![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
List and discuss the five homeostatic functions of bones
|
Regulation of blood calcium levels: skeletal system serves as a store house for about 98% of body calcium reserves. Development of bone-osteogenesis, intramembraneous ossification, endochondral ossification
|
|
|
Identify the six major structures of a typical long bone
|
Diaphysis-main shaft like portion Epiphysis-proximal and distal ends of a long bone Articular cartilage-thin layer of hyaline Periosteum-dense white fibrous membrane Medullary cavity-tube-like hollow space Endosteum-thin fibrous membrane that lines the medullary cavity of long bones |
|
|
Parts of a flat bone
|
Have hard walls called internal and external tables (between is a region called the diploe cancellous bone) covered in periosteum and inner spaces are lined with endosteum. Flat bones (i.e. sternum) contain red marrow
|
|
|
Cancellous Bone
|
Trabeculae, supports red bone marrow (myeloid tissue), internal support for the bone and has reticular tissue
|
|
|
Compact Bone
|
Forms hard shell of bone, Haversian system, lacunae, lamellae
|
|
|
Identify the two main subdivisions of the skeleton and the primary subdivisions of the axial skeleton
|
Axial skeleton-80 bones-cranium, face, ear bones, hyoid bone, vertebral bones, sternum and ribs Appendicular skeleton-126 bones upper and lower extremities legs, arms, clavicle etc |
|
|
List the sutures and fontanels of the skull
|
Coronal suture-border with the frontal bone, Lamboidal suture-border with the occipital bone, Squamos suture-borders with the temporal bones, Sagittal suture-borders between the 2 parietal bones Fontanel- is the soft spot in infants |
|
|
Discuss the clinical significance of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
