![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Summit of a mountain followed by a rapid descent onto the flat desert surface. Can view the highway stretching across a dry valley & up the next range. Repeats. A series of ranges running north & south each between 75-250 km long, separated by parallel valleys. Most of the region is high with valley floors standing more than __ meters above sea level, & the highest peaks exceeding __ meters. What is this? |
1,000 meters; 4,000 meters; The Basin and Range Province; |
Extends from eastern CA to central Utah, southernmost Oregon & Idaho on the north to southern Arizona & southwestern New Mexico & into the Sonoran state of Mexico. |
|
|
The California portion of the Basin & Range Province includes what? |
northeastern corner of the state and a much larger areas bordered by the Sierra Nevada on the west and the Mojave on the east. |
|
|
|
__, perhaps the most famous of the basins in the entire Basin and Range Province, contains the lowest point in the U.S. __ meters below sea level. |
Death Valley; 86 meters; |
|
|
|
The highest point east of Owens Valley in the ___ stands 4,341 meters above sea level. |
White Mountains; |
|
|
|
Prominent CA ranges include which 4? |
Warner Range; White & Inyo Mountains; Panamint Range; Funeral Mountains; |
|
|
|
The major Valleys of CA's Basin and Range Province are which 4? |
Owens Valley (east edge of Sierra Nevada); Saline; Panamint; Death Valleys; |
Like all CA deserts, Basin & range has low rainfall & scarce vegetation. Only higher parts of some ranges support a forest. |
|
|
__ is a triangle on the east by Colorado River & California-Nevada border, north by the Garlock fault, and southwest by the San Gabriel & San Bernardino Mountains and San Andreas Fault. How is its topography different and similar to the Basin and Range Province? |
Mojave Desert; Similar: Basins & ranges are characteristic. Differences: - Most ranges shorter & lower. - Basins broader & fairly flat. - Basins & ranges are less aligned. |
This can be explained by their recent geologic history. |
|
|
Major earthquake in U.S. 7.8 in __ on the eastern Sierra Nevada fault system through ___, leveling the entire town of __ (killed 23). Felt as far as Salt Lake City. |
1872; Owens Valley; Lone Pine; |
|
|
|
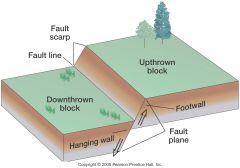
A __, a break in the topography caused by surface faulting, is seen in Lone Pine. Forms when an earthquakes ruptures the ground surface, displacing the landscape along a sharp break. Will fade away as erosion & deposition smooth out the land surface. |
Fault scarp |
shifted land surface about 1 to 2 meters vertically & 6 meters horizontally. |
|
|
The fault scarp west of Lone Pine built by 3 earthquakes. Over geologic time, repeated earthquakes along the faults of the Owens Valley system have gradually elevated the ___ 3,300 meters above the floor of Owens Valley. Process still continues today. |
Sierra Nevada; |
|
|
|
__ is a young fault along the edge of an uplifting mountain range. |
range-front fault; |
|
|
|
Sharp, well-preserved fault scarps along base of ranges indicate that earthquakes occurred there during the past few thousand years. If they are subtle or ___, this indicates a long period of erosion & deposition has passed since the last ground breaking earthquake. Freshness of scarps can estimate the __ of the most recent earthquake on a fault. |
well-preserved; absent; age; |
Old scarp faults can be buried by alluvial fans while young ones ca break through recent alluvial fans. |
|
|
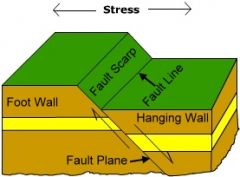
Along the faults of Basin and Range Province, recent movement has elevated the ranges relative to the basins. Most of the range-front faults are __ where movement drops one side along the fault surface in the direction that one would expect by gravity, given the geometry of the fault. It's repeated vertical movements produce the characteristics Basin and Range topography. |
normal faults |
|
|
|
The overall shape of the mountain fronts and sharpness of basin/ranges shows faulting history. If steep, straight mountain fronts means ___ movement of normal faults. If subdued, softened mountains, and sinuous (snakelike) fronts, than __ recent. (Like Mojave) |
recent; less; |
|
|
|
Many of the faults in southeastern CA show ___ as well as normal movement. Ex. Owens, Panamint, Death, & Furnace Creek. 3 zones in Mojave desert. |
