![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where is DNA found in a cell ? |
The DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell |
|
|
Where is DNA contained inside the nucleus ? |
The DNA is contained in chromosomes |
|
|
What is a small section of DNA on a chromosome called ? |
The small section of DNA is called a gene |
|
|
What are the four structure parts of DNA found in nucleotides ? |
Adrenine - A Thymine - T Cytosine - C Guanine - G |
|
|
What two structural bases pair together ? |
Adrenine and thymine Cytosine and guanine |
|
|
What is DNA made up of ? |
Repeating nucleotides which consist of : A sugar A phosphate One of the four bases : A,C,G or T |
|
|
What is the structure of the DNA strands ? |
Double helix |
|
|
What did Gregor Mendel do ? |
He discovered that characteristics are determined by “units” that are inherited and do not blend together
Then he observed chromosomes during cell division |
|
|
What is the term for genes different forms ? |
Allleles |
|
|
What are pathogens ? |
microorganisms that cause infectious (communicable ) diseases |
|
|
What are protists ? |
Protists are eukaryotic ,single celled organisms Example is malaria which is a protists which uses a vector to infect a person as they are bitten by the vector (mosquito ) |
|
|
Example of fungal disease ? |
Rose black spot which travels from plant to plant through air or water Causes black or yellow spots on the plant which make leaves die |
|
|
Human body’s defences against pathogens : |
Hydrochloric acid in stomach kills bacteria Skin Hair Mucus Enzymes in tears destroy micro organisms |
|
|
What is phagocytosis ? |
When white blood cells surround a pathogen and engulf it to destroy it |
|
|
White blood cells also ... |
Produce antibodies which attach to an pathogens antigen This causes all of that pathogen to clump which lets the white blood cells come and digest them Produce antitoxins which are chemicals that neutralise the poisonous effects of the toxins |
|
|
What is immunity ? |
When a same pathogen re enters the body , the white blood cells have already made the antibodies which fit that specific pathogen making a quicker response to it |
|
|
What does vaccination do ? |
Vaccination is when small quantities of dead or inactive forms of a pathogen are injectors into the body This makes the body’s immune system react in a normal way to produce antibodies for that specific pathogen Therefore in the future they have immunity against that pathogen |
|
|
What can pathogens affect and how do they spread ? |
They can effect plants or animals and can be spread by direct contact ;water ; air and vectors |
|
|
What is a vector ? |
Organisms that carry and pass on a pathogen without getting the disease themselves |
|
|
What are symptoms of measles virus ? |
Fever Red skin rash |
|
|
What does HIV do ? |
It fights against the body’s immune system |
|
|
What are symptoms of Tobacco mosaic virus ? |
Discolouration in leaves Affects plants photosynthesis and growth |
|
|
Viruses .... |
Reproduce rapidly in body cells causing damage to the cells |
|
|
Bacteria ... |
May damage cells directly or produce toxins that damage tissues |
|
|
What does salmonella do ? |
Salmonella is a bacteria that secretes toxins which cause cramps vomiting and diarrhoea |
|
|
What is gonorrhoea and it’s effects ? |
Gonorrhoea is a std bacteria and cause thick yellow or green discharge from the vagina or penis and pain when urinating |
|
|
Properties of animal cells ? |
The nucleus Cell membrane Cytoplasm |
|
|
Features of a plant cell : |
Nucleus Cell membrane Cytoplasm Vacuole Chloroplasts Cell wall |
|
|
What does a nucleus do ? |
Controls the activities of a cell Holds chromosomes |
|
|
What does the cell membrane do ? |
Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell |
|
|
What does the cytoplasm do ? |
Holds chemical reactions |
|
|
What does the vacuole contain ? |
Permanent structures in plants containing sap |
|
|
What are chloroplasts ? |
Contains chlorophyll that absorbs light for photosynthesis |
|
|
What does the cell wall do ? |
Extra later outside cell membrane which contains strong fibres called cellulose |
|
|
What does a nucleus do ? |
Controls the activities of a cell Holds chromosomes |
|
|
What does the cell membrane do ? |
Controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell |
|
|
What does the cytoplasm do ? |
Holds chemical reactions |
|
|
What does the vacuole contain ? |
Permanent structures in plants containing sap |
