![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where is urea formed and from what? |
formed in the liver from excess amino acids |
|
|
Where is carbon dioxide excreted through? |
the lungs |
|
|
What do the kidney's excrete? |
-urea -excess water and salts |
|
|
Define deamination |
as the removal of the nitrogen-containing part of amino acids to form urea |
|
|
Describe the role of the liver in the assimilation of amino acids by converting them to proteins, including plasma-proteins (fibrogen) |
-liver removes amino acids from plasma of the bloodstream and builds them up into proteins -including fibrogen for blood clotting |
|
|
Explain the need for excretion |
-some compounds made in reactions in the body are potentially toxic if their concentrations build up |
|
|
Explain the need for excretion in terms of the carbon dioxide |
-carbon dioxide dissolves in fluids such as tissue fluids and blood plasma to form carbonic acid -this increase in acidity can effect actions of enzymes |
|
|
Explain the need for excretion in terms of the toxicity of urea |
-ammonia is made in the liver when excess amino acids are broken down -ammonia is very alkaline and toxic -it is converted to urea which is much less poisonous, making it a safe way of excreting excess nitrogen |
|
|
What effects the concentration of urine produced? |
exercise -when you sweat, you lose more water from the body through evapouration from the skin temperature -cold day, sweating decreases, more water is removed from blood by kidneys water intake -if blood flowing through kidneys is too dilute, less water is reabsorbed -after drinking a lot, a dilute urine is produced |
|
|
Structure of the kidney diagram |
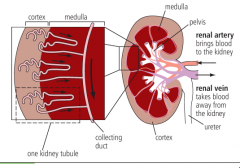
|
|
|
Structure of a kidney tubule diagram |
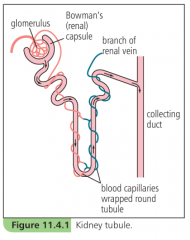
|
|
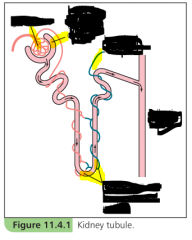
Label it |
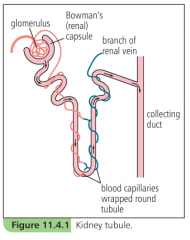
|
|
|
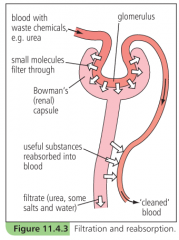
Outline the role of the glomerulus in the functioning of the kidney tubule |
-blood pressure in a glomerulus causes part of the blood plasma to leak through capillary walls -red blood cells and plasma proteins are too big to pass out of the capillary, so the fluid that does filter through doesn't have these in it -fluid consists mainly of water and dissolved salts, glucose and urea and uric acid |
|
|
What process is the name ultrafiltration given to? |
blood pressure in capillaries causes part of the blood plasma to leak through capillary walls red blood cells and plasma proteins are too big to pass out of capillaries so the fluid that does pass through consists of water, dissolved salts, glucose and urea and uric acid process by which the fluid is filtered out of the blood by the glomerulus |
|
|
Outline the role of the tubule in the functioning of the kidney tubule |
-filtrate from the glomerulus collects in the renal capsule and trickles down the renal tubule -as it does, the capillaries absorb back into the blood those substances which the body needs: some salts, most of the water, all of the glucose |
|
|
What process is the name selective reabsorption given to? |
the process of absorbing back the substances needed by the body, from the renal tubule by the capillaries these substances are: most of the water, all of the glucose, some of the salts |
|
|
What does the selective reabsorption in the renal tubule by the capillaries lead to? |
high concentration of urea in the urine loss of excess water and salts |
|
|
Advantages of kidney transplants compared with kidney dialysis |
patient can return to normal lifestyle -dialysis may require a lengthy session in hospital, patient is tired dialysis machine will be available for others to use dialysis machines are expensive to buy and maintain |
|
|
Disadvantages of kidney transplants compared with kidney dialysis |
transplants require a suitable donor -with a good tissue match, donor may be from a dead person or close living relative operation is very expensive risk of rejection not accepted by some religions |
|
|
How does a dialysis machine work? |
-machine consists of long cellulose tube coiled up in a water bath -patients blood is lead from vein in the arm and pumped through cellulose (dialysis) tubing -tiny pores in the tubing allow small molecules (salts, glucose and urea to leak out into water bath -blood cells and protein molecules are too large to get through pores |
|
|
Which process in kidney dialysis is similar to the filtration process in the glomerulus? |
patients blood is lead from vein in the arm and pumped through cellulose (dialysis) tubing
-tiny pores in the tubing allow small molecules (salts, glucose and urea) to leak out into water bath -blood cells and protein molecules are too large to get through pores |
|
|
How is the glucose concentration maintained during kidney dialysis and how does this remove the urea? |
-liquid in water bath consists of a solution of salts and sugar of the correct composition -so that only the substances above this concentration can diffuse out of the blood into the bathing solution -thus, excess salts uric acid and urea are removed, as the glucose in the blood cannot diffuse out |
|
|
Define assimilation |
as the absorption of substances which are then built up into other compounds in the organism |
|
|
Filtration and reabsorption diagram |
|

