![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
79 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The urinary system
|
rids the body of wastes while regulating water, electrolyte, and acid-base balance of the blood.
|
|
|
The structures within the urinary system include...
|
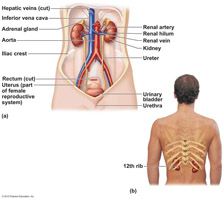
the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
|
|
|
The kidneys
|
are located in the lower back and extend from the T12 to L3 vertebra, also called the retroperitoneal area.
In that location, the kidneys receive some protection from the lower part of the rib cage. |
|
|
The kidney has a medial indentation called...
|
the renal hilum.
Several structures, including the ureters, the renal blood vessels, and nerves, enter or exit the kidney at the hilum. |
|
|
A fatty mass...
|
the perirenal fat capsule, surrounds each kidney and acts to cushion it against blows.
|
|
|
The outer region, which is lighter in color, is the
|
renal cortex
|
|
|
Deep in the cortex is a darker reddish-brown area...
|
the renal medulla
|
|
|
Lateral to the hilum is a flat cavity...
|
the renal pelvis
|
|
|
Extensions of the pelvis...
|
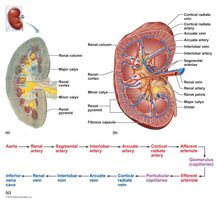
calyces,
collect urine, which continuously drains into the renal pelvis. Urine then flows from the pelvis into the ureter, which transports it to the bladder for temporary storage. |
|
|
The kidneys have a rich blood supply and are continuously cleansing the blood and adjusting its composition. Approximately ___________ of the total blood supply of the body passes through the kidneys each minute.
|
one-quarter
|
|
|
Each kidney contains over a million tiny structures called_______________.
|
nephrons
|
|
|
__________ are the structural and functional units of the kidneys and are responsible for forming urine
|
Nephrons
|
|
|
Each nephron consists of two main structures: a ____________, which is a knot of capillaries, and a ____________.
|
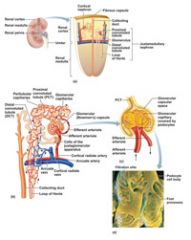
glomerulus
renal tubule |
|
|
Most nephrons are called ______________ because they are located almost entirely within the cortex.
|
cortical nephrons
|
|
|
The _______________, each of which receives urine from many nephrons, deliver the final urine product into the _______________ and ____________.
|
collecting ducts
calyces and renal pelvis |
|
|
Each and every nephron is associated with __ capillary beds, the __________ and the ______________.
|
two
glomerulus peritubular |
|
|
The ______________ is specialized for filtration, and the _______________ is specialized for absorption and surrounds the renal tubule.
|
glomerulus
peritubular |
|
|
The three processes involved in urine formation are ________ filtration, ________ reabsorption, and _________ secretion.
|
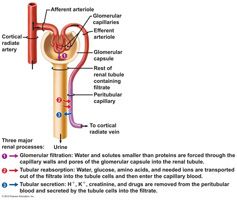
glomerular
tubular tubular |
|
|
Glomerular filtration
|
is a nonselective, passive process in which fluid passes from the blood into the glomerular capsule part of the renal tubule.
|
|
|
Once in the capsule, the fluid is called __________, and it is primarily blood plasma without blood proteins.
|
filtrate
|
|
|
Both proteins and blood cells are normally too large to pass through the filtration membrane, and when either of these appear in the urine, it is likely due to problem with the ____________ filters.
|
glomerular
|
|
|
Tubular reabsorption
|
begins as soon as the filtrate enters the proximal convoluted tubule.
|
|
|
The tubule cells are...
|
transporters, taking up needed substances from the filtrate so it can be reabsorbed.
Some reabsorption is done passively, but reabsorption of most substances depends on active transport processes, which use membrane carriers and which are very selective. There is an abundance of carriers for substances that need to be retained, and few or no carriers for substances of no use to the body. |
|
|
Needed substances _____,_____ are usually entirely removed from the filtrate.
|
glucose and amino acids
|
|
|
Nitrogenous waste products
|
including urea, uric acid, and creatinine are poorly reabsorbed, if at all.