|
|
What are chloroplasts ? |
Contains chlorophyll that absorbs light for photosynthesis |
|
|
What does the cell wall do ? |
Extra later outside cell membrane which contains strong fibres called cellulose |
|
|
What does an antibiotic do ? |
Kills bacteria inside the body but cannot destroy viruses |
|
|
Why shouldn’t doctors prescribe antibiotics? |
As if patients don’t complete their full course of antibiotics then not all the bacteria is killed and some may live and adapt to be resistant to antibiotics |
|
|
Why is there a constant demand for new drugs ? |
As antiviral drugs need to be adapted so the don’t damage the body’s tissue New antibiotics need to be developed so they can kill the new strains of bacteria that are resistant to old medication |
|
|
Name three drugs made from plants |
Digitalis - heart drug that originated from foxgloves Aspirin - pain killer originated from willow Penicillin - discovered by Alexander Fleming from the penicillium mould |
|
|
Stages of new drugs ? |
1) made by chemist in lab 2) tested to see if it’s toxic 3) tested on humans to see if it works and find the optimum dose |
|
|
Stages of new drugs ? |
1) made by chemist in lab 2) tested to see if it’s toxic 3) tested on humans to see if it works and find the optimum dose |
|
|
How are the drugs tested on humans ? |
Usually through double blind trials where the patients are given either the drug or a placebo -patients allocated randomly -neither doctors or patients know who has the drug |
|
|
What’s the equation for photosynthesis ? |
Carbon dioxide + water + light = Glucose + oxygen
CO2 + H20 + light = C6 H12 06 + 02 |
|
|
What’s the equation for photosynthesis ? |
Carbon dioxide + water + light = Glucose + oxygen
CO2 + H20 + light = C6 H12 06 + 02 |
|
|
Is photosynthesis endothermic or exothermic ? |
Endothermic as it takes heat in Trapped by the green chemical called chlorophyll which is found in chloroplast |
|
|
What are some factors affecting photosynthesis? |
Temperature Carbon dioxide concentration Light intensity Chlorophyll concentration |
|
|
What is glucose converted into in plants ? |
Insoluble starch -in stems and leaves Fat or oil - in seeds Cellulose - to strengthen cell walls Proteins -used for growth and enzymes |
|
|
Is respiration exothermic or endothermic? |
Exothermic as it releases energy from glucose molecules |
|
|
What is glucose converted into in plants ? |
Insoluble starch -in stems and leaves Fat or oil - in seeds Cellulose - to strengthen cell walls Proteins -used for growth and enzymes |
|
|
Is respiration exothermic or endothermic? |
Exothermic as it releases energy from glucose molecules |
|
|
What is respiration ? |
When organisms use glucose to release energy for : Chemical reactions Movement Keep warm It can be aerobic or anaerobic |
|
|
What is aerobic respiration equation? |
Glucose +oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
C6 H12 O6 + 02 = CO2 + H20 |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration in animals equation : |
Glucose = lactic acid As glucose is not completely broken down meaning it transfers a lot less energy |
|
|
Anaerobic respiration in plants and yeast equation : |
Glucose = ethanol + carbon dioxide Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells is called fermentation |
|
|
What happens to respiration during excercise ? |
At first the body aerobically respirates until more energy is needed - this I when anaerobic respiration happens to give the extra energy , however to much anaerobic respiration leads to a build up of lactic acid which is a poison and creates an oxygen debt |
|
|
What does lactic acid do to the muscles ? |
Lactic acid causes the muscles to hurt and stops them contracting efficiently After exercise is done lactic acid is transported to the liver where it’s broken down |
|
|
What is an oxygen debt ? |
An oxygen debt is the amount of extra oxygen the body needs after exercise to react with the lactic acid to remove it from cells |
|
|
What is metabolism ? |
Metabolism is the sum of al chemical reactions in a cell or in the body - these reactions are controlled by enzymes and many need a transfer of energy |
|
|
What cells are eukaryotic ? |
Plant animal and fungal |
|
|
What cells are prokaryotic ? |
Bacterial |
|
|
What is the flagella ? |
Tail like structures on bacteria cells to help them move |
|
|
Equation for magnification |
Size of image / size of real object |
|
|
What is mitosis ? |
