![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Diffusion |
Substance is moving from higher to lower |
|
|
What causes diffusion? |
Brownian Movement |
|
|
Diffusion is a type of __________ _____________. |
passive transport |
|
|
___________ diffuse fastest. |
Gases |
|
|
What effect does temperature have on diffusion? |
higher temperatures diffuse fastest |
|
|
Lighter weight leads to (faster/slower) diffusion? |
Faster |
|
|
Osmosis |
diffusion of water from area of greater pressure to area of lower pressure |
|
|
In a hypertonic environment, water moves ____. |
out |
|
|
What occurs in a hypertonic plant cell? |
Plasmolysis |
|
|
What happens in a hypertonic animal cell? |
Cremation |
|
|
In a hypotonic environment, water moves ___. |
In |
|
|
What happens in a hypotonic plant cell? |
Turger pressure - cell will not burst due to the cel wall |
|
|
What happens in a hypotonic animal cell? |
Cytolosis |
|
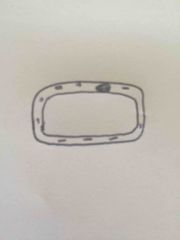
Is this a hypertonic or hypotonic plant cell? |
Hypotonic |
|
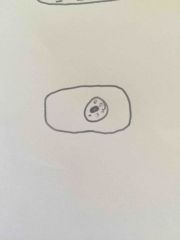
Is this a hypertonic or hypotonic plant cell? |
Hypertonic |
|
|
Active transport requires _______. |
Energy |
|
|
A plasma membrane has __________ ____________. |
Selective permeability |
|
|
What are the three types of cell division? |
Binary fission, mitosis, meiosis |
|
|
What is binary fission? |
Only in prokaryotes and bacteria |
|
|
What is binary fission? |
Only in prokaryotes and bacteria |
|
|
What is mitosis? |
Occurs in all eukaryotic cells |
|
|
What is binary fission? |
Only in prokaryotes and bacteria |
|
|
What is mitosis? |
Occurs in all eukaryotic cells |
|
|
What is meiosis? |
Only occurs in germ cells to produce sex cells |
|
|
Meiotic division is the process of meiosis leading to the formation of specific cells in animals. Name this cell |
gametes |
|
|
Meiotic division is the process leading to the formation of specific cells in plants. |
Meiospores |
|
|
The human body has ___ chromosomes and a ___loid. |
46; diploid |
|
|
Gametes (sperm/egg) have ___ chromosomes |
23 chromosomes |
|
|
Haploid is represented by ___ |
n |
|
|
Haploid is represented by ___ |
n |
|
|
Diploid is represented by _____ |
2n |
|
|
What are the two stages of the cell cycle? |
Interphase (90%) & Mitosis (10%) |
|
|
What happens in interphase? |
DNA replication that occurs in the S (synthesis) phase |
|
|
Interphase has ___ sister chromatids that are held together by a _____________. |
2; centromere |
|
|
What percentage of the cycle is interphase? |
90% |
|
|
What percentage of the cycle is interphase? |
90% |
|
|
What occurs in mitosis? |
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
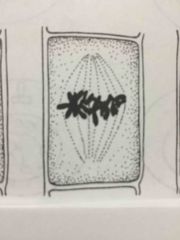
What step of meiotic division is this? |
Prophase |
|
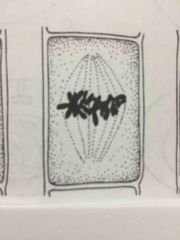
What step of meiotic division is this? |
Metaphase |
|
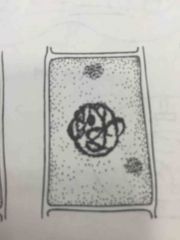
What step of meiotic division is this? |
Prophase |
|

What step of meiotic division is this? |
Anaphase |
|

What step of meiotic division is this? |
Telophase |
|
|
What is cytokinesis? |
Division of cytoplasm at the end of mitosis |
|
|
What is cytokinesis? |
Division of cytoplasm at the end of mitosis |
|
|
What does a plant cell require in cytokinesis? |
cell plate |
|
|
What is cytokinesis? |
Division of cytoplasm at the end of mitosis |
|
|
What does a plant cell require in cytokinesis? |
cell plate |
|
|
What doss an animal cell require in cytokinesis? |
cleavage farrow |
|