|
Cribriform plate-olfactory nerve pass through numerous holes (horizontal plate) Ethmoid Bone-forms the anterior cranial floor, medial orbital wall, upper parts of the nasal septum and sidewall of the nasal cavity |
|
|
List the primary subdivisions of the appendicular skeleton
|
Upper extremities-shoulder girdle, humerus, ulna, radius, carpal bones, metacarpals Lower extremities-pelvic girdle, femur, patella, tibia, fibula,foot |
|
|
List the bony structures of the shoulder
|
Clavicle and Scapula
|
|
|
Discuss the structures and functions of the thigh and leg
|
Thigh bone (femur)-longest and heaviest bone in the body Tibia-larger, stronger and more medially and superficially located of the two long bones Fibula-the smaller, more laterally located and deeply placed of the two leg bones |
|
|
Identify the hyoid bone
|
Does not articulate with any other bony structure, part of axial skeleton and is U shaped, and is above the larnyx
|
|
|
Name the regions of the vertebral column and give the number of vertebrae in each segment
|
Cervical vertebrae-has 7 bones Thoracic vertebrae-has 12 bones Lumbar vertebrae-has 5 bones Sacrum has 1 bone Coccyx has 1 bone |
|
|
Discuss the bony components of the rib cage, or chest
|
Jugular notch, manubrium, body of sternum, xiphoid process
|
|
|
Discuss disorders of the axial skeleton and the three primary types of abnormal vertebral curvatures
|
Lordosis-"Sway back" often seen during pregnancy, abnormally accentuated Kyphosis-"hunchback" increased roundness in the thoracic curvature, often seen in elderly people Scoliosis-Abnormal side to side curvature |
|
|
Discuss the structures and functions of the arm, forearm, hand
|
