![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explain the sliding filament theory in its 5 major steps. Start with the release of Ca+2 ion from the sarcoplasmic reticulum into the myofibril. What is the end result of this process?
|
Ca binds troponin on G-actin. Configuration changes of the actin exposing the active site. Myosin head binds to the active site forming a cross-bridge. Myosin head kinks (towards the M-line) causing the actin filament to slide over the myosin filament. ATP molecule binds the empty myosin head causing detachment of the cross-bridge. Myosin (ATPase) hydrolizes ATP back to ADP + P. The net result of the process is sliding of actin filaments over myosin filaments resulting in a sarcomere shortening (I will also accept muscle or myofibril or muscle fascicle contracting).
|
|
|
What is Rigor Mortis? (cause and symptoms)
|
When death occurs, the blood supply of Oxygen diminishes in the body. Hence the muscle fibers do not have oxygen for energy to make enough ATP for the myosin heads to detach from the actin molecules. Further more, the Ca ions can not be reabsorbed by the sarcoplasmic reticulum causing a lot of them to be floating in the myofibril allowing more and more myosin heads binding to the actin molecules. Therefore we have more cross-bridge formation and no cross-bridge detachments. This causes the muscle of the body to super contract and stay in that position making a stiff appearing body. This phenomenon is known as rigor mortis.
|
|
|
Define Tendon:
|
Epimyseum + Perimyseum + Endomyseum unite at both ends of the muscle fiber in skeletal muscle forming a tendon. Tendon attaches a muscle to bone.
|
|
|
Define Twitch:
|
For a contracting skeletal muscle, one full cycle of stimulus + contraction + relaxation is known as one twitch for a fiber
|
|
|
Define Isometric contraction:
|
Type of contraction where the muscle does not shorten but it contracts. The load/resistance is higher than the energy exerted by the muscle. In short the load does not move but the muscle still contracts
|
|
|
Energy stored in the resting muscles comes from __________. It is stored in the cell as ATP, CP, and glycogen.
|
Fatty Acids
|
|
|
During moderate activity, _______ and __________ are broken down (catabolized) to produce ATP from pyruvic acid via Krebs cycle. The number of ATP produced during this process is __ (hint: the total #, not the # by each pyruvic acid. Think of how many pyruvic acid is made and what other source the cell has during this process)
|
Fatty Acid
Glycogen 36 |
|
|
During peak activity the ATP is mostly produced by glycolysis. ___________ is made as a by-product in this process.
|
Lactic Acid
|
|
|
Explain how ankylosis is caused?
|
In Rheumatoid arthritis, destruction of the joints causes accumulation of the synovial fluid in the joint cavity. Eventually this forms a pannas or rag. Progression of the disease results in to a scar tissue from the rag. The bones than fuses to each other causing a complete immobile joint, this condition is called ankylosis.
|
|
|
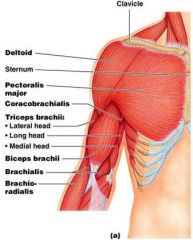
In flexing the forearm at the elbow, the ______ acts as antagonist
|
Triceps Brachii
|
|
|
The Suprahyoid muscles
|
Are a group of muscles that lie superior to the hyoid bone and help form the floor of the oral cavity
|
|
|
When the term biceps, triceps, or quadriceps forms a part of a muscle’s name, you can assume that the muscle
|
as two, three, or four origins, respectively
|
|
|
Which of the following muscles is the flexor of the thigh?
|
rectus femoris
|
|
|
T/F Muscles are only able to pull, they never push.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F In the muscles of mastication, buccinators aid in grinding.