Because tubule cells have few membrane carriers to reabsorb these substances, they tend to remain in the filtrate and are found in high concentrations in urine excreted from the body. |
|
|
Approximately ___% of the filtrate is eventually reabsorbed into the bloodstream.
|
99
|
|
|
Tubular secretion
|
is essentially tubular reabsorption in reverse.
|
|
|
Some substances, such as _______,_________,________, also move from the blood of the peritubular capillaries into the filtrate to be eliminated in urine.
|
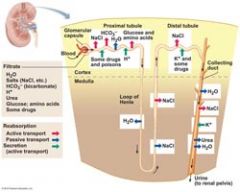
hydrogen, potassium ions, and creatinine
This process seems to be important for getting rid of substances not already in the filtrate, such as certain drugs, excess potassium, or as an additional means for controlling blood pH. |
|
|
In 24 hours, the kidneys filter ________________ of blood plasma through the glomeruli into the tubules.
|
150‒180 liters
|
|
|
The tubules process the filtrate by taking substances out of it _________ and adding substances to it ________, and about 1‒1.8 liters of urine is produced.
|
reabsorption
secretion |
|
|
Freshly voided urine is generally clear and pale to deep yellow. The normal yellow color is due to ___________, a pigment that results from the body's destruction of hemoglobin.
|
urochrome
|
|
|
When more solutes are in the urine...
|
the color becomes a deeper yellow.
|
|
|
Dilute urine is a...
|
pale, straw color.
|
|
|
Urine pH is...
|
slightly acidic, but changes in body metabolism and certain foods may cause it to be much more acidic or basic. Bacterial infection of the urinary tract also may cause the urine to be alkaline.
|
|
|
Specific gravity
|
is used to compare how much heavier urine is than distilled water.
The specific gravity of pure water is 1.0, and the specific gravity of urine ranges from 1.001 to 1.035. |
|
|
Urine is generally dilute (low specific gravity) when...
|
a person drinks excessive fluids, uses diuretics, or has chronic renal failure.
|
|
|
Conditions that produce urine with a high specific gravity include
|
inadequate fluid intake, fever, and a kidney inflammation called pyelonephritis.
|
|
|
Solutes normally found in urine include...
|
sodium and potassium ions, urea, uric acid, creatinine, ammonia, bicarbonate ions, and various other ions, depending on blood composition.
|
|
|
Urine composition can change dramatically with...
|
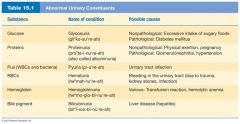
certain diseases, and the presence of abnormal substances in urine is often helpful in diagnosing the problem. Substances not normally found in urine are described above.
|
|
|
The ________, __________, and _______ provide storage reservoirs for urine or serve as transportation channels to carry it from one body region to another.
|
ureters
urinary bladder urethra |
|
|
The ______ are two slender tubes, 10‒12 inches long and ¼ inch in diameter, and run from the renal hilum to the posterior aspect of the bladder.
|
ureters
|
|
|
The ureters are...
|
passageways that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
|
|
|
Once urine has entered the bladder, it is prevented from flowing back into the ureters by...
|
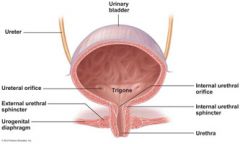
small folds of bladder mucosa that flap over the ureter opening.
|
|
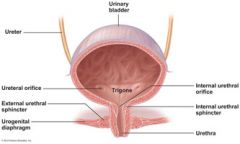
The ________ is a smooth, collapsible, muscular sac that temporarily stores urine.
|
urinary bladder
It is located in the pelvis, just posterior to the pubic symphasis. |
|
|
The bladder has three openings: the ______________ and the single opening of the _________ which drains the bladder.
|
two ureter openings
urethra |
|
|
In males, the ______________ surrounds the neck of the bladder where it empties into the urethra.