When a cell divides into two identical daughter cells after its duplicated it’s sub cellular structures |
|
|
What are stem cells ? |
Undifferentiated cells that have not become specialised - this means they can divide to make different types of cells Found in human embryos organs and tissues |
|
|
What is therapeutic cloning ? |
When a cloned embryo of the patient is used as a source of stem cells to treat the patients conditions where cells are damaged or not working properly |
|
|
What are meristems ? |
A special place where plants store the stem cells for easy growth - can be used to clone a rare species of plant |
|
|
What is diffusion in cells |
When a substance move in and out of cells through the cell membranes - Number of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration e.g oxygen and carbon dioxide diffuse in the lungs |
|
|
Factors affecting diffusion ? |
Difference in concentrations Temperature Surface area of membrane |
|
|
What is osmosis ? |
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane |
|
|
What is active transport ? |
When substances move from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration - allows mineral ions to be absorbed into root hairs |
|
|
What are specialised cells ? |
Cells that have adapted through its lifetime to do a job e.g sperm ,nerve and muscle cells Can change it’s shape or sub cellular structures so it can do its job better |
|
|
What is a tissue |
A group of cells arranged with simulate structure and function which all work together to do a job |
|
|
What is a tissue |
A group of cells arranged with simulate structure and function which all work together to do a job |
|
|
What are organs ? |
Groups of different tissues which all work together to perform a specific job |
|
|
What are enzymes ? |
Are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions |
|
|
What are enzymes ? |
Are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions |
|
|
Properties of enzymes ? |
Large proteins Work best at optimum temperature They have a space called active site Each enzyme works for a specific reaction |
|
|
What is the lock and key theory ? |
Model explained on how enzymes work -the chemical that reacts is the key and it fits into the enzymes activation site lock |
|
|
What is the lock and key theory ? |
Model explained on how enzymes work -the chemical that reacts is the key and it fits into the enzymes activation site lock |
|
|
What are the three digestive enzymes ? |
Protease - breaking down proteins Lipase - breaks down fats and oils (lipase ) Carbohydrase - breaks down carbohydrates |
|
|
Amylase and where it’s produce |
Is a carbohydrase that breaks down starch into sugar Produced in salivary gland and pancreas |
|
|
Amylase and where it’s produce |
Is a carbohydrase that breaks down starch into sugar Produced in salivary gland and pancreas |
|
|
Protease and where it’s produced ? |
Breaks down proteins into amino acids Produced in stomach , pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Amylase and where it’s produce |
Is a carbohydrase that breaks down starch into sugar Produced in salivary gland and pancreas |
|
|
Protease and where it’s produced ? |
Breaks down proteins into amino acids Produced in stomach , pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Lipase and where it’s produced |
Breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol Produced in the pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Amylase and where it’s produce |
Is a carbohydrase that breaks down starch into sugar Produced in salivary gland and pancreas |
|
|
Protease and where it’s produced ? |
Breaks down proteins into amino acids Produced in stomach , pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
Lipase and where it’s produced |
Breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol Produced in the pancreas and small intestine |
|
|
What is bile and where it’s produced |
Bile is an alkaline which neutralises the hydrochloric acid from the stomach and partially breaks down lipids Produced in liver and stored in gall bladder |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What do platelets do ? |
Are fragments of cells which collect at should and trigger blood clotting |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What do platelets do ? |
Are fragments of cells which collect at should and trigger blood clotting |
|
|
Properties of arteries |
Take blood from heart to organs Thick walls made from muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What do platelets do ? |