Arm-humerus-long bone that articulates proximally with the scapula and distally with radius and ulna Forearm-Radius on thumb side, ulna on little finger side Hand-has 8 carpal bones, pisiform bone is an example of a sesamoid bone, thumb bone is the most movable joint |
|
|
List the bony components of the pelvic girdle
|
Pelvic Girdle-stable circular base that supports the trunk and attaches lower extremities Ilium-largest, uppermost bone Ischium-strongest and lowermost Pubis-most anteriorly placed |
|
|
List the skeletal differences between men and women
|
General differences (size and weight) Men-larger and heavier, male pelvis is deep and funnel shaped w/ a narrow subpubic angel, males have larger skulls w/ more pronounced features Women-have more rounded mandibles, pelvis is shallow, broad and flaring |
|
|
Coronal Suture
|
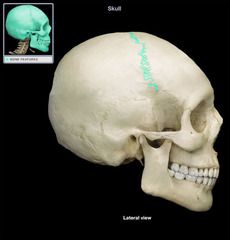
|
|
|
Sagittal Suture
|
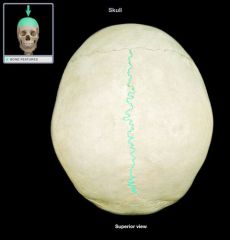
|
|
|
Squamos Suture
|
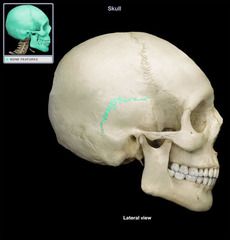
|
|
|
Lamboidal Suture
|
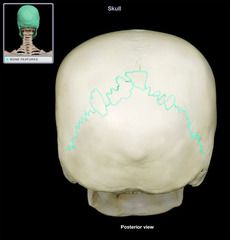
|
|
|
Frontal Cranial Bone
|
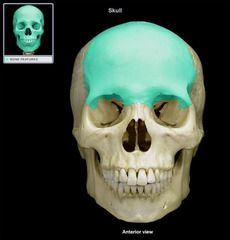
|
|
|
Parietal Cranial Bone
|
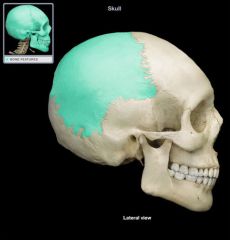
|
|
|
Occipital Cranial Bone
|
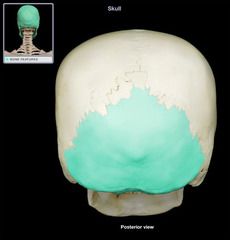
|
|
|
Occipital Condyle
|
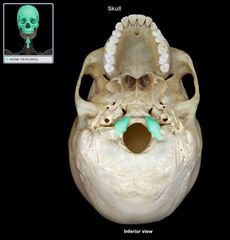
|
|
|
Foramen Magnum
|
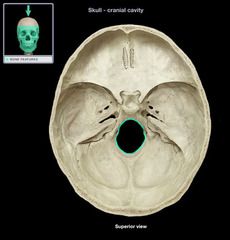
|
|
|
Jugular Foramen
|
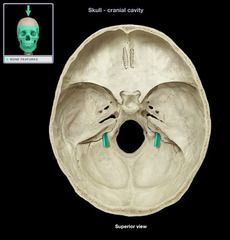
|
|
|
Temporal Cranial Bone
|
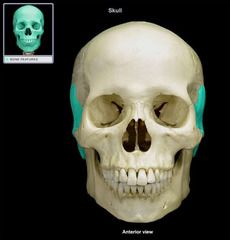
|
|
|
Temporal Cranial Bone
|
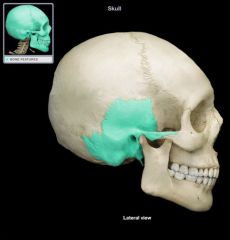
|
|
|
Zygomatic Process
|
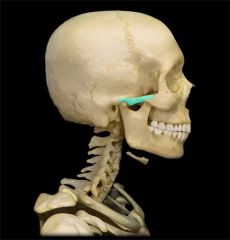
|
|
|
Zygomatic Process
|
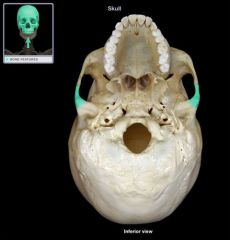
|
|
|
Mastoid Process
|
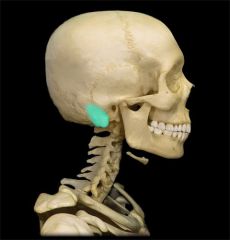
|
|
|