lateral displacement; San Andreas system; Garlock fault; CA shear zone |
|
|
|
Lateral motion on faults __ of the San Andreas system accommodates some of the relative motion between the Pacific & North American Plates that is not taken up by the San Andreas itself. |
east |
|
|
|
Many normal faults are steep at the surface, but have a more shallow dip at depth. In some areas, multiple normal faults converge or are cut off along a single, gently dipping fault surface. A large, gently dipping fault, along which a large crustal block moves over deeper rocks is a ___. Can extend below the Earth's surface to great depths, perhaps more than 10 km. |
Detachment fault; |
|
|
|
At depths where temperature & pressure are great enough, the rocks along a detachment fault can be altered. The shearing motion of the fault blocks subjects the rocks in fault zone to great stresses creating a metamorphic rock ___. Has a smeared texture (because deformed in plastic manner), rather than being crushed or broken. |
Mylonite |
In areas where mylonite is now seen at Earth's surface along detachment faults, geologists can conclude that 8 to 15 kilometers of overlying rock must have been removed. |
|
|
As crust in Basin and Range and Mojave desert stretched, the rocks at the surface responded by normal faulting. Extension ___ the Earth's crust, and some areas became so extended that the surface rocks no longer covered the extended area. These areas called ____, the mylonite & other metamorphic rocks from the lower plate beneath the detachment can be seen at the Earth's surface. |
thinned; highly extended terranes; |
|
|
|
Detachment faulting caused by __ might explain unusual surfaces along the eastern side of Death Valley called __ for their curved shapes. Puzzling origin. One explanation is they are ___ of detachment faults & that marble & sheared rocks along their surface are mylonite produced by the fault movement. Region extended in NW/SW direction. Valley opened up with younger sedimentary units moving downward. The detachment faults became exposed. |
Cenozoic extension; turtlebacks; surfaces; |
|
|
|
Geologists hypothesize that Paleozoic rocks of the Panamint Range west of central Death Valley were originally located above or next to the pre-Cambrian rocks of the ___. Extension & detachment carried them, exposing the older rocks in Black Mountains. Same with Amargosa Chaos fault zone. |
Black Mountains; |
|
|
|
Many areas of Mojave Desert, the upper crust moved along detachment faults sufficiently to expose the rocks beneath the detachments. Many uncovered metamorphic rocks that were 8 to 15 km below the surface before the detachments formed. |
Ex. Old Woman Mountains, Chemehuevi Mountains, Whipple Mountains, and other ranges. In central, Buillion Mountains, Newberry Mountains, & Waterman Hills. |
|
|
|
Beginning 16/19 million yrs ago in Miocene time, lava erupted from several sources scattered throughout CA's Basin and Range Province. Are a result of ___ of the crust. Recent eruptions have left young cinder cones, craters, & lava flows. |
Extension |
Ex. Ubehebe Craters in Death Valley, cones & flows in Owens Valley near Big Pine, Bishop tuff, recent features in Modoc Plateau. |
|
|
__ is a center of recent volcanic activity along south Owens Lake, western edge of Basin. Both high-silica and mafic lavas erupted here, pattern known as ___. Due to mafic magma rising up & causing crustal rocks to melt to form high silica lava. |
Coso volcanic field; bimodal volcanism; |
The youngest dated feature is a basalt flow that erupted about 40,000 years ago. |
|
|
Interesting feature of Coso field is __ pattern of eruptions during the past 500,000 years. Discovered by dating rocks in eruptions & measuring __ of erupted materials. Volume of erupted could be predicted by calculating the time that had passed since the previous eruption. __ lava was erupted if more time had passed since the last eruption. |
regular pattern; volume; More; |
|
|
|
Coso volcanic eruptions controlled by opening of __ that carried magma to the volcanic vents. These form when magma is injected into linear conduits. Believe extension of the crust created these pathways for the eruptions. |
feeder dikes |
|
|
|
Volcanic eruptions have occurred along a depression in Mojave area, both are thought to be caused by continuing ___. Basalt has been the dominant rock produced in the zone, as would be expected in an extensional environment. Many of the volcanic features appear unweathered, evidence of both ___ activity & excellent ___ in the desert. |
