![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypertension: Causes
|
Essential. Drug (withdraw, overdose). Medication Interaction (ex MOA inhibitors with tyramines). Cushing reflex (ICP). Renal failure. Renal artery stenosis. Coarctation. Pain. Anxiety. Endocrine (Conn, Hyperthyroid, pheochromacytoma).
|
|
|
Hypertension: Hypertensive Emergency Presentation
|
Patient will have a BP >180 SBP or >120 DBP and will have end organ damage. Signs and symptoms include Headache, blurred vision, papilledema, altered mental status, chest pain (MI, aortic dissection), olgiuria, edema, hematuria.
|
|
|
Hyperetension: Hypertensive Emergency Managment
|
ICU admission. Aterial line and reuction of BP. Reduction of BP by 25% with in 2 hours
IV Nitroprusside 0.2-5mcg/kg/min (A and V dilation) IV Nitroglycerine 10-400mcg/min (1st heart ischemia,V) IV Labetalol 20mg IV bolus then 2mg/min (MI, Aortic dissection |
|
|
Hypertension: Hypertensive Urgency Definition
|
Is BP >220/120 with out organ damage.
|
|
|
Hypertension: Hypertensive Urgency Managment
|
Clonidine (watch for sedation, brady with av blockers, rebound hypertension)
Captopril 12.5-25mg Metoprolol 12.5-100mg PO BID Topical Nitropaste |
|
|
Hypotension: Initial Assessment
|
Palpate for pulse. No pulse call code and proceed with chest compressions and ABC assessment. If palpable (radial >80 SBP, carotid >60 SBP). Take BP. Assess relative hypotension.
|
|
|
Hypotension: Causes
|
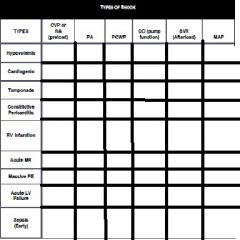
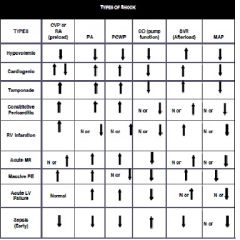
Causes of shock. Hypovolemia (vascular dissection, GI losses, over diuresis, post dialysis, third spacing). Cardiogenic (MI, arrythmia, valvular dysfuction)
Obstructive (PE, tamponde, tension pneumo, atrial myxoma). Distributive (Sepsis, anaphylaxis, medication, neurogenic, adrneal insufficency) |
|
|
Hypotension: Evaluation
|
Any signs of shock? Altered mental status, diaphoresis, cool clammy skin, oliguria, decreases pulses. Call for back up.
Physical exam focusing on signs of cardiac ischema, arrythmia, tamponade, pneumothorax, PE, hemorrage, Anaphylaxis, Sepsis, Adrenal insuffiency |
|
|
Hypotension: Initial Managment
|
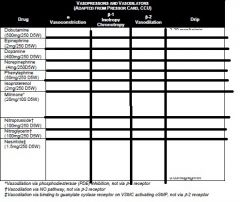
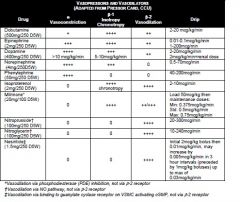
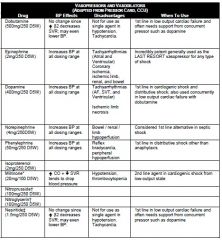
ABC. Two large bore needles 18G or higher 2L bolus. If no response to fluid resuccitation consider pressors. Sepsis Levophed (norepi). can consider dopamine, dobutamine, vasopression, phenylephrine, epinephrine.
|
|
|
Hypotension: Specific Managment
|
Cardiac ischemia: see acute MI protocol.
• Tamponade: call CCU fellow for emergent echo and pericardiocentesis • Pneumothorax: don’t wait for CXR; place 14 or 16 gauge needle into second intercostal space at midclavicular line ASAP. Call pulmonary fellow for chest tube placement. • Pulmonary Embolism: start thrombolytics/heparin. Dose: tPA: no loading dose, start 100 mg infuse over 2 hrs (ok to give w/ heparin), unless contraindications to tPA are present. Attain an echo to assess for RV function/strain. Please consult pulmonary fellow or attending prior to administration. • Bleeding: large bore IV, NS, blood product repletion, reverse any coagulopathy, • Anaphylaxis: epinephrine 0.1 mg (1cc of 1:10,000) slow IVP or 0.3 mg (0.3cc of 1:1,000) SQ • Sepsis: start broad spectrum antibiotics emergently (always double gram negative, and don’t be afraid to give aminoglycosides) and pressors (Levophed > dopamine > vasopressin > Neo-Synephrine) as needed • Adrenal insufficiency: hydrocortisone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

