Oxidation |
the loss of electrons |
|
|
Reduction |
the gain of electrons |
|
|
Inorganic compounds |
Usually lack carbon and are structurally simple |
|
|
Organic compounds |
Always have carbon, usually have hydrogen and always have covalent bonds |
|
|
Acid |
a substance that disassociates into one or more hydrogen ion (H+) |
|
|
Base |
removes h+ from a solution |
|
|
What are the three major carbohydrate groups? |
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharies |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
3 to 7 carbon atoms/end in -ose |
|
|
Disaccharides |
a combination of two monosaccharides combined by dehydration synthesis |