Mastoid Process
|
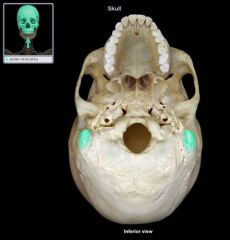
|
|
|
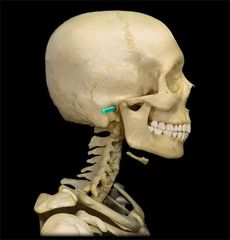
External Auditory (Acoustic) Meatus
|
|
|
|
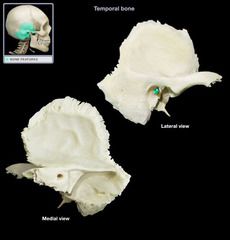
External Auditory (Acoustic) Meatus
|
|
|
|
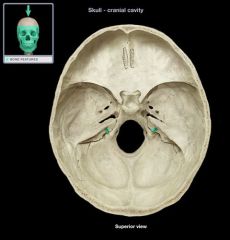
Internal Auditory (Acoustic) Meatus
|
|
|
|
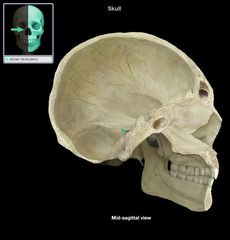
Internal Auditory (Acoustic) Meatus
|
|
|
|
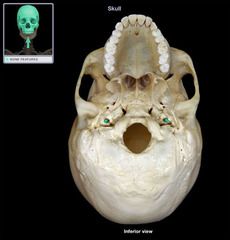
Carotid Canal
|
|
|
|
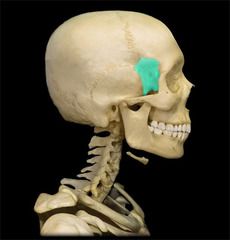
Sphenoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
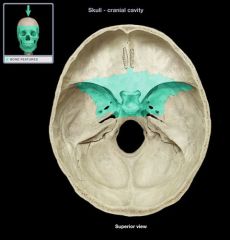
Sphenoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
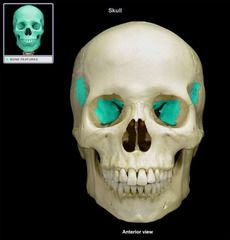
Sphenoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
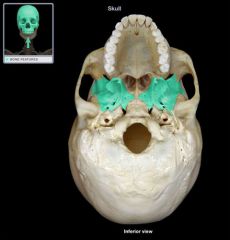
Sphenoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
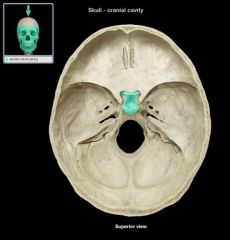
Sella Turcica
|
|
|
|
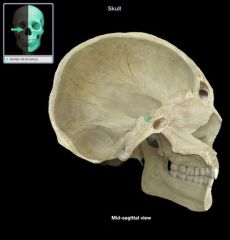
Sella Turcica
|
|
|
|
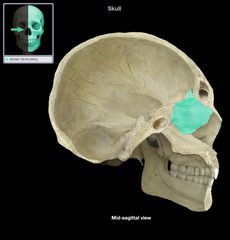
Ethmoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
Ethmoid Cranial Bone
|
|
|
|
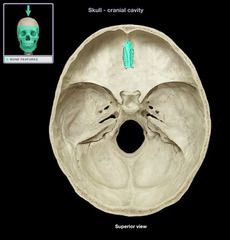
Crista Galli
|
|
|
|
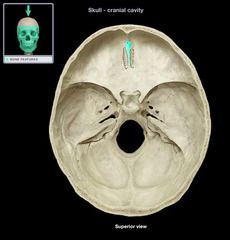
Crista Galli
|
|
|
|
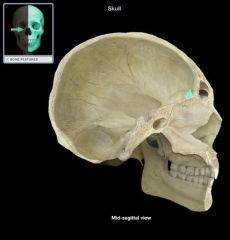
Cribiform Plate
|
|
|
|
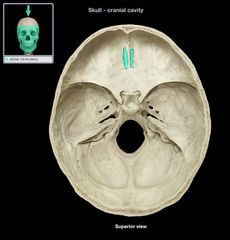
Cribiform Plate
|
|
|
|
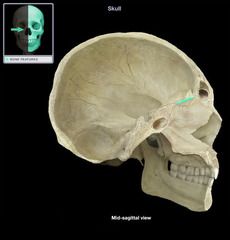
Nasal Bone
|
|
|
|
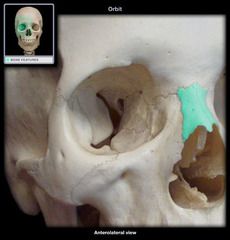
Maxilla Bone
|
|
|
|
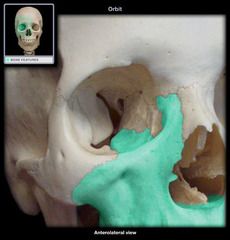
Maxilla Bone
|
|
|
|
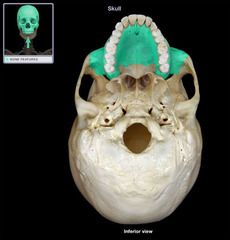
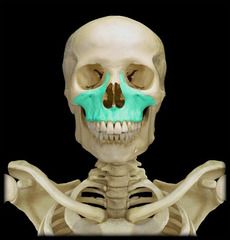
Maxilla Bone
|
|
|
|
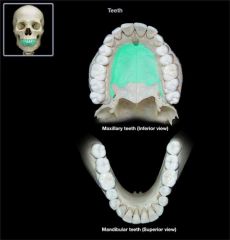
Palatine Process
|
|
|
|
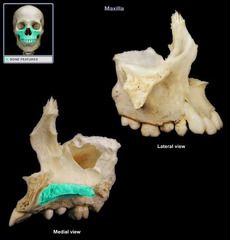
