![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the permanent dental formula of horses?
|
I 3/3, C 1/1, P 3(4)/3(4), M 3/3
|
|
|
What is the deciduous dental formula of horses?
|
I 3/3, C 0/0, P 3/3
|
|
|
Where should a tracheotomy be performed on the horse?
|
Cranial 3rd of the neck, 3 or more rings caudal to larynx
|
|
|
Which muscles must be parted during an equine tracheostomy?
|
Sternothyroideus mm. (or sternothyrohyoideus)
|
|
|
What are the surgical boundaries of the maxillary sinus?
|
Rostral border of orbit
Rostral end of facial crest to infraorbital foramen Facial crest Line from infraorbital foramen parallel to facial crest |
|
|
Which structures are located within the lateral compartment of the guttural pouch? What divides the guttural pouch?
|
Maxillary a and v
CN VII Stylohyoid divides the two |
|
|
What structures are located within the medial compartment of the guttural pouch?
|
Internal carotid a.
CN IX, X, XI, XII Sympathetic trunk Cranial cervical ganglion Common medial septum |
|
|
Which of the following structures are located within both the lateral and medial compartments of the guttural pouch?
a) stylohyoid bone b) maxillary artery c) CN VII d) CN IX e) none of the above |
a) stylohyoid bone (divides the two)
|
|
|
What are the boundaries of the frontal sinus in the horse?
|
Line transverse through zygomatic process of frontal bone
Line 2 cm off midline Line perpindicular to a line midway between orbit and infraorbital foramen From supraorbital foramen to rostral end of medial limit |
|
|
Which teeth are within the maxillary sinus?
|
M1, 2, and 3 +/- P4
(P4 and rostral M1 in rostral maxillary sinus) |
|
|
What muscle is involved in roaring?
|
cricoarytenoideus dorsalis
|
|
|
Which of the following is NOT commonly cured via formalin injection?
a) Ethmoid hematoma b) Sinonasal cysts c) Nasal inclusion cysts d) Nasal tumors e) Redundant alar folds |
d) Nasal tumors
e) Redundant alar folds |
|
|
Which of the following typically involves a thick mucoid fluid?
a) Ethmoid hematoma b) Sinonasal cysts c) Nasal inclusion cysts d) Nasal tumors e) Redundant alar folds |
b) Sinonasal cysts
c) Nasal inclusion cysts |
|
|
Standardbreds or saddlebreds are predisposed to which of the following?
a) Ethmoid hematoma b) Sinonasal cysts c) Nasal inclusion cysts d) Nasal tumors e) Redundant alar folds |
e) Redundant alar folds
|
|
|
T or F:
Guttural pouch mycotic disease is only life threatening after the first time. |
False!
Usually horses don't bleed-out the first time but it is ALWAYS life threatening |
|
|
Which vascular structure is responsible for retrograde hemorrhage in guttural pouch mycoses?
|
Circle of (what'chu talkin' 'bout) Willis
|
|
|
What is the most common cause and signalment of guttural pouch empyema?
|
Strep in young horses
|
|
|
Styloid osteoarthropathy commonly involves damage to which nerves?
a) CN VII b) CN VIII c) CN IX d) CN X e) CN XII |
a) CN VII
b) CN VIII |
|
|
How can guttural pouch chondroids that are irretrievable via endoscopy be removed?
|
Modified Whitehouse approach
|
|
|
Which are appropriate treatments for stylohyoid osteoarthropathy?
a) laser stoma between guttural pouches b) Saline/Kpen/lavage of pouch c) Stylohyoid ostectomy d) Ceratohyoid ostectomy e) Temporary tarsorrhaphy |
d) Ceratohyoid ostectomy
(the tarsorrhaphy is used to protect eye until nerve fxn is restored but doesn't directly influence the condition) |
|
|
What is the most common procedure used to repair Dorsal Displacement of the Soft Palate?
|
Tie-forward procedure (tie basihyoid to thyroid cartilage, moving larynx rostro-dorsal)
|
|
|
What is the most common repair for pharyngeal collapse?
|
NO REPAIR!
tx via rest, NSAIDs, throat spray |
|
|
Choose the grade of laryngeal hemiplegia...
...normal adduction/abduction of arytenoids. |
Grade 1
|
|
|
Choose the grade of laryngeal hemiplegia...
...full abduction of arytenoids with some asynchronous movement of left arytenoid. |
Grade 2
|
|
|
Choose the grade of laryngeal hemiplegia...
...asynchronous movement of left arytenoid with partial abduction. |
Grade 3
|
|
|
Choose the grade of laryngeal hemiplegia...