|
False
|
|
|
A muscle that opposes and reverses teh action of another muscle is:
|
Antagonist
|
|
|
A muscle that stabilizes the origin of another muscle is:
|
Fixator
|
|
|
A muscle that is primarily responsible for bringing about a particular movement is:
|
Agonist
|
|
|
A muscle that aids another by promoting the same movement is:
|
Synergist
|
|
|
Define Peristalsis and list the muscles involved in this process (I do not want the name of all the muscles, just a general idea or group)
|
Pharyngeal constrictor muscles work in a group and sequence with the other infrahyoid muscles in propelling the food down in the esophagus by constricting the pharynx. The process is called peristalsis. Constrictor and infrahyoid muscles (suprahyoid aid in this too but the other two are the major ones, so if you forgot suprahyoid, it will be fine)
|
|
|
Based on name alone - what might this muscle would be responsible for:
Flexor pollicis longus: |
Flexing of the thumb (pollex)
|
|
|
Based on name alone - what might this muscle would be responsible for:
Opponens digiti minimi |
Oposition of the little finger
|
|
|
Based on name alone - what might this muscle would be responsible for:
Adductor longus |
Adduction of the thigh
|
|
|
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh are:
|
Responsible for the flexion of the thigh and extension of the knee
|
|
|
The muscles in the posterior compartment of the thigh are:
|
Responsibel for the extension of the thigh and flexion of the knee
|
|
|
The muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm does:
|
Flexors of the wrist and fingers
|
|
|
lantar interossei _______ the toes
|
adducts
|
|
|
Which part of the neural tissue transmits stimuli away from the cell body?
|
Axon
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter is released from
|
presynaptic membrane
|
|
|
Postsynaptic membrane contains mostly
|
chemically regulated channel
|
|
|
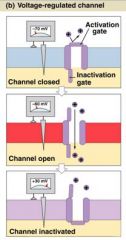
The propagation of action potential through axon is carried out by
|
voltage regulated channel
|
|
|
T/F The large diameter myelinated fibers have much higher propagation speed than the small diameter myelinated fibers or unmyelinated fibers.
|
True
|
|
|
Neuromodulators affect ________
|
the efficiency of synapse
|
|
|
The type of cells lining the ventricles of brain and central canal of spinal cord is
|
Ependymal cell
|
|
|
The type of cells lining the blood vessels to form blood-brain barrier is
|
astrocytes
|
|
|
Myelin sheath (in PNS) is surrounded by:
|
Schwann cell
|
|
|
3 characteristics of the Sodium-potassium pump
|
a. moves sodium ions out of the cell
b. moves potassium ions in to the cell c. requires ATP to work. |
|
|
hen neural transmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane,
|
the postsynaptic membrane potential move from -70 mV toward 0 mV
|
|
|
T/F Reterograde flow means the direction of action potential is backwards (from synaptic knob to cell body of the same neuron)
|
False
|
|
|
Myelin sheath acts like insulation. Its function is
|
To speed up the propagation of action potential.
|
|
|
The ___________ movement of ions on the inside and outside of the cell is
|
parallel
|
|
|
Continuous propagation occurs in ____________ axons
|
unmyelinated
|
|
|
altatory propagation occurs in ________ axons
|
myelinated
|
|
|
Temporal summation has _________ effect to generate the action potential.
|
repetitive
|
|
|
Spatial summation has _________ effect to generate the action potential.
|
cumulative
|
|
|
The central nervous system has the basic structure of gray matter surrounding the CSF filled center. In the cerebrum, the gray matter surrounding the ventricles is called
|
basal nuclei
|
|
|
The central sulcus of the cerebral cortex separates
|
The frontal and parietal lobes
|
|
|
The cerebral cortex is
|
gray matter
|
|
|
Which of these is NOT a degenerative disease of the BRAIN?
