![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
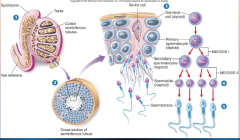
1. Male mammals are more ________ in their reproductive activity (spermatogenesis). |
![1. Male mammals are more [CONSTANT] in their reproductive activity (spermatogenesis).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/28/84/7002884_m.png)
1. Male mammals are more [CONSTANT] in their reproductive activity (spermatogenesis). |
|
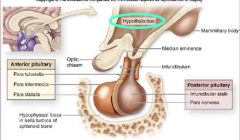
2. GnRH – ____________-Releasing hormone. |
![2. GnRH – [GONADOTROPIN]-Releasing hormone.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/28/99/7002899_m.png)
2. GnRH – [GONADOTROPIN]-Releasing hormone. |
|
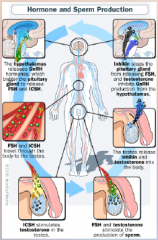
3. ICSH – ____________ Cell-Stimulating hormone. |
![3. ICSH – [INTERSTITUAL] Cell-Stimulating hormone.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/05/7002905_m.png)
3. ICSH – [INTERSTITUAL] Cell-Stimulating hormone. |
|
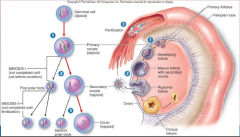
4. Female mammals generally undergo _____ reproductive cycles, sometimes at given times of the year. |
![4. Female mammals generally undergo [SHORT] reproductive cycles, sometimes at given times of the year.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/17/7002917_m.png)
4. Female mammals generally undergo [SHORT] reproductive cycles, sometimes at given times of the year. |
|
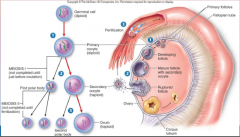
5. At times of ovulation (______ cycle) the female is considered “in heat” or estrus. |
![5. At times of ovulation ([ESTRUS] cycle) the female is considered “in heat” or estrus.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/26/7002926_m.png)
5. At times of ovulation ([ESTRUS] cycle) the female is considered “in heat” or estrus. |
|
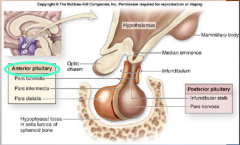
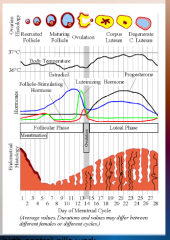
6. During the estrous cycle changes in the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutenizing hormone (LH) by the anterior pituitary gland cause changes in egg cell ___________ and hormone _________ on the ovaries. |
![6. During the estrous cycle changes in the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutenizing hormone (LH) by the anterior pituitary gland cause changes in egg cell [DEVELOPMENT] and hormone [SECRETION] on the ovaries.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/32/7002932_m.png)
6. During the estrous cycle changes in the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and lutenizing hormone (LH) by the anterior pituitary gland cause changes in egg cell [DEVELOPMENT] and hormone [SECRETION] on the ovaries. |
|

7. Rabbits and cats are _______ ovulators (ovulate only after __________ as a result of a reflex stimulation of LH secretion). |
![7. Rabbits and cats are [INDUCED] ovulators (ovulate only after [COPULATION] as a result of a reflex stimulation of LH secretion).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/44/7002944_m.png)
7. Rabbits and cats are [INDUCED] ovulators (ovulate only after [COPULATION] as a result of a reflex stimulation of LH secretion). |
|
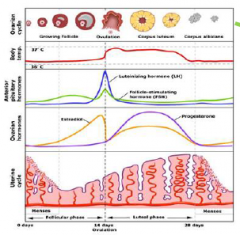
8. Humans and apes have _________ cycles (cyclic pattern of hormone secretion and ovulation) that are similar to the _______ cycles of other mammals. |
![8. Humans and apes have [MENSTRUAL] cycles (cyclic pattern of hormone secretion and ovulation) that are similar to the [ESTROUS] cycles of other mammals.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/62/7002962_m.png)
8. Humans and apes have [MENSTRUAL] cycles (cyclic pattern of hormone secretion and ovulation) that are similar to the [ESTROUS] cycles of other mammals. |
|
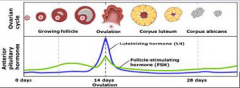
9. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![9. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Follicle [STIMULATING] hormone (FSH).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/71/7002971_m.png)
9. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
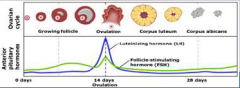
10. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![10. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH).