...complete paralysis of arytenoid. |
Grade 4
|
|
|
T or F:
Only laryngeal hemiplegia grades 3 and 4 are commonly treated surgically. |
Tru dat!
|
|
|
With the slap test, you expect to see...
a) adduction of the ipsilateral arytenoid via CN IX b) abduction of both arytenoids c) abduction of the contralateral arytenoid via CN IX d) adduction of the contralateral arytenoid via CN XI e) abduction of the ipsilateral arytenoid via CN XI |
d) adduction of the contralateral arytenoid via CN XI
|
|
|
Permanent tracheostomy may be an option in which laryngeal condition?
|
Arytenoid chondritis
|
|
|
Epiglottic entrapment occurs under which flap of mucosa?
|
Aryepiglottic fold
|
|
|
Which of the following is considered a congenital anomaly?
a) epiglottic entrapment b) laryngeal hemiplegia c) rostral displacement of the palatopharyngeal arch d) arytenoid chondritis e) subepiglottic cyst |
c) rostral displacement of the palatopharyngeal arch
(I'd also argue that epiglottic entrapment could be d/t an abnormally large aryepiglottic fold) |
|
|
Which laryngeal condition is often secondary to strangles?
|
Retroversion of epiglottis
|
|
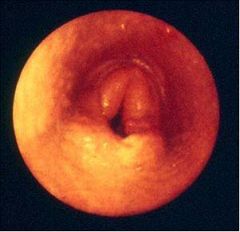
What's going on here?
|
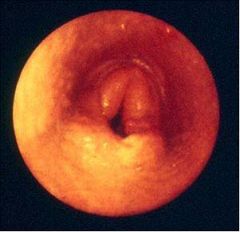
Dorsal displacement of the soft palate
Arytenoid chondritis/inflammation |
|
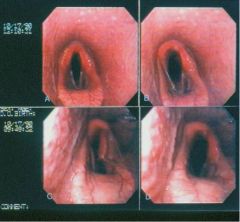
What gives here?
|
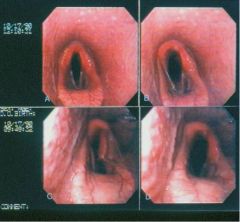
Class III to IV laryngeal hemiplegia
|
|
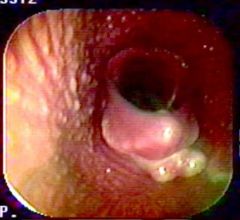
What's going here?
|
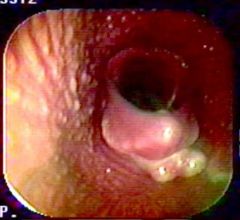
Epiglottic entrapment w/epiglottic cyst
|
|
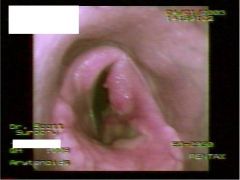
What gives here?
|
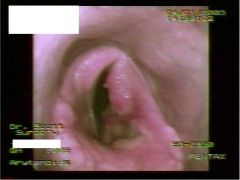
Laryngeal hemiplegia
Arytenoid chondritis |
|
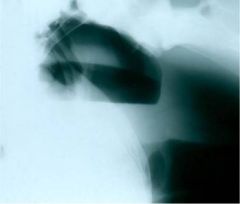
What gives?
|
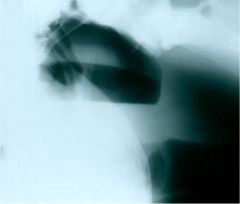
Guttural pouch empyema
|
|
|
What is probably the MAJOR sign of dental or sinus disease?
|
Unilateral nasal discharge
|
|
|
T or F:
Radiography is the best diagnostic tool when investigating tooth root abscesses. |
False!
50% of the time its right all of the time |
|
|
Which bones comprise the maxillary sinus?
|
maxilla
lacrimal zygomatic |
|
|
Which of the following are true?
a) the rostral maxillary sinus communicates with the middle nasal meatus via nasomaxillary opening b) caudal maxillary sinus communicates with the rostral maxillary sinus via the frontomaxillary opening c) rostral maxillary sinus communicates with the sphenopalatine and frontal sinuses via the frontomaxillary opening d) caudal maxillary sinus communicates with the sphenopalatine and frontal sinuses via the frontomaxillary opening e) the sinuses do not communicate |
a) the rostral maxillary sinus communicates with the middle nasal meatus via nasomaxillary opening
d) caudal maxillary sinus communicates with the sphenopalatine and frontal sinuses via the frontomaxillary opening |
|
|
Which of the following is treated via flap sinusotomy and has a good prognosis?