Huntingtons Alzheimers Poliomyelitis Parkinson's |
Poliomyelitis
|
|
|
T/F Broca’s area and Wernicke’s area are involved in visual functions
|
False
|
|
|
T/F “Lateralization” implies the perfect symmetry of cerebral cortical functions
|
False
|
|
|
The nuclei that controls the automatic motor functions such as breathing are at
|
Brain Stem
|
|
|
The largest cerebral white matter (commissure) connecting left and right cortex is
|
Corpus Collossum
|
|
|
The tissue that secretes cerebral spinal fluid is
|
Choroid Plexus
|
|
|
All the sensory neural fibers destined to the cerebral cortex makes relay synapse at
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Which one is not part of the brain stem:
Amygdala Pons Midbrain medulla oblongata |
Amygdala
|
|
|
Which part of the diencephalon directly controls the secretion of hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
The major function of the cerebellum is
|
Coordinates movement
|
|
|
The system that associates emotional response to odors is
|
Limbic System
|
|
|
The toughest meninges is
|
dura mater
|
|
|
When the blood circulation to the brain is blocked, the brain tissue is damaged within a few minutes. This event is called
|
stroke
|
|
|
The sensory neuron soma resides in the
|
dorsal root ganglion
|
|
|
Cauda equina is in the vertebral foraman of
|
lumbar vertebrae
|
|
|
T/F The soma of the motor neuron may be found in the ventral horns of the spinal cord.
|
True
|
|
|
The pathway that does not have decussation is the
|
posterior spinocerebellar tract
|
|
|
Pathways that *do* have decussation are:
|
a. non-specific ascending pathway
b. specific ascending pathway c. direct pyramidal system |
|
|
Right handedness is caused by
|
both lateralization and contralateralization
|
|
|
Part of the brain that is vitally important for the overall maintainance of homeostasis is:
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Decussation of pyramids occurs at:
|
Medulla oblongata
|
|
|
The drug LSD interferes with the normal functioning of :
|
RAS
|
|
|
The epidural space is made up of:
|
Fat
|
|
|
The sensory receptor that does not exhibit any adaptation is
a. pain b. smell c. light d. touch |
pain
|
|
|
The most rapid and precise controlling skeletal muscles of the body are:
|
extrinsic eye muscles
|
|
|
Which one is not a taste sensation of the taste buds?
a. Sweet b. Hot (spicy) c. Salty d. Sour |
Hot (spicy)
|
|
|
T/F There are only five taste sensations but hundreds smell sensations
|
True
|
|
|
The transparent membrane covering the front of the eyeball is called
|
cornea
|
|
|
Part of the retina that has acute color sense is:
|
macula lutea
|
|
|
A deficiency of what would likely be responsible for color blindness?
|
a deficiency of cone cell function
|
|
|
The symptom of losing the accommodation ability of the lens in the old age is called
|
presbyopia
|
|
|
The layer of eye ball that contains the light sensing cells is
|
retina
|
|
|
Neural integration in the somatosensory system does not occur at:
|
cerebellum level
|
|
|
T/F During transduction, graded potential must be converted to the receptor potential.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F Inner ears are part of the tonic receptors that are slow in adaptation
|
True
|
|
|
Information processing in the PNS occurs in what order at the circuit level?
|
first order neurons, second order neurons, third order neurons
|
|
|
T/F Third order neurons are usually found in the cerebellum
|
False
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT a chemoreceptor?
A. gustatory receptors B. olfactory receptors C. photoreceptors |
Photoreceptors
|
|
|
Basal cells are ____
|
stem cells
|
|
|
The most regenerated neurons (unique) of the body are:
|
Olfactory neurons
|
|
|
The olfactory receptor cells synapse with:
|
Mitral cells
|
|
|
Tears are secreted by:
|
lacrimal gland
|
|
|
_________ is the visual pigment of rods that absorbs green light and is made from vitamin A
|
Rhodopsin
|
|
|
T/F Proprioceptors are located on the surface of the tongue.
|
False
|
|
|
Umami sensation can be felt because of:
|
Glutamate
|
|
|
A sewage worker can eat lunch ‘happily’ in his lunch break because he can ignore the smell of his work environment. The ignoring can occur due to:
|
GABA cells
|
|
|
The blind spot of the eye occurs at:
|
Optic disk
|
|
|
The vitreous humor is present in the posterior segment and is present throughout the life.