|
prostate gland
|
|
|
As urine accumulates, the bladder expands and rises ________ in the abdominal cavity. Its muscular wall stretches, and the transitional epithelial layer thins, increasing its volume and allowing the bladder to store more urine without increasing internal pressure. The average bladder is moderately full with _____ of urine.
|
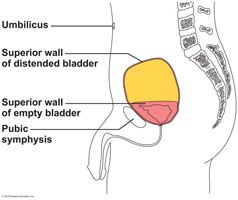
superiorly
500 mL |
|
|
The urethra
|
is a thin-walled tube that carries urine by peristalsis from the bladder to the outside of the body.
|
|
|
At the bladder-urethra junction, a thickening of the smooth muscle forms the ___________________, an involuntary sphincter that keeps the urethra closed when urine is not being passed.
|
internal urethral sphincter
|
|
|
A second sphincter, the _______________, is fashioned by skeletal muscle as the urethra passes through the pelvic floor.
|
external urethral sphincter
This sphincter is voluntarily controlled. |
|
|
The length and relative function of the urethra differ in the two sexes. In women it is about_______, and its external orifice, or opening, lies __________ to the vaginal opening.
|
3 to 4 cm
anteriorly Its function is to conduct urine to the body exterior. |
|
|
In men the urethra is approximately ____ long.
|
8 cm
The urethra opens at the tip of the penis after traveling down its length. |
|
|
The urethra of the male has a double function...
|
It carries urine out of the body, and it provides the passageway through which sperm is ejected from the body.
Thus, in males, the urethra is part of both the urinary and reproductive systems. |
|
|
Micturition, or voiding
|
is the act of emptying the bladder.
|
|
|
Two sphincters (or valves), the ____________________ and the ___________________, control the flow of urine from the bladder.
|
internal urethral sphincter
external urethral sphincter |
|
|
Ordinarily the bladder continues to collect urine until it contains about ___ ml.
|
200
At about this point, stretching of the bladder wall activates stretch receptors. Impulses transmitted to the spinal cord and then back to the bladder cause the bladder to go into reflex contractions. As the contractions become stronger, stored urine is forced past the internal urethral sphincter into the upper part of the urethra. It is then that an individual feels the urge to void. Because the lower external sphincter is skeletal muscle and is voluntarily controlled, an individual can choose to keep it closed and postpone emptying the bladder temporarily. When a person chooses not to void, the reflex contractions of the bladder stop within a minute or so and urine continues to accumulate in the bladder. After 200 to 300 ml more have been collected, the micturition reflex occurs again. Eventually, micturition occurs whether the person wills it or not. |
|
|
the kidneys have four major roles which help keep the blood composition relatively constant. These are...
|
excretion of nitrogen containing wastes, maintaining water and electrolyte balance of the blood, and ensuring proper blood pH.
|
|
|
Blood composition depends on three major factors including ____, ____________, and _________ ______ .
|
diet
cellular metabolism urine output |
|
|
About two-thirds of body fluid, the _________ ________, is contained within the living cells.
The remainder, called ____________ _______, includes all body fluids located outside the cells. |
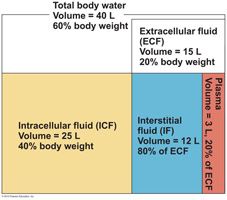
intracellular fluid (ICF)
extracellular fluid (ECF) |
|
|
Although ____ most importantly includes blood plasma and interstitial (or tissue) fluid, it also accounts for cerebrospinal and serous fluids, the humors of the eye, lymph, and others.
|
ECF
|
|
|
Plasma circulates throughout the body and links the external and internal environments. Exchanges occur almost continuously in the lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and kidneys.
|
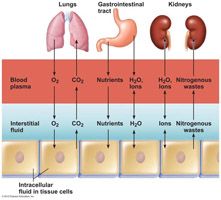
Although these exchanges alter plasma composition and volume, adjustments in the other two fluid compartments follow quickly so that balance is restored.