Stimulates the [DEVELOPMENT] of a primary follicules (oocytes).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/30/04/7003004_m.png)
10. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
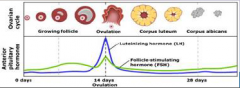
11. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![11. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH).
Increases the number of follicular cells which in turn produce [OESTROGENS].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/95/7002995_m.png)
11. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
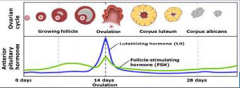
12. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![12. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH).
Produces [FOLLICULAR] fluids.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/86/7002986_m.png)
12. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
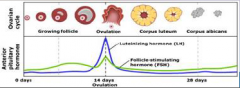
13. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![13. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Follicle Stimulating hormone (FSH).
Develops the [OOCYTE] in the follicle.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/29/80/7002980_m.png)
13. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
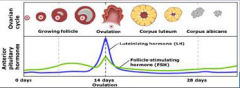
14. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![14. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
[LUTEINISING] hormone (LH).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/30/76/7003076_m.png)
14. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
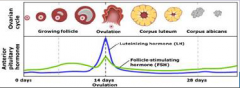
15. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![15. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Luteinising hormone (LH).
Surges in mid cycle (12 days) to bring about [OVULATION].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/12/7003112_m.png)
15. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
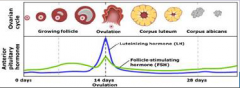
16. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![16. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Luteinising hormone (LH).
High LH is associated with resumption of [MEIOSIS] in the oocyte.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/03/7003103_m.png)
16. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
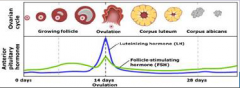
17. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
![17. Anterior Pituitary Hormones.
Luteinising hormone (LH).
Stimulates the development of the [CORPUS] luteum.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/30/85/7003085_m.png)
17. Anterior Pituitary Hormones. |
|
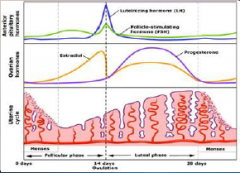
18. Ovarian Hormones. |
![18. Ovarian Hormones.
[OESTROGEN].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/18/7003118_m.png)
18. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
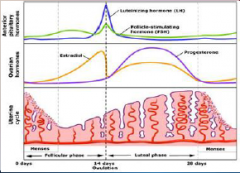
19. Ovarian Hormones. |
![19. Ovarian Hormones.
Oestrogen.
Stimulates the development of the endometrium (lining of the uterus) and its associated [BLOOD] supply.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/51/7003151_m.png)
19. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
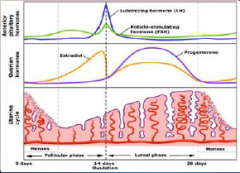
20. Ovarian Hormones. |
![20. Ovarian Hormones.
Oestrogen.
During the first half of the cycle there is positive feedback through increased [SENSITIVITY] of the follicle cells to FSH.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/39/7003139_m.png)
20. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
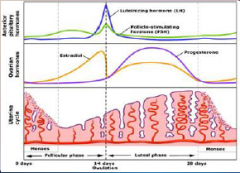
21. Ovarian Hormones. |
![21. Ovarian Hormones.
Oestrogen.