Are fragments of cells which collect at should and trigger blood clotting |
|
|
Properties of arteries |
Take blood from heart to organs Thick walls made from muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
Properties of veins |
Take blood from organs to heart Thinner walls and valves to protect backflow |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What do platelets do ? |
Are fragments of cells which collect at should and trigger blood clotting |
|
|
Properties of arteries |
Take blood from heart to organs Thick walls made from muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
Properties of veins |
Take blood from organs to heart Thinner walls and valves to protect backflow |
|
|
Properties of capillaries |
Allow substances need by cells to pass out of the blood Allow substances produced by cells pass into blood Narrow and thin walled |
|
|
What is blood and what’s it made up of |
Blood is a tissue and is made up of a liquid called plasma |
|
|
What is in plasma |
Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets |
|
|
What does plasma do ? |
Transports chemical substances around the body such as oxygen hormones and antibodies |
|
|
What do red blood cells do |
They contain haemoglobin which binds with oxygen to transport it from the lungs to tissue and cells Didn’t contain nucleus Very small can fit through tiny capillaries Shaped in a biconcave discs |
|
|
What do white blood cells do ? |
Help protect body against infection Can change shape so they can squeeze out of blood vessels into tissues to engulf microorganisms |
|
|
What do platelets do ? |
Are fragments of cells which collect at should and trigger blood clotting |
|
|
Properties of arteries |
Take blood from heart to organs Thick walls made from muscle and elastic fibres |
|
|
Properties of veins |
Take blood from organs to heart Thinner walls and valves to protect backflow |
|
|
Properties of capillaries |
Allow substances need by cells to pass out of the blood Allow substances produced by cells pass into blood Narrow and thin walled |
|
|
How does the heart pump blood ? |
In a double circulatory system where the blood passes through the heart twice on each circuit Four chamber Left and right atria which receive blood from veins Left and right ventricles which pump the blood out into arteries |
|
|
Diagram of heart |
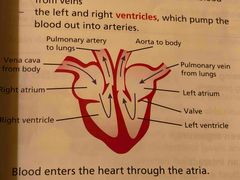
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Eyes of gas exchange |
Blood leaves heart to lungs via pulmonary artery Air goes down tranchea where it separates into two tubes the bronchi Bronchi divides more into bronchioles which divide even more into its just tiny air Sacs called aveoli Aveoli diffuse oxygen and carbon dioxide Blood taken back to heart by poulmanory vein |
|
|
Where is the pacemaker located in the heart ? |
The right atrium |
|
|
Risk factors of non communicable disease |
Persons lifestyle E.g lack of excercise Substances in persons body e.g chemicals from smoking |
|
|
Name a heart disease |
Coronary heart disease |
|
|
Name a heart disease |
Coronary heart disease |
|
|
What is conorary heart disease and how is it fixed |
When layers of fatty material build up inside the coronary arteries and narrow them Treatments : Stents and statins |
|
|
What are stents |
Mesh that’s inserted into arteries to keep them open |
|
|
What are stents |
Mesh that’s inserted into arteries to keep them open |
|
|
What are statins |
Medication that reduce blood cholesterol levels and slow down the rate in which fats build up |
|
|
What is cancer ? |
Cancer is a non communicable disease which is caused by uncontrollable cell division.this leads to tumours |
|
|
What is cancer ? |
Cancer is a non communicable disease which is caused by uncontrollable cell division.this leads to tumours |
|
|
What are the two types of tumours ? |
Benign - tumours which do not spread around the body Malignant - tumours that spread in the blood and from second tumours |
|
|
Name some plant tissues |
Epidermis - skin of plant Palisade mesophyll -main site of photosynthesis Spongy mesophyll - air spaces between cells allow air to diffuse Xylem vessels - transports water and minerals Phloem vessels - transports dissolves food materials |
|
|
What is transpiration |
When water is loaded from the leaves through the small pores called stomata |
|
|
What is translocation |
When phloem tissue transports dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant |

