![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The percentage of oxygen in the atmosphere has increased since the Earth’searliest atmosphere. Describe the process that has caused this change.
|
- Photosynthesis /absorbcarbon dioxide andreleases oxygen
- (green) plants |
|
|
Describe a test to show a gas is oxygen
|
second marking is dependent onthe first
- a glowing splint - relights |
|
|
When heated, copper reacts with oxygen in the air to form copper oxide. State why an excess of copper must be used.
|
- to ensure the oxygen iscompletely removed
|
|
|
The copper is heated strongly and the air is passed backwards and forwards overthe copper until no more copper reacts. The apparatus is then left to cool. Explain how this experiment can be used to find the volume of oxygen in100 cm3 of air.
|
- measure the volume of gasin the syringe at the end ofexperiment
- subtract from {100 cm3 /original volume} to givevolume of oxygen |
|
|
What is the formula of calcium carbonate?
|
CaCO3
|
|
|
Give a large scale use of limestone.
|
- making {glass / concrete /cement / quick lime} - aggregates in road making
- extracting iron - neutralising {soil/ lake} acidity - neutralisingacidic gases in power stations |
|
|
Marble is an example of a metamorphic rock. Explain how marble is formed from limestone.
|
- heat
- pressure |
|
|
whats the difference between intrusive and extrusive |
- intrusive rocks form largercrystals/extrusive rocks formsmaller crystals
- extrusive cooled faster /intrusive cooled slower |
|
|
Write the balanced equation for the reaction of calcium oxide with water to formcalcium hydroxide.
|
- CaO + H2O -> Ca(OH)2 (2)
|
|
|
the ease of ignition decreases as you go from the _____ of the column to the _____ of the column |
- top to the bottom of the column |
|
|
Describe problems caused by one product of the incomplete combustion of ahydrocarbon fuel.
|
- carbon monoxide / CO
- is toxic / poisonous or - carbon / soot - causes respiratory problems/particles blocks jets |
|
|
Explain why some people are concerned about the release of large quantitiesof carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
|
- greenhouse gas
- traps heat (in atmosphere) - may lead to increased (global)temperature / global warming |
|
|
Fuel oil can contain sulfur as an impurity. Explain how burning this impurity can cause problems in the environment.
|
- sulfurreacts/combusts/burns with oxygen/air
- forms sulfur dioxide - sulfur dioxide dissolves/reacts in rain/water/clouds and forms acid rain - acid rain causes damage tobuildings/plants/kills fish inlakes |
|
|
Describe advantages of replacing fossil fuels with biofuels.
|
- biofuels are renewable / fossilfuels are finite
- biofuels are produced fromplants - growing plants remove carbondioxide from the atmosphere (photosynthesis) - reduces demand for fossilfuels - biofuels do not containimpurities such as sulfur |
|
|
Explain what is meant by saturated hydrocarbon.
|
- contains carbon (atoms)and hydrogen (atoms)
- only - all single bonds/no doublebonds |
|
|
A saturated hydrocarbon is mixed with bromine water and shaken. What colour would you observe?
|
- remains orange
|
|
|
In the oil industry some fuel oil fraction is converted into petrol. This is done by heating the fuel oil fraction to thermally decompose it andproduce smaller molecules. State the name given to this process.
|
- Cracking |
|
|
Give two reasons why it is necessary to crack fuel oil to make morepetrol.
|
- insufficient petrol / supply (fromcrude oil)
- higher demand for petrol - more fuel oil fraction thanneeded - petrol is more useful than fuel oil |
|
|
Methane can be burned in excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water. Write the balanced equation for this reaction.
|
- CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O (3)
|
|
|
Magnesium carbonate reacts with dilute nitric acid. Give the names of the products formed in this reaction.
|
- magnesium nitrate
- water - carbon dioxide |
|
|
Zinc oxide, ZnO, reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride, ZnCl2,and water. This reaction is an example of...
|
- neutralisation
|
|
|
Describe how the apparatus can be used to electrolyse hydrochloric acid and howthe gases produced can be tested to show that they are hydrogen and chlorine. (6 marks)
|
experiment set up
- hydrochloric acid in container -carbon rods in acid -attach rods to electrical supply - d.c. supply(or reference to positive and negative) -test tubes to collect gases test hydrogen - lighted splint -squeaky pop (with air)/burns test chlorine - (damp blue) litmus paper - (turns red then) bleaches/white |
|
|
Is tin oxide oxidised or reduced when reacting with carbon? |
- tin oxide is reduced |
|
|
In terms of the arrangement of metal atoms, explain why gold alloys arestronger than pure gold.