During the second half of the cycle ([HIGH] oestrogen) there is negative feedback on FSH and LH.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/31/30/7003130_m.png)
21. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
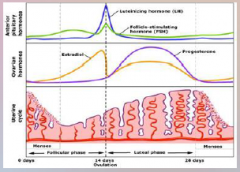
22. Ovarian Hormones. |
![22. Ovarian Hormones.
[PROGESTERONE].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/34/7003334_m.png)
22. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
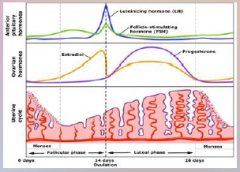
23. Ovarian Hormones. |
![23. Ovarian Hormones.
Progesterone.
Maintains the [LINING] of the endometrium.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/28/7003328_m.png)
23. Ovarian Hormones. |
|
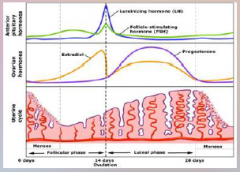
24. Ovarian Hormones. |
![24. Ovarian Hormones.
Progesterone.
[NEGATIVE] feedback on FSH and LH.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/22/7003322_m.png)
24. Ovarian Hormones. |
|

25. While there are many types of _____________ methods, we will focus on the birth control pill. |
![25. While there are many types of [CONTRACEPTIVE] methods, we will focus on the birth control pill.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/52/7003352_m.png)
25. While there are many types of [CONTRACEPTIVE] methods, we will focus on the birth control pill. |
|

26. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills. |
![26. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills.
Estrogen and [PROGESTIN].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/58/7003358_m.png)
26. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills. |
|
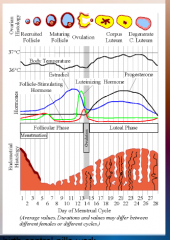
27. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills. |
![27. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills.
Estrogen and progestin.
[PROGESTIN]-only.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/33/70/7003370_m.png)
27. 2 types of hormonal birth control pills. |
|
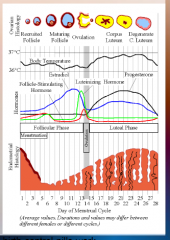
28. Estrogen. |
![28. Estrogen.
Stop the [PITUITARY] gland from producing FSH and LH in order to prevent ovulation.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/37/96/7003796_m.png)
28. Estrogen. |
|
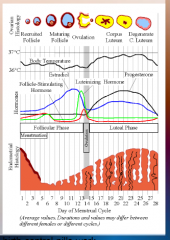
29. Estrogen. |
![29. Estrogen.
Support the endometrium to prevent [BLEEDING] mid-cycle.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/37/90/7003790_m.png)
29. Estrogen. |
|
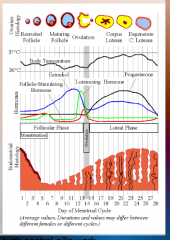
30. Progestin. |
![30. Progestin.
Stop the pituitary gland from producing LH in order to [PREVENT] egg release.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/38/26/7003826_m.png)
30. Progestin. |
|
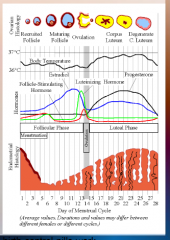
31. Progestin. |
![31. Progestin.
Make uterine lining [INHOSPITABLE] to a fertilized egg.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/38/14/7003814_m.png)
31. Progestin. |
|
32. Progestin. |
![32. Progestin.
Thicken the [CERVICAL] mucus to hinder sperm movement.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/38/08/7003808_m.png)
32. Progestin. |
|
33. ________ – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
![33. [SYPHILIS] – Treponema pallidum pallidum.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/01/7003901_m.png)
33. [SYPHILIS] – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
|
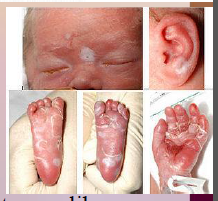
34. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
![34. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum.
Can be passed to fetus as it is born resulting in fetal [DEATH] or mental retardation and [MALFORMATION].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/34/7003934_m.png)
34. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
|
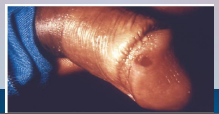
35. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
![35. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum.