extension; recent; preservation; |
|
|
|
___ in Mojave contains 30 cinder cones and flows. Cones & flows in __ part are as old as 10 million years while the __ part of the field is younger. Thought to have erupted only a few centuries ago cuz of excellent preservation. |
Cima volcanic field; north; south; |
Other Mojave examples: Aiken Mine red cinders for gardens, decoratives; Pisgah Crater; Three craters known as Sunshine Peak Craters. |
|
|
Dish Hill contains two cinder cones erupted about 2 million years ago. Both at Dish hill & Cima volcanic field, volcanic eruptions have brought pieces of the lower crust & the mantle to the Earth's surface in the form of __ a fragment of older rock incorporated into a younger igneous rock. Important because they provide samples of rocks from as deep as 70 to 80 meters below the surface that even drilling can't reach. |
xenoliths/inclusions (synonyms) |
Fragments of gabbro (mafic plutonic rock) suggest that the lower part of the crust in the Mojave is composed of gabbro. |
|
|
Throughout SE CA, extension resulted in the formation of down dropped basins between the ranges. Sediments eroded from newly raised mountains & accumulated in those basins. By identifying oldest sedimentary rocks there, we can determine when crustal extension began. When was it? |
Miocene period 22-16 million years ago (same time as early volcanic eruptions caused by it in SE CA) |
The Miocene sedimentary units include alluvial fan gravels carried from the Miocene ranges into the ancient basins. Gravels contain recognizable pieces of older rocks recycled into Miocene sediments. Ex. Miocene alluvial fan deposits the Artists Drive Formation, 14-16 million years old in Death Valley. As Miocene basin developed, younger lake sediments & intermixed volcanic layers accumulated above the fan gravels formed earlier. |
|
|
Sediments in areas known as __. A section of sedimentary rocks up to 650 meters thick records the history of deposition in and around the lake during __ time. __ extension created the down-dropped basin in which the sediments accumulated. The rocks which have been named the ___ are a mixture of mudstone, sandstone, & conglomerate, with interbedded ash layers. Based on ages of volcanic rocks above & below the sediments, age of ___ is placed between 16 to 13 million years ago. |
Rainbow Basin; Miocene time; Miocene extension; Barstow Formation; Barstow Formation; |
|
|
|
The most interesting feature of the Barstow Formation is that it contains a diverse assortment of __. |
fossils |
dogs, bears, cats, mammoths, horses, camels, antelope, bison, sheep, turtles, shellfish, palm trees, and even flamingos. |
|
|
Travelers on State Highway 14 pass through __ north of Mojave. Red, orange, pink rocks. Interlayered volcanic & sedimentary rocks like conglomerate, sandstone & white mudstone. Fossils of diverse animals. Rocks belong to the Ricardo group. |
Red Rock Canyon |
|
|
|
Basin and Range in western US agree extension of earth's crust began about 40 million years ago & continues today. CA portion of the Basin and Range extension began about __ million years ago. Some areas like Death valley might have been stretched by 100%. Estimated that entire Basin & Range province has lengthened by 250 km during 40 million years. 10 hour drive from SF to Salt Lake City would be shortened by at least __ hours. Present rate of extension is __ per year. |
16 (20) million years ago; 2.5 hours; 1 millimeter; |
|
|
|
Basin and Range Province's distinctive north-south alignment of faults has unknown mechanism. Only east-west extension could have created this. What theories to explain mechanism? |
- Change in relative motion between Pacific & North American plate. - Giant-scale collapse of crust in response to thickening from Mesozoic compression & crustal shortening. - Several causes operated together. |
|
|
|
What is the major reason for the differences in landscape between Mojave and Basin & Range Province? |
crustal extension in Mojave is much less active since Miocene time. More right-lateral faulting instead. Active faulting is much less widespread. |
|
|
|
