![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Corporate-Level Strategy |
specifies actions a firm takes to gain competitive advantage by selecting and managing a group of different businesses competing in different product markets |
|
|
|
Economies of Scope |
Cost savings that the firm creates by successfully sharing some of its resources and capabilities or transferring one or more corporate-level core competencies that were developed in one of its businesses to another of its businesses |
|
|
|
Corporate-level Core Competencies |
Complex sets of resources and capabilities that link different businesses primarily through managerial and technological knowledge, experience, and expertise |
|
|
|
Market Power |
Exists when a firm is able to sell its product above the existing competitive level or to reduce the cost of its primary and support activities below the competitive level, or both |
|
|
|
Multipoint Competition |
Exists when two or more diversified firms simultaneously compete in the same product areas or geographical markets |
|
|
|
Vertical Intergration |
Exists when a company produces its own inputs or owns its own source of output distribution |
Backward/Forward intergration |
|
|
Financial Economies |
Cost savings realized through improved allocations of financial resources based on investments inside or outside the firm |
|
|
|
Synergy
|
Exists when the value created by business units working together exceeds the value that those same units create working independently
|
|
|
|
Levels of diversifications
|
1. Low
2. Moderate to high 3. Very high |
|
|
|
Types of low level diversification
|
1. Single Business
2. Dominant Business |
|
|
|
Types of moderate to high diversification
|
1. Related constrained
2. Related linked ( mixed related and unrelated ) |
|
|
|
Types of very high diversification
|
1. Unrelated
|
|
|
|
Single business diversification
|

95% or more of revenue comes from a single business
|
|
|
|
Dominant Business
|
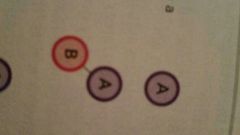
Between 70% and 95% of revenue comes from a single business
|
|
|
|
Related Constrained diversification
|
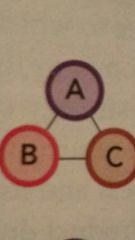
less than 70% of revenue comes from the dominant business and all businesses share product, technological, AND distribution linkages
|
|
|
|
Related Linked diversification
|
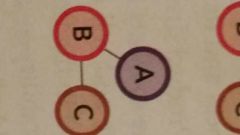
less than 70% of revenue comes from the dominant businesses, and there are only limited links between businesses
|
|
|
|
Unrelated diversification
|
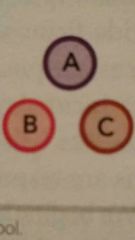
less than 70% of revenue comes from the dominant business , and there are no common links between businesses
|
|