Primary syphilis – small painless reddened lesion, heals in 3-6 [WEEKS].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/40/7003940_m.png)
35. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
|
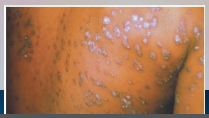
36. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
![36. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum.
Secondary syphilis – rash appears 1-6 months [AFTER] exposure and lasts 6-8 weeks.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/49/7003949_m.png)
36. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
|
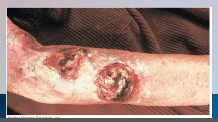
37. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
![37. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum.
Tertiary syphilis – appears 1-10 [YEARS], gummas, soft, tumor-like growths that can occur anywhere including on skeleton, cardiovascular and neurological symptoms that can lead to [DEATH].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/58/7003958_m.png)
37. Syphilis – Treponema pallidum pallidum. |
|
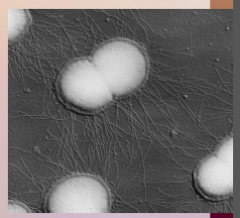
38. _________ – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![38. [GONORRHEA] – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/73/7003973_m.png)
38. [GONORRHEA] – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
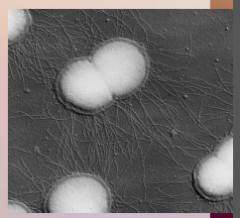
39. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![39. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in [MEN].
Acute inflammation of [URETHRA] in 2-5 days.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/94/7003994_m.png)
39. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
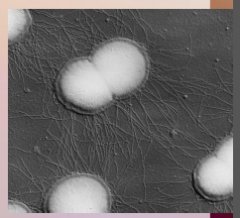
40. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![40. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Men.
Painful [URINATION].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/85/7003985_m.png)
40. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
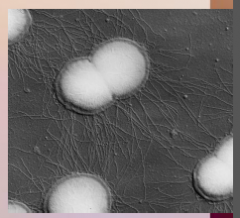
41. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![41. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Men.
[PURULENT] discharge (aka. gleet).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/39/79/7003979_m.png)
41. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
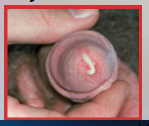
42. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![42. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Men.
Sometimes causes painful swollen [TESTICLES].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/40/15/7004015_m.png)
42. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
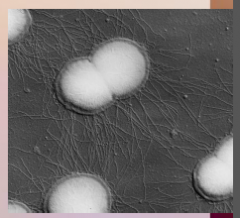
43. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![43. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Men.
Can cause epididymitis – a painful condition of the ducts attached to the testicles that may lead to [INFERTILITY] if left untreated.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/40/27/7004027_m.png)
43. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
|
44. Free Bee |
44. Free Bee |
|
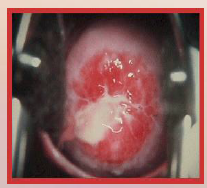
45. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![45. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in [WOMEN].
[50]% asymptomatic.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/02/7004102_m.png)
45. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
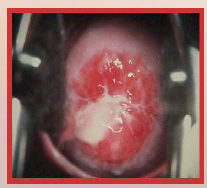
46. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![46. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Women.
Appear as [BLADDER] or [YEAST] infection.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/08/7004108_m.png)
46. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
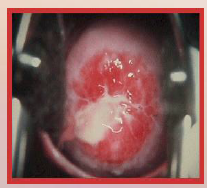
47. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![47. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Women.
Attaches to [CERVIX], uterus and fallopian tubes.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/14/7004114_m.png)
47. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
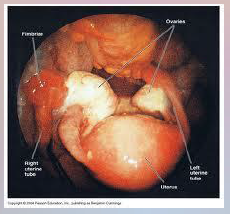
48. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![48. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Women.