|
|
|
The types and amounts of solutes in body fluids, especially electrolytes such as _______, __________, and ___________, are also vitally important to overall body homeostasis and water and electrolyte balance.
|
sodium
potassium calcium ions |
|
|
Most water intake comes from ingested fluids and foods. However, a small amount is produced during _______ _________.
|
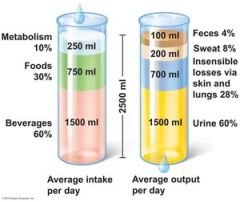
cellular metabolism
|
|
|
The thirst mechanism
|
is the driving force for water intake.
|
|
|
An increase in plasma solute content of only 2% to 3% excites highly sensitive cells in the hypothalamus called ____________, which in turn activate the hypothalamic thirst center.
|
osmoreceptors
|
|
|
The kidneys determine how much water to excrete in urine. If large amounts of water are lost in other ways, the kidneys compensate by putting out less urine to conserve body water.
|
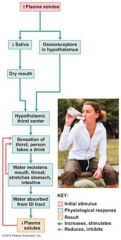
When water intake is excessive, the kidneys excrete generous amounts of urine.
|
|
|
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
|
This hormone prevents excessive water loss in the urine. ADH travels in the blood to its main target, the collecting ducts of the kidneys, where it causes the duct cells to reabsorb more water. As more water is returned to the bloodstream, blood volume and blood pressure increase to normal levels, and only a small amount of very concentrated urine is formed. ADH is released more or less continuously unless the solute concentration of the blood drops too low.
|
|
|
Electrolytes
|
are charged particles (ions) that conduct an electrical current in an aqueous solution.
|
|
|
Besides ADH, ____________ is a second hormone that helps to regulate blood composition and blood volume by acting on the kidney.
|
aldosterone
|
|
|
Aldosterone
|
is the major factor regulating sodium ion content of the ECF, and in the process, helps regulate the concentration of other ions as well.
|
|
|
_____________ is the electrolyte most responsible for osmotic water flows.
|
Sodium ion
|
|
|
When too little __________ is present in the blood, the blood becomes too dilute.
|
sodium
Consequently, water leaves the bloodstream and flows out into the tissue spaces, causing edema and possibly a shutdown of the circulatory system. |
|
|
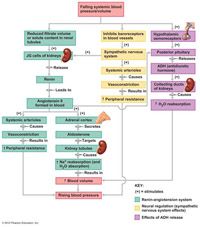
When the cells of the renal tubule are stimulated by low blood pressure or changes in solute content of the filtrate, they respond by releasing the enzyme ________ into the blood.
|
renin
|
|
|
Renin causes a series of reactions that produce _________ __, which in turn acts directly on the blood vessels to cause ___________, and on the adrenal cortical cells to promote aldosterone release.
|
angiotensin II
vasoconstriction As a result, blood volume and blood pressure increase. The renin-angiotensin mechanism is important for regulating blood pressure. The pressure drop also excites baroreceptors in the large blood vessels. These baroreceptors alert sympathetic nervous system centers of the brain to cause vasoconstriction which increase the peripheral resistance. |
|
|
Whenever the pH of arterial blood rises above 7.45, a person is said to have ___________.
|
alkalosis
|
|
|
A drop in arterial pH to below 7.35 results in ___________.
|
acidosis
|
|
|
Because a pH of 7.0 is neutral, a pH of 7.35 is not acidic, chemically speaking; however, it represents a higher-than-optimal hydrogen ion concentration for the functioning of most body cells. Therefore, any arterial pH between 7.35 and 7.0 is called __________ ___________.
|
physiological acidosis
|
|
|
Although small amounts of acidic substances enter the body in ingested foods, most hydrogen ions originate as by-products of cellular metabolism, which continuously adds substances to the blood that tend to disturb its _____________.
|
acid-base balance
|
|
|
The bicarbonate buffer system is a mixture of __________ _____ and its ____ ________ _________.
|
carbonic acid
salt, sodium bicarbonate |