a) tooth repulsion b) sinus cyst c) ethmoidal hematoma d) sinonasal neoplasia |
b) sinus cyst
|
|
|
Which of the following is treated via flap sinusotomy and has a fair to poor prognosis or high complication rate?
a) tooth repulsion b) sinus cyst c) ethmoidal hematoma d) sinonasal neoplasia |
a) tooth repulsion
c) ethmoidal hematoma d) sinonasal neoplasia (for malignant tumors) |
|
|
Which tumor types are the most common in the sinuses of the horse?
|
SCC
Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Tension band wiring of mandibular fractures should be removed after ____________ (time period).
|
8 weeks
|
|
|
Which bones form the orbit?
|
Lacrimal
Zygomatic Frontal Sphenoid Palatine Temporal |
|
|
Bright light shone into eye causing a blink describes the...
a) pupillary light reflex b) corneal reflex c) dazzle reflex d) palpebral reflex e) Purkinje-Sanson reflex |
c) dazzle reflex
|
|
|
What are the anterior parts of the eye that are evaluated?
|
Conjunctiva
Cornea Anterior chamber Uvea (Iris + ciliary body) Purkinje-Sanson Reflexes |
|
|
What drug dilates the pupils?
|
Tropicamide (makes 'em wide)
|
|
|
What are posterior structures of the eye that are evaluated?
|
Lens
Vitreous Fundus (tapetal, non-tapetal, retina, optic disc) |
|
|
Which reflex tests CN V, VI, and VII?
a) palpebral b) menace c) dazzle d) Purkinje-Sanson e) corneal |
e) corneal
(palpebral is V & VII menace is II, cortex, & VII dazzle is II, VII, and some central) |
|
|
Sensory innervation to the eyelids and cornea is provided by the __________ nerve while motor to the eyelid by the _________ nerve.
|
Frontal nerve (sensory)
Palpebral n. (motor) |
|
|
Retrobulbar blocks to the horse eye block which nerves?
|
Optic (CN II)
Oculomotor (CN III) Abducens (CN IV) Trochlear (CN VI) maxillary and ophthalmic branches of trigeminal (CN V) |
|
|
What are common therapies for entropion in foals?
|
mattress sutures
Sub Q PPG injection Maybe skin removal (Michele clips for large animal) |
|
|
T or F:
Eyelid lacerations should ALWAYS be closed in 2 layers. |
TRUE
|
|
|
Which of the following will successfully stain with fluorescein?
a) penetrating eye wound b) deep corneal ulcer c) epithelial abrasion d) anterior uveitis e) wide, deep corneal ulcer where center penetrates Descemet's membrane |
b) deep corneal ulcer
e) wide, deep corneal ulcer where center penetrates Descemet's membrane (would stain ulcer but be dark in middle) |
|
|
What is a major side effect of atropine use in the eye?
|
GI STASIS
|
|
|
Which of the following are acceptable topical treatments for corneal ulcers?
a) Flunixin b) antibiotics +/- antifungal c) atropine d) anticollagenase serum |
b) antibiotics +/- antifungal
c) atropine d) anticollagenase serum (flunixin is systemic; use flurbiprofen) |
|
|
What is the gold standard treatment for corneal ulcers (hint - its surgery)?
|
Conjunctival flap (+/- tarsorrhaphy)
|
|
|
What does the consentual pupillary light reflex test?
|
Retina, CN II, midbrain, CN III, iris
|
|
|
What is the most common type of equine cast and what is it used for?
|
Half-limb cast
for P1/P2 fractures; fetlock luxations |
|
|
Which cast style includes the olecranon or stifle?
a) half-limb b) full-limb c) phalangeal d) tube cast e) transfixation cast |
b) full-limb
d) tube cast (doesn't include the foot) |
|
|
Which cast style is commonly used for correction of angular deformities?
a) half-limb b) full-limb c) phalangeal d) tube cast e) transfixation cast |
d) tube cast
|
|
|
Which cast style is commonly used for cannon bone fractures?
a) half-limb b) full-limb c) phalangeal d) tube cast e) transfixation cast |
b) full-limb
|
|
|
What are the major aspects of cast monitoring?
|
Strict stall rest
Use of cast limb Palpate for heat Check top of cast for swelling or sores Check toe for wear Monitor for odor Monitor for discharge or staining |
|
|
When should a cast be normally removed?
|
2-8 wks (use radiographic evaluation)
|