Palatine Process
|
|
|
|
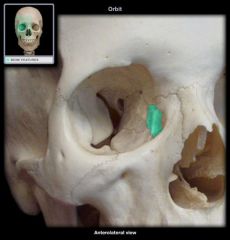
Lacrimal Bone
|
|
|
|
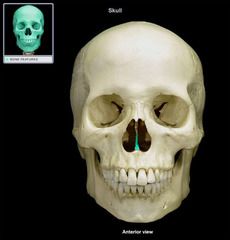
Vomer Bone
|
|
|
|
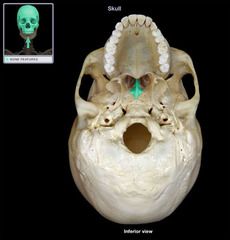
Vomer Bone
|
|
|
|
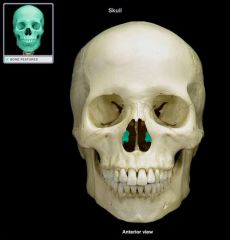
Inferior Nasal Conchae Bone
|
|
|
|
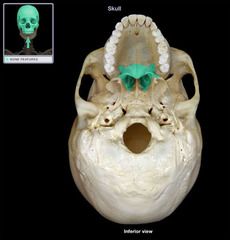
Palatine Bone
|
|
|
|
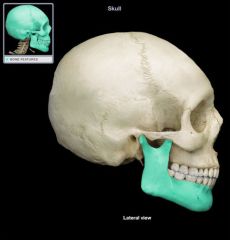
mandible
|
|
|
|
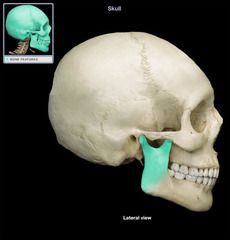
Ramus of the Mandible
|
|
|
|
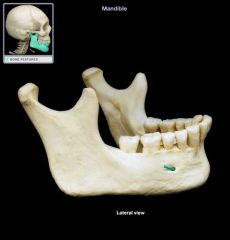
Mental Foramen
|
|
|
|
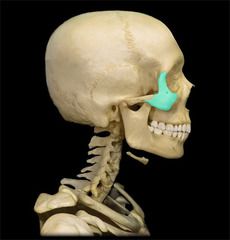
Zygomatic Bone
|
|
|
|
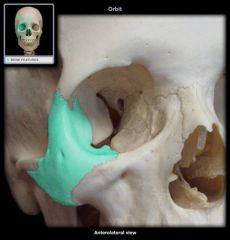
Zygomatic Bone
|
|
|
|
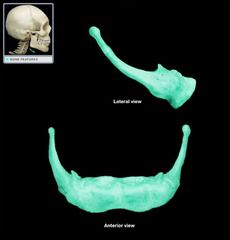
Hyoid Bone
|
|
|
|
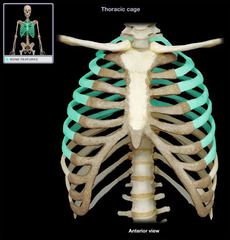
True ribs
|
|
|
|
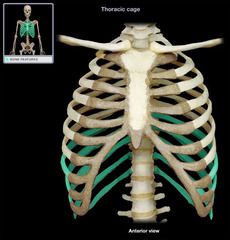
False Ribs
|
|
|
|
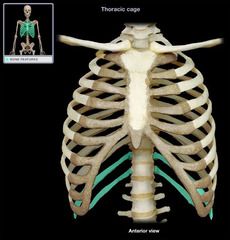
floating ribs
|
|
|
|
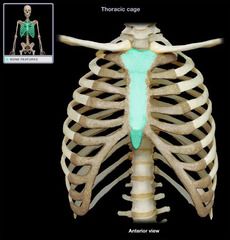
Sternum
|
|
|
|
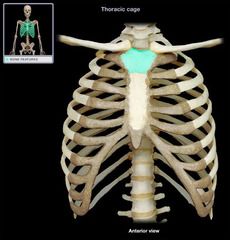
Manubrium
|
|
|
|
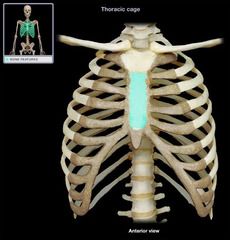
Body of the Sternum
|
|
|
|
Xiphoid Process
|
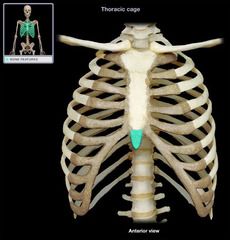
|
|
|
Jugular or Clavicular Notch
|
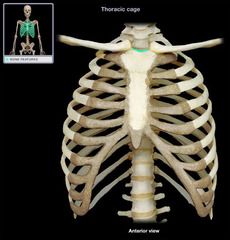
|
|
|
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7)
|
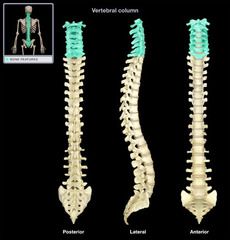
|
|
|
Atlas (C1)
|
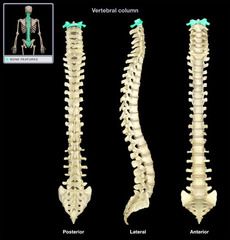
|
|
|
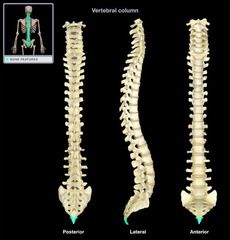
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12)
|
|
|
|
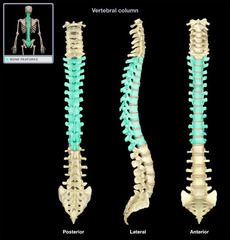
Lumbar Vertebrae (L1-L5)
|
|
|
|
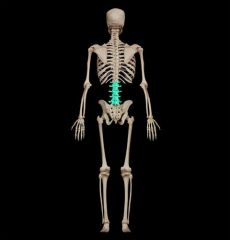
Sacrum (made of sacral fused Vertebrae S1-S5)
|
|
|
|
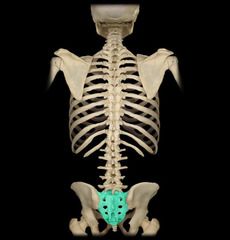
Coccyx (Made of Coccygeal Fused Vertebrae Co1-Co4)
|
|
|
|
|
|

