![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The study of how the body is shaped and structured |
Anatomy |
|
|
The study of body functions |
Physiology |
|
|
The basic unit of life |
Cell |
|
|
What do cells do? |
They determine the functional and structual characteristics of the entire body. |
|
|
The human body is composed of approximately ______ trillion, living, functioning cells. |
100 trillion |
|
|
What are the 3 main parts of a cell? |
Plasma membrane, intracellular environment and the nucleus |
|
|
This part of the cell includes the cytoplasm |
The intracellular environment |
|
|
The part that surrounds the cell creating an outer covering |
Plasma membrane |
|
|
Intracellular refers to |
The area within the cell membrane |
|
|
This part of the cell contains the living material that carries on the cell's function |
Intracellular environment |
|
|
Intercellular refers to |
The space between cells |
|
|
The study of tissues is known as |
Histology |
|
|
Epithelial tissue makes up what parts of the body? |
The skin, glands and linings of body cavities and organs. |
|
|
Which type of tissue supports and binds other body tissues? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which tissue is packed closely together with little or no intercellular material? |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
Name some types of connective tissue? |
Collagen, bone, cartilage, adipose, ligaments, tendons, blood and lymph |
|
|
Which body tissue produces movement when contracted? |
Muscle |
|
|
Muscle tissue is attached to? |
Bone |
|
|
What tissue forms the heart wall? Is it voluntary or involuntary? |
Cardiac muscle tissue (involuntary ) |
|
|
What type of muscle tissue lines the walls of the blood vessels and hollow organs? |
Smooth muscle (involuntary?) |
|
|
Rhythmic contraction of involuntary muscles lining the gastrointestinal tract |
Peristalis |
|
|
This type of tissue conducts impulses between the periphery and central nervous system |
Nervous tissue |
|
|
Supportive structures of the nervous tissue are called |
Neuroglial cells |
|
|
This tissue helps control the body's functions to maintain homeostasis |
Nervous tissue |
|
|
Two or more types of tissue bound together to form a more complex structure |
Organ |
|
|
Which part of the body produces insulin? |
Pancreas |
|
|
Which blood cells carry oxygen? |
Red blood cells |
|
|
This body system consists of arteries, arterioles, veins, venules, WBC, RBC, platelets and plasma |
Blood |
|
|
The pituitary and pineal gland are part of which body system? |
Endocrine |
|
|
The gastrointestinal system's functions are |
Mastication, digestion, absorption, and excretion |
|
|
The cardiovascular system is the_______system |
Circulatory |
|
|
The sebaceous glands are part of which body system? |
Integumentary |
|
|
This system maintains fluid balance within the body |
Lymphatic and Immune |
|
|
Which body system produces heat? |
Musculoskeletal |
|
|
This body system maintains homeostasis |
Nervous |
|
|
This system produces the hormones estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone |
Reproductive |
|
|
The trachea is part of which body system? |
Respiratory |
|
|
This system's functions include vision, hearing, balance, taste, and smell |
Sensory |
|
|
Which body system maintains electrolyte, water, and acid base balances? |
Urinary |
|
|
Which part of the body system does the hypothalamus, adrenal cortex and medulla belong to? |
Endocrine |
|
|
Which system regulates temperature? |
Integumentary |
|
|
Which system carries sensory stimulus to the brain and motor impulses to the periphery? |
Nervous |
|
|
Which system regulates blood pressure? |
Urinary |
|
|
The structural development of the body are as follows: |
Cells Tissues Organs Body Systems |
|
|
This type of provider treats patients of all ages for a broad range of diseases and complaints. |
Primary Care Physician (PCP) |
|
|
The small intestine absorbs ______ meanwhile the large intestine absorbs ______. |
Nutrients Water |
|
|
The purpose of a physical examination is to determine |
The patient's overall state of well-being. |
|
|
Verifying the patient's insurance information and documenting current medications and allergies is part of |
Patient preparation Before the examination |
|
|
This method of examination is done by observing to detect significant physical features or objective data |
Observation |
|
|
In this method of examination the physician uses touch |
Palpation |
|
|
This method of examination involves tapping or striking the body |
Percussion |
|
|
Direct percussion is performed by |
Striking the body with one finger |
|
|
__________ percussion is performed by tapping or striking the hand placed on the area with the opposite hand producing a sound and a sense of vibration |
Indirect |
|
|
To listen to the sounds arising from the body that are originated within the body |
Auscultation |
|
|
The process of measuring |
Mensuration |
|
|
This method is used to determine the range of extension, strength or flexion of a body part |
Manipulation |
|

What position is this? |
Semi-Folwer's |
|
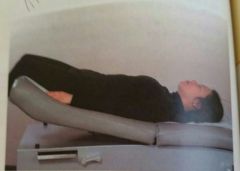
What position is this? What is it used for? |
Trendelenburg Position Used for: -severe hypotension -pt is going into shock Helps blood flow back up to the head |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Knee-Chest Position Used for: -proctologic exam -simoid, rectal, & vaginal exam |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Prone Position Used for: -exam of the back side |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Sims' Position aka Lateral Position Used for: -rectal exams -administration of rectal meds |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Lithotomy Position -vaginal exams w/ speculum -Pap smear |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Dorsal Recumbent -exam of rectal, vaginal, & perneal areas Relieves abdominal muscle tension & is more comfortable than supine |
|
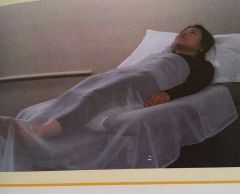
What position is this? What is it used for? |
Horizontal Recumbent -exam of front of body i.e.) heart, breasts, & abdominal organs |
|

What position is this? What is it used for? |
Fowler's Position -exam head, neck, chest Used for patients who have difficulty breathing while lying down |
|
|
Narcotics |
Action: depress cns Examples: |