Recent young alluvium covers the __, whereas a variety of Mesozoic and older rocks can be seen at the surfaces of the ___. Can drill beneath recent deposits and locate older rocks below them and estimate amount of vertical offset. However, practical way to understand geologic history prior to Basin & Range faulting is to study the rocks exposed in the __. |
basin floors; ranges; ranges; |
|
|
|
Harsh, barren desert ranges like Panamint Range, Inyo Mountains, Funeral range reveal perplexing array of rock types & structures. Scientists can reconstruct the environment that once existed. |
EL PACHUCO |
|
|
|
Exposed in most of the ranges in CA's Basin and Range are thick sequences of __ sedimentary rock. Limestone, dolomite abundant. Marine formations and fossils like Gastropods & coral found. Used to be __ environment uniform far w/ warm sea and gentle continental slope __ to __ million years ago. This __ seas were similar to Bahama Banks or Australia's Great Barrier Reef. Estimate 7,000 meters of deposition. |
carbonate; marine; 600 to 250 million; (late Proterozoic) Paleozoic |
Any slight rise or fall in sea level would cause the shoreline to shift many miles east or west. |
|
|
The carbonates of Cambrian time were built by sponge like creatures called Archaeocyathids. They caused layers of carbonate to precipitate from the surrounding sea, building masses known as __. |
stromatolites |
|
|
|
The type of sedimentary rock and the fossils provide clues to each formation's environment deposition. |
Formation and Environment of Deposition. - Vaughn Gulch Limestone with Abundant corals = Open Ocean. - Ely Springs Dolomite, rare corals = Shallow marine. - Eureka Quartzite, no fossils = Beach, very nearshore. - Badger Flat Dolomite, shallow-water snails = Shallow marine. |
|
|
|
West of ancient North America, the edge of the ___ began to __ or sink about 600 million years ago in late Proterozoic time. Maybe due to __ within North American continent. Sediments gradually accumulated on what was then the ___. The beginning of this 350 million year period is represented today by formations of quartz sandstone, siltstone, & shale. Early sediments washed onto the shelf from ancient land mass, carried by rivers that flowed from the coastal plain. |
continental shelf; subside; rifting; continental shelf; |
Ex in Death Valley area, Johnnie Formation, Wood Canyon Formation, & Zabriskie Quartzite are some of the recorders of these events. |
|
|
The environment along the continental margin of western North America during the Paleozoic period, a broad continental shelf along a tectonically quiet margin, where carbonate-secreting organisms were dominant. Lasted for __ million years. It was a ___ meaning it was far from active plate boundaries. |
Stable carbonate platform; 350 million years; passive margin; |
Ocean plates motion offshore to the west of this margin during Paleozoic time, creating stuff. |
|
|
Less is known about the geologic environment of southeastern CA before the development of the passive continental margin, because rocks older than latest Proterozoic age are found only in a few places. rocks of Pahrump group & Kingston Peak Formation in ___ are really old 1.2 to 700 million and seem to provide some evidence of the ___ geologists believe happened as an ancient super-continent broke apart during this period which they think gave rise to the passive continental margin. |
Death Valley; rifting; |
|
|
|
The tectonic quite of the Paleozoic ceased in southeastern CA beginning of ___ about 245 million years ago. Active boundary starting between N. America and plates of Mesozoic ocean. Evidence seen in rocks. Active boundary dominant force shaping CA's geology. Many granitic plutonic & volcanic rocks found (Sierran Batholith especially). |
Mesozoic |
Evidence for widespread compression during Mesozoic time is preserved. Older sedimentary formations disturbed by folds & thrust faults. Date back to Mesozoic because younger rocks are not affect by the folds and faults. Also, cross-cutting relations. Mesozoic igneous activity & faults & folds produced by compression are typical events that occur along subduction zone boundary. |
|
|
The __, rare igneous plutonic rock mostly made of carbonate, at ___ is the largest concentration (15%) of rare earth elements in the Western Hemisphere which are necessary for some of our most advanced technology (optic glass, TV, X-rays, magnets, lighting, contrast). They are some of the oldest rocks. |
carbonatite; Mountain Pass Mine; |
Ex. Cerium, Lanthanum, Neodymium, Praseodymine, Europium, yttrium. |

