![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypha (plural: hyphae) |
Branching filaments that make up mycelium of a fungus |
|
|
What is the purpose of a vast network of hyphae? |
Large surface area-to-volume ratio (absorption) |
|
|
What is the purpose of mycelium and their hyphae? |
To secrete enzymes for extracellular digestion and to absorb digested nutrients |
|
|
Why are fungi called absorptive heterotrophs? |
They gain their energy from organic molecules they absorb made by other organisms |
|
|
Chitin |
The substance that makes up the cell walls of fungi |
|
|
Saprophytes |
Obtain food from dead organic matter |
|
|
Parasites |
Feed on living organisms |
|
|
Mutualistic |
When two species rely on each other and both benefit |
|
|
How do fungi reproduce? |
Sexually and asexually |
|
|
Phylum Zygomycota |
-Saprophytes -Common genus: Rhizopus -Reproduction both asexual (sporangia) and sexual (zygosporangia) - + and — mating types meet and form zygosporangia -Example: Phycomyces |
|
|
Phycomyces |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Phylum Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) |
-Yeasts, some molds, morels, truffles -Sexual reproduction (ascus) and asexual reproduction (conidia) -Asexual reproduction through budding or cell fission -Examples: Penicillium, aspergillus, peziza asci, saccharomyces |
|
|
Aspergillus |
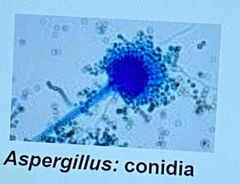
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Pennicillium |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Peziza asci |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Saccharomyces |
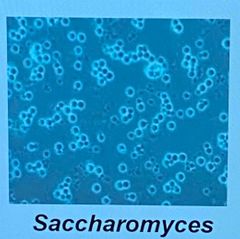
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Phylum Ascomycota (Lichens) |
-Symbiosis between a fungus and an alga or cyanobacteria -Fungus provides the “house” -Photosynthetic partner provides the food -Absorb nutrients from the air |
|
|
3 types of ascomycota (lichens) |
Foliose, Fruticose, and Crustose |
|
|
Foliose |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Fruticose |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Crustose |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Phylum Basidiomycota (Club Fungi) |
-Produce a fleshy fruiting body called a basidiocarp -Spores form on club-shaped cells called basidia -Includes smuts, rusts, and symbiotic partners -Examples: smut fungus, rust fungus, typical mushrooms, shelf fungus |
|
|
Smut fungus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Rust fungus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Shelf fungus |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Typical mushrooms |

Back (Definition) |

