![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Japanese Encephalitis |
-significant viral encephalitis |
|
|
|
J. Encephalitis Vector: |
Culex Mosquitoes |
|
|
|
J. Encephalitis Incubation Period (IP) |
5-15 days |
|
|
|
J. Encephalitis Intervention |
1. Wear long sleeves 2. Apply insect repellant |
|
|
|
J. Encephalitis S/sx: |
- non-specific febrile illness - N&V - diarrhea - cough - acute flaccid paralysis - Severe encephalitis (memory, thinking, & movement affected |
|
|
|
J. Encephalitis TX: |
No DOC 1. Symptomatic treatment 2. Supportive Vaccine: 2 IM (28 days apart; 1 wk. prior to travel |
|
|
|
Meningitis |
Inflammation lining around brain & spinal cord Classified septic (bacteria) or aseptic (viral/leukemia) |
|
|
|
Meningitis S/sx: |
- HA & fever (high grade) - PS⭐ Nuchal rigidity (stiff neck) - Photopobia - (+) Kernig's sign (pt. lying w/ thigh flexed on abd, leg cannot be completely extended) (+) Brudzinki's sign (pt's neck is flexed, flexion of knees & hips is produced) |
|
|
|
Meningitis MOT: |
Droplet |
|
|
|
Meningitis Vaccine: |
HIBV - H. Influenzae in children Pneumococcal Vaxx (PCV)- Strep. Pneumoniae in adult Rash: Meningococcemia (highly contagious) N. Meningitidis infxn: Purpuric rash |
|
|
|
Meningitis Dx: |
Lumbar puncture for CSF Analysis BACTERIAL: low Glucose & protein VIRAL: Normal Glucose & Protein |
|
|
|
Meningitis Prevention: |
Ciprofloxacin: meningococcal meningitis in close contact Vaxx: HIBV (child) PCV (adult) |
Meningitis |
|
|
Meningitis Medical Mgt: |
Antibiotics: Ceftriaxone Anti-seizures: Phenytoin (Dilantin) -Gum care> SE: Gingival hyperplasia |
Meningiti |
|
|
Triad of Meniere’s Dse |
Vertigo Tinnitus Sensory neural Hearing Loss |
|
|
|
Ear Conductive Hearing Loss |
External Ear -Otitis Externa -Otosclerosis Middle Ear -Otitis Media |
|
|
|
An inner ear problem that can cause dizzy spells also called vertigo, and hearing loss Attacks may be triggered by increase fluid in Labyrinth |
Meniere’s Dse |
|
|
|
Inflammation of the pericardium (outer), sac-like structure with 2 thin layers of tse that surround the heart to hold it in place and help it work |
Pericarditis |
|
|
|
Pericarditis Causes: |
-Viral -Post MI (Dressler’s syndrome) -Neoplasms - Renal Failure -Radiation |
|
|
|
Pericarditis S/sx: |
Chest pain (aggravated by breathing>inspiration; relieved w/ sitting/ lean forward) Increased WBC, fever, Malaise Friction rub (on auscultation)>sign ST elevations -> MI, Pericarditis |
|
|
|
Heart Murmurs |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Vulvular Disorders |
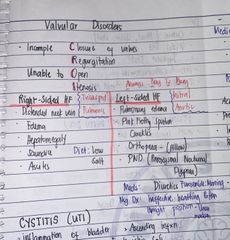
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Inflammation of bladder >Ascending Infxn |
CYSTITIS (UTI) Most common organism: Eschirichia Coli |
|
|
|
Cystitis S/sx: |
Frequency Urgency Cloudy urine Lower abd discomfort Back pain Int: ⬆️ OFI 3L/day |
|
|
|
Inflamed of renal pelvis & parenchyma >ascending infxn thru E. Coli |
Pyelonephritis |
|
|
|
Pyelonephritis S/sx |
Fever Flank pain Chills Costrovertebral angle tenderness |
|
|
|
Inflamed and damage to the filtering part of the kidneys (glomerulus) >descending infxn >immunologic/autoimmune |
Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis Cause: |
GABHS (Group A Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus URTI infxn hx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis) - 2-3 wks before symptoms |
|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis S/sx |
Gross hematuria Cola-colored, red brown urine Hypertension Edema Proteinuria Oliguria ⬆️ ASO (Antistreptolysin O) |
|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis S/sx |
Gross hematuria Cola-colored, red brown urine Hypertension Edema Proteinuria Oliguria ⬆️ ASO (Antistreptolysin O) |
|
|
|
Glomerulonephritis Mgt |
Diuretics Anti-hypertensives Antimicrobials (Penicillin) |
|
|
|
Renal Failure |
Acute 1. Prerenal: prob above kidney; shock 2. Intrarenal: inside kidney;dse-pyelo,glomerulo 3. Post renal: after kidney/ below; store in ureter, bladder, prostate Chronic -DM |
|
|
|
Renal failure S/sx |
Acidosis (metabolic) Anemia (⬇️ erythropoietin) Epogen subQ 3x a wk Azotemia (⬆️ BUN & Crea) BP ⬆️ Ca ⬇️ (hypocal) = ⬆️Phosphorus D vit ⬇️ = ⬆️K+ Edema |
|
|
|
Renal failure Diet |
Low Protein High Biologic Protein (veggies>veg sandwich, broccoli) |
|
|
|
ECG |
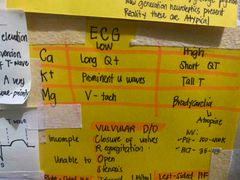
Back (Definition) |
|