|
FALSE TRUE TRUE FALSE |
#3G |
|
|
Meiosis I |
homologous pairs |
|
|
Meiosis II |
not paired in metaphase, chromatids separating |
|
|
What do karyotypes do? |
tells gender |
|
|
What do karyotypes do? |
tells gender |
|
|
What is the female karyotype? |
XX |
|
|
What do karyotypes do? |
tells gender |
|
|
What is the female karyotype? |
XX |
|
|
What is the male karyotype? |
XY |
|
|
What syndrome has a trisomy on chomosome 21? |
Down Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has a trisomy on chomosome 21? |
Down Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has 1 X chromosome on 21? |
Turner Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has a trisomy on chomosome 21? |
Down Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has 1 X chromosome on 21? |
Turner Syndrome |
|
|
Klinefelter's Syndrome |
2 or more X chromosomes but also a Y |
|
|
What syndrome has a trisomy on chomosome 21? |
Down Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has 1 X chromosome on 21? |
Turner Syndrome |
|
|
Klinefelter's Syndrome |
2 or more X chromosomes but also a Y |
|
|
How is a male identified in a pedigree? |
Square |
|
|
What syndrome has a trisomy on chomosome 21? |
Down Syndrome |
|
|
What syndrome has 1 X chromosome on 21? |
Turner Syndrome |
|
|
Klinefelter's Syndrome |
2 or more X chromosomes but also a Y |
|
|
How is a male identified in a pedigree? |
Square |
|
|
How is a female shown in a pedigree? |
Circle |
|
|
How is an affected pedigree shown? |
Shaded |
|
|
In a pedigree, how are carriers shown? |
1/2 shaded |
|
|
Nuclear membranes and nucleolus disappear |
Prophase |
|
|
Spindle is formed |
Prophase |
|
|
Sister chromatids separate |
Anaphase |
|
|
Sister chromatids separate |
Anaphase |
|
|
Daughter cells are formed |
Telophase |
|
|
Sister chromatids separate |
Anaphase |
|
|
Daughter cells are formed |
Telophase |
|
|
Rod-shaped chromosomes are first visible |
Prophase |
|
|
Sister chromatids separate |
Anaphase |
|
|
Daughter cells are formed |
Telophase |
|
|
Rod-shaped chromosomes are first visible |
Prophase |
|
|
Chromosomes line up on equatorial plane |
Metaphase |
|
|
New nuclei are formed |
Telophase |
|
|
New nuclei are formed |
Telophase |
|
|
Daughter chromosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell |
Prophase |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Cell divisiob in prokaryotes |
Binary fission |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Cell divisiob in prokaryotes |
Binary fission |
|
|
Enables growth in multicellular organisms |
Miotic cell division |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Cell divisiob in prokaryotes |
Binary fission |
|
|
Enables growth in multicellular organisms |
Miotic cell division |
|
|
Produces gametes in animals |
Meiotic cdll division |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Cell divisiob in prokaryotes |
Binary fission |
|
|
Enables growth in multicellular organisms |
Miotic cell division |
|
|
Produces gametes in animals |
Meiotic cdll division |
|
|
Occurs in both haploid and diploid cells |
Mitotic cell divison |
|
|
Produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
Meiotic cell division |
|
|
Cell divisiob in prokaryotes |
Binary fission |
|
|
Enables growth in multicellular organisms |
Miotic cell division |
|
|
Produces gametes in animals |
Meiotic cdll division |
|
|
Occurs in both haploid and diploid cells |
Mitotic cell divison |
|
|
Produces meiospores in plants |
Meiotic cell division |