|
- alloys have different sized atoms
- atoms/layers slide over eachother (easily) in pure metal - structure/layers disrupted (inalloy) -stop atoms/layers sliding/moving overone another (easily) |
|
|
Explain, using aluminum, gold and iron as examples, how the method used toobtain the metal is related to its position in the reactivity series and to the cost ofthe extraction process.
|
gold
- gold is an unreactive metal/at the bottom of the reactivityseries - it does not combine with other elements in the Earth’s crust - so is found as uncombined metal - cost of recovery is low iron -iron is a more reactive metal than gold and less reactivethan aluminium/middle of reactivity series -found combined with other elements - it is extracted by heating with carbon -electrolysis can be used -but electrolysis is more expensive (than heating withcarbon) aluminium -aluminium is a very reactive metal/near to top of thereactivity series -found combined with other elements -it is extracted by electrolysis -because it is very difficult to reduce -electrolysis is a powerful method of reduction -use of electricity makes this method expensive |
|
|
Explain what is meant by electrolysis? |
- decomposition (ofcompound /electrolyte)
- using (direct) current / electricity |
|
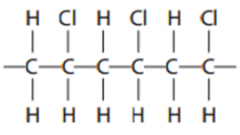
State the name of the polymer |
- poly(chloroethene)/ PVC / polyvinylchloride /polychloroethene /poly(chlorethene)
|
|
|
The reaction produces silver chloride as a precipitate. In an equation this would be shown as ...
|
- AgCl(s)
|
|
|
State how the total mass before a reaction would compare with the total mass after a reaction (if the reaction takes place in one container, fully) |
same/no change
|
|
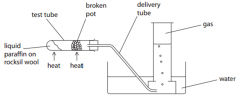
When the experiment is complete there is a danger that water will rise up thedelivery tube into the hot test tube. State what you would do to prevent this
|
- remove delivery tube from waterbefore stopping heating
|
|
|
State what is meant by unsaturated
|
- contains a double bond |
|
|
In industry, long chain hydrocarbon molecules are cracked to form shorter chainhydrocarbon molecules. Explain why this process is important.
|
- shorter chain molecules aremore useful
- demand for shorter chainmolecules - meets demand - reduces the excess of longerchain molecules - (cracking) produces alkenes - alkenes used to makepolymers |
|
|
The percentage of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere today is
|
- less than 0.5%
|
|
|
The percentage of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere today is less thanthat in the Earth’s earliest atmosphere. Explain what has caused the percentage of carbon dioxide to decrease.
|
- dissolves /is absorbed
- in the oceans - incorporated into marineorganisms - formed carbonate rocks - increase in (green)plants/plants start growing - photosynthesis /plantsremove carbon dioxide |
|
|
Carbon dioxide and other gases in the atmosphere help to keep the Earthwarm. State how these gases keep the Earth warm.
|
- traps heat / reflects heat back to Earth
|
|
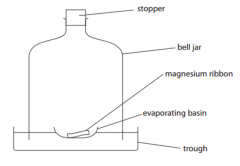
When the magnesium flame went out, there was some magnesium left in thebasin. When the apparatus had cooled, the water in the bell jar had risen. Explain why the water has risen.
|
- volume of gas in bell jardecreases/water rises tofill the space
- oxygen is removed fromthe air |
|
|
Explain what you understand by the term alloy.
|
-a mixture of (reject compound, ignore combined/joined) - metals |
|
|
Explain why calcium carbonate can be used to treat waste gases produced incoal-fired power stations.
|
- removes waste gasesthat are acidic
- contain sulfur dioxide - produced from sulfurimpurities in coal - limestone/calciumcarbonate reactswith/neutralises gases -> it is a base |
|
|
Limestone is a sedimentary rock. Marble is a metamorphic rock. Granite is an igneous rock. Explain how the three rock layers were formed
|
limestone
- formed from sediments/shells - sediments fall to bottom of sea - layers of sediments build up - long time period - compaction - by pressure - rocks appear out of the sea granite - magma /molten rock - forced up - cools - solidifies - intrusive rock - forms crystals marble - limestone {changed/metamorphosed} - by heat - (from) magma/molten rock - and pressure |
|
|
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of using bio-methane rather thannatural gas as a source of energy
|
advantages
- renewable / sustainable - more plants can be grown - crops use up carbon dioxide and produce oxygenwhen growing /photosynthesising - carbon neutral because the carbon produced duringcombustion is used when growing the plants -does not use up crude oil/non-renewable resources disadvantages - crops grown for bio-fuels use up land - land could otherwise be used to provide homes / lessfarmland available for growing food crops - lots of crops required to provide a small amount ofbio-methane -bad season reduces availability - carbon emissions due to transport and production ifqualified |