|
True
|
|
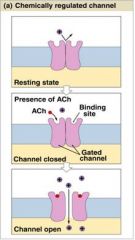
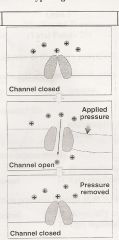
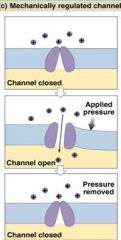
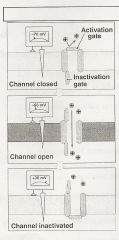
What type of Channel is this?
|
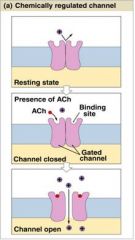
Chemically Regulated Channel
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The secretions of the adrenal medulla act to supplement the effects of
|
Sympathetic Activity
|
|
|
Preparing the body for the "fight-or-flight" response is the role of the
|
Sympathetic Nervous System
|
|
|
The parasympathetic nervous system is characterized by
|
Peripheral ganglia usually near the organs and by short postganglionic fibers
|
|
|
The majority of the parasympathetic fibers are derived from
|
Vagus Nerve
|
|
|
Control of temperature, endocrine activity, and thirst are functions associated with the
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Sympathetic responses generally are widespread because
|
Norepinephrine and epinephrine are secreted into the blood
|
|
|
Adrenergic receptors respond to:
|
Norepinephrine
|
|
|
Beta-blockers are drugs that attached to beta adrenergic receptors. ________ is the effect of a beta-blocker.
|
Decrease in heart rate and blood pressure.
|
|
|
Which of the body's regulatory functions is uniquely sympathetic?
|
Body Temperature
|
|
|
Contraction of arrector pili muscles and sweat glands are stimulated by _______
|
Sympathetic Nerve
|
|
|
The ANS consists of mortor neurons that:
|
- innervate smooth and cardiac muscle and glands
-make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body cavities -operate via subconcious control |
|
|
T/F? The sympathetic division is involved in all the E activities and the parasympathetic division is involved in all the D activities.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F? The preganglionic fibers pass through the white rami communicantes and the postganglionic fibers pass through the gray rami communicantes.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F? Pathways to the Thorax serves the stomach and the intestines
|
False
|
|
|
T/F? Unlike somatic reflexes, visceral reflexes are NOT polysynaptic.
|
False
|
|
|
Acetylcholine can bind to
|
Muscarinic receptor
|
|
|
Neostigmine is a drug that inhibits the enzyme acetylcholinestrase which is responsible for the break down of ACh. _________ is treated by this drug.
|
Myasthinia Gravis
(This results from a hyper-active thyroid) |
|
|
T/F? Parasympathetic tone is critical in maintaining the blood-pressure.
|
False
|
|
|
T/F? The maculae responds to the static movements and critae ampullares respond to the angular movements.
|
True
|
|
|
T/F? The organ of corti is the balance receptor.
|
False.
|
|
|
List 5 statements to describe how action potential is generated for hearing in the ear.
|
1. Sound enters the Eustachian canal and pushes against the tympanic membrane.
2. The ossicles in the middle ear move according to the sound vibration. 3. The vibration is passed on by the oval window to the fluids in the inner ear. 4. The perilymph in the scala tymphani and the scala vestibuli moves causing the basilar membrane to vibrate. 5. Hair cells move causing an action potential to travel via the cochlear nerve. |
|
|
Depolarization occurs at what voltage?
|
70 Milivolts
|
|
|
In a sodium-potassium pump:
__________ travels out of the cell and __________ travels in. |
Sodium out
Potassium in |
|
|
Name the 8 major organs in the endocrine system
|
Pituitary
Thyroid Parathyroid Adrenal Pineal Thymus Pancreas Ovary in Females Testes in Males |
|
|
What catecholines are associated with the cAMP pathway? (7)
|
ACTH
FSH LH Glucagon PTH TSH Calcitonin |
|
|
What catecholines are associated with the PIP pathway? (4)
|
TRH
ADH Oxytocin LHRH |
|
|
Which hormone is the only one to respond on a positive feedback loop?
|
Oxytocin
|
|
|
What are the 6 hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
|
FSH
LH TSH ACTH GH Prolacin |

