![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Segments of DNA that contain the information to make proteins |
Gene |
|
|
Variants of the same Gene that result in specific traits |
Alllele |
|
|
An organisms genetic makeup (a trial alleles |
Genotype |
|
|
Physical, physiological, and behavioral features that result from the genotype |
Phenotype |
|
|
Two copies of one allele (ex hh) |
Homozygous |
|
|
Two different copies of one allele (ex Hh) |
Heterozygous |
|
|
What is an allelic interaction |
The "interaction" that occurs between two alleles in a given genotype, that will determine how the phenotype is expressed |
|
|
What are the 3 forms of allelic interaction |
1. Dominance/recessiveness 2. Incomplete dominance 3. Codominance |
|
|
What are the stages of cell reproduction (mitosis) |
1. Prophase 2. Metaphase 3. Anaphase 4. Telophase |
|
|
What is something that animal cells have but plants don't when reproducing |
A cleavage furrow |
|
|
What to plant cells have that animals don't when reproducing |
Cell plate |
|
|
What is a tight coiled/packed DNA ready for cell division called |
Chromosomes |
|
|
Copies of a replicated chromosomes that remain attached through parts of mitosis |
Sister chromatids |
|
|
Found in a the daughter cells, are just sister chromatids that are no longer attached |
Daughter chromatids |
|
|
The region of the cell where DNA is stored |
Nucleus |
|
|
Small, round structure inside the nucleus (location of ribosomal RNA) |
Nucleolus |
|
|
Where spindle fibers develop from |
Centrosomes |
|
|
Uncoiled DNA |
Chromatid |
|
|
Is interphase part of mitosis (cell reproduction) |
No |
|
|
What happens in interphase |
DNA becomes replicated to form sister chromatids and prepares for cell division. DNA is loosely coiled (called chromatin) |
|
|
What happens in prophase |
Chromatin fibers become more tightly coiled into chromosomes. The nuclear membrane is no longer visible. Mitotic spindles start to form. And each duplicated chromosome appears as sister chromatids joined together by the centromere |
|
|
What happens in the metaphase |
Sister chromotids align along the "equator" of the cell but remain attached to spindle fibers |
|
|
What happens in the anaphase |
The sister chromotids that are attached to the spindle fibers are pulled apart and move towards opposite ends of the cell. (Now that the sister chromotids are separate we call these "daughter chromosomes") |
|
|
What happens in telophase and cytokinesis |
Nuclear membrane re-forms around the daughter chromosomes. Chromosomes uncoil. ANIMAL CELLS will form a cleavage furrow and ANIMAL CELLS form a cell plate during cytokinesis. |
|
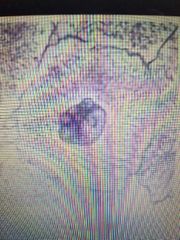
What phase is this cell in |
Interphase |
|
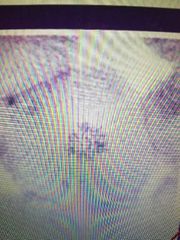
What stage is this cell in |
Prophase |
|

What stage is this cell in |
Metaphase |
|
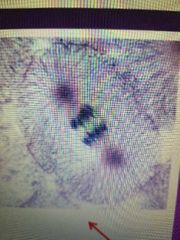
What stage is this cell in |
Anaphase |
|
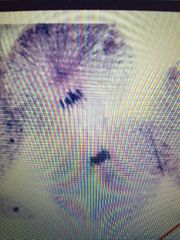
What stage is this cell in |
Telophase and cytokinesis |
|
|
What does chromatin look like under a microscope compared to chromosomes |
Chromatin looks "spotty" because it is loosely coiled. Chromosomes look like "noodles" because it is tightly coiled |
|
|
Aerobic respiration means... |
With oxygen |
|
|
What is the goal of cellular respiration |
To transform chemical energy to ATP |
|
|
What are the 4 steps of aerobic cellular respiration |
1. Gycolosis 2A. Pyruvate oxidation (acetyl CoA) 2B. Krebs cycle 3. Electrons transport chain |
|
|
What are the reactants of cellular respiration |
C6H12O6 + O2 |
|
|
What are the products of cellular respiration |
CO2 + H2O + ATP |
|
|
What is made up of long strands of nucleic acid called DNA |
Chromosomes |
|
|
Haploid (n) |
One copy of each chromosome |
|
|
Diploid (2n) |
Two copies of each chromosome |

