![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are evidences of evolution? |
Fossils, Homologous Structures, Vestigial Organs, Embryology |
|
|
Fossils? |
any remains, impression, or trace of a living thing of a former geologic age, as a skeleton, footprint,etc. |
|
|
Homologous structures? |
an example of an organ or bone that appears in different animals, underlying anatomical commonalities demonstrating descent from a common ancestor. |
|
|
Vestigial organs? |
A rudimentary structure in humans corresponding to a functional structure or organ in ancestral animals. |
|
|
Embryology? |
the branch of biology and medicine concerned with the study of embryos and their development. |
|
|
Adaptation? |
any inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival. |
|
|
Species? |
organisms that can produce fertile offspring when mated naturally. |
|
|
Population? |
a group of individuals of the same species in a defined area who interbreed. |
|
|
Who was Jean Lamarck? What was his theory regarding evolution? |
Living things have changed over time, All species were descended from other species, Organisms were somehow adapted to their environments. Lamarck proposed that by selective use or disuse of organs, organisms acquired or lost certain traits. |
|
|
Was Lamarck’s theory correct? What was the “evidence” for his theory? |
No. August Weismann disproved Lamarck’s theory by cutting the tails off of 20 generations of mice. As all of the rest of the generations, the 21st generation of baby mice still had tails. |
|
|
Why was August Weismann’s work important? |
Because he helped Lamark discover if his theory was correct. |
|
|
Who was Charles Darwin? What was his theory regarding evolution? |
a scientist that founded natural selection He founded natural selection in evolution which means that all animals came from one species |
|
|
Was Darwin’s theory correct? What was the “evidence” for his theory? |
No. If the human race continued to grow unchecked, sooner or later there would be insufficient living space and food for everyone. The only forces he observed that worked against this growth were war, famine, and disease. |
|
|
What did Thomas Malthus say would happen to the human population? |
He said that it would decrease. |
|
|
How was Malthus work helpful to Darwin? |
It helped Darwin continue his process in discovering if his theory is correct and seeing if natural selection was correct. |
|
|
Why was Charles Lyell’s work important? |
It explained how geological phenomena occurred over long periods of time. |
|
|
What is another way to describe natural selection? |
Fitness, Adaptation, Survival of the Fittest. |
|
|
Natural selection exists because of 5 main elements. What are they? |
Genetic variation exists, Environments vary and present different challenges, .Organisms produce offspring in abundance. (competition for resources), Some individuals are better adapted by chance, Those individuals best suited to the environment become dominant in that population leaving more offspring. |
|
|
What dictates the direction and extent of changes in evolution? |
The enviornment |
|
|
Describe Reproductive Isolation. |
Physical barrier between a population may eventually produce 2 different species, Mating habits (ie: frogs) |
|
|
What is speciation? |
the formation of new and distinct species in the course of evolution. |
|
|
Fitness? |
an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. |
|
|
Reproductive isolation? |
the situation where different species may live in the same area, but properties of individuals prevent them from interbreeding. |
|
|
Artificial Selection? |
the breeding of plants and animals to produce desirable traits. |
|
|
What are the 4 basic mechanisms that drive evolution? |
Natural Selection, Mutation, Genetic Drift, Gene Flow (Migration). |
|
|
What is a mutation? How does it affect evolution? |
a permanent, heritable change in the nucleotide sequence in a gene or a chromosome. If it causes an improvement in fitness of the individual, then the gene will be passed onto future generations. |
|
|
What is genetic drift? Give examples of two types of genetic drift. |
It’s a part of the species that contain new genes, which makes the next generation lucky (not necessarily better). EXs: The Bottleneck effect, and the Founder Effect |
|
|
Be able to describe and give examples of “bottle neck”. How does this affect evolution? |
When there is a drastic reduction in population the surviving individuals may have a different allele/gene frequency than the original population. |
|
|
Be able to describe and give examples of “founder effect”. How does this affect evolution? |
a few individual from a population start a new population with a different allele/gene frequency than the original population. |
|
|
What is gene flow? How does it affect evolution? |
the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. It’s responsible for a marked change in allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). |
|
|
Mutation? |
the action or process of mutating. |
|
|
Genetic Drift? |
Variation in the relative frequency of different genotypes in a small population, owing to the chance disappearance of particular genes as individuals die or do not reproduce. |
|
|
Bottle Neck? |
When there is a drastic reduction in population the surviving individuals may have a different allele/gene frequency than the original population. |
|
|
Founder Effect? |
the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. |
|
|
Gene Flow/Migration? |
the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another. |
|
|
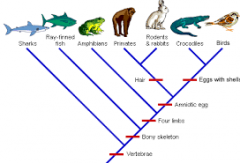
What does a Cladogram represent? |
It shows relations among organisms. |
|
|
Why is it helpful? |
It is to help you see what genetic traits any species or organisms contain. |
|
|
KNOW THE CLADOGRAM. |
|