Leads to PID (pelvic [INFLAMMATORY] disease).](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/20/7004120_m.png)
48. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
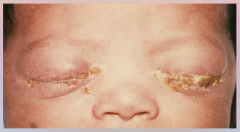
49. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
![49. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Symptoms in Newborns (infected during delivery) – inflammation of cornea and conjunctiva leading to [BLINDNESS].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/26/7004126_m.png)
49. Gonorrhea – Neisseria gonorrhoeae. |
|
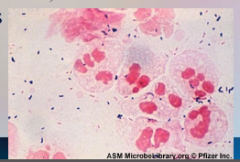
50. _________ – _________ trachomatis. |
![50. [CHLAMYDIA] – [CHLAMYDIA] trachomatis](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/38/7004138_m.png)
50. [CHLAMYDIA] – [CHLAMYDIA] trachomatis |
|
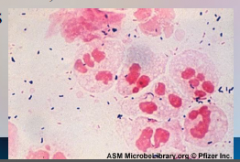
51. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
![51. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis.
Lymphogranuloma venereum.
Stage 1 – lesions at site of infection [HEAL] rapidly, headache, muscle pain and [FEVER].](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/50/7004150_m.png)
51. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
|
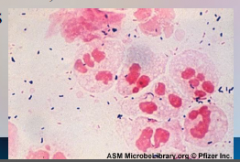
52. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
![52. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis.
Lymphogranuloma venereum.
Stage 2 – buboes develop associated with lymphatic vessels [DRAINING] at site of infection, may enlarge and rupture producing draining sores, fever, chills, anorexia and [MUS...](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/59/7004159_m.png)
52. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
|
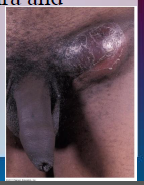
53. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
![53. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis.
Lymphogranuloma venereum.
Stage 3 – (few cases) genital sores, constriction of urethra and genital [ELEPHANTIASIS], arthritis.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/53/7004153_m.png)
53. Chlamydia – Chlamydia trachomatis. |
|
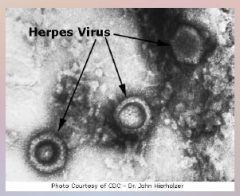
54. Hepes – Herpesviruses – ___ virus. |
![54. Hepes – Herpesviruses – [DNA] virus.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/68/7004168_m.png)
54. Hepes – Herpesviruses – [DNA] virus. |
|
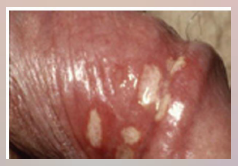
55. Hepes – Herpesviruses – DNA virus. |
![55. Hepes – Herpesviruses – DNA virus.
Infections include [ORAL] herpes, genital herpes, [OCULAR] herpes, Whitlow, neonatal herpes.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/74/7004174_m.png)
55. Hepes – Herpesviruses – DNA virus. |
|
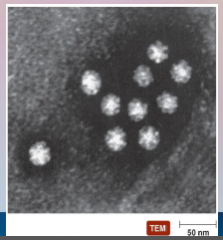
56. HIV – Human _______________ Virus – RNA Virus. |
![56. HIV – Human [IMMUNODEFICIENT] Virus – RNA Virus.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/80/7004180_m.png)
56. HIV – Human [IMMUNODEFICIENT] Virus – RNA Virus. |
|
57. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus. |
![57. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus.
Only replicates in [HUMANS] and destroys the [IMMUNE] system.](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/86/7004186_m.png)
57. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus. |
|
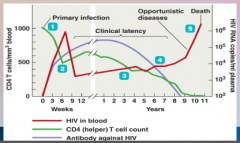
58. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus. |
![58. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus.
AIDS is not a disease, but a [SYNDROME] – certain opportunistic or rare infections that occur in the presence of antibodies against HIV and CD4 [WHITE] blood cell count below 200 cells/mic...](https://images.cram.com/images/upload-flashcards/00/41/92/7004192_m.png)
58. HIV – Human Immunodeficient Virus – RNA Virus. |

