![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The purpose of coupling two biochemical reactions is to |
use an exergonic reaction to drive an endergonic reaction |
|
|
In a pair of coupled reactions, if the favorable reaction releases more energy than the amount required by the unfavorable reaction, the excess energy is |
released as heat and used to maintain body temperature |
|
|
Endergonic reactions are those that have a _ value of ΔG and _ spontaneous |
positive; non-spontaneous |
|
|
Which sequence illustrates the order of the steps from food to biochemically useful energy? |
digestion; acetyl-SCoA production; citric acid cycle; ATP production |
|
|
All of the following are energy strategies used in biochemical reactions except |
Chemical reactions occur in pairs in order to change the value of ΔG for one of the reactions |
|
|
ATP is the molecule most often used for energy transport because |
its hydrolysis releases an intermediate amount of energy and is relatively slow except in the presence of the appropriate enzymes
|
|
|
Which statement is true concerning the relationship between FAD and FADH2? |
FADH2 is the reduced form of FAD
|
|
|
In addition to producing ATP, the citric acid cycle produces _ as high energy molecules and _ as its major chemical waste product |
reduced coenzymes; CO2 |
|
|
In the first step of the citric acid cycle, acetyl-SCoA reacts with _ to produce _ which is isomerized to _ in the second step |
oxaloacetate; citrate; isocitrate |
|
|
The mitochondria are the location where _ takes place and most _ is produced |
citric acid cycle; ATP |
|
|
The common molecule produced from all foods at the second stage of catabolism is |
acetyl-SCoA |
|
|
In a pair of couple reactions, if the favorable reaction releases more energy than the amount required by the unfavorable reaction, the excess energy is |
released as heat and used to maintain body temperature |
|
|
In steps 5-8 of the citric acid cycle, the high-energy molecules _, _, and _, are produced and _ is regenerated to begin another turn of the cycle |
GTP; FADH2; NADH/H+; oxaloacetate |
|
|
The ultimate source of energy for all but very few biochemical reactions is |
The sun |
|
|
The driving force which provides the energy for synthesis of ATP in the fourth stage of metabolism |
the concentration gradient of hydrogen ions between the two sides of the inner mitochondrial membrane |
|
|
The metal that acts as an electron carrier in the cytochromes in the electron transport is |
Iron |
|
|
ATP is the molecule most often used for energy transport because |
its hydrolysis releases an intermediate amount of energy and is relatively slow except in the presence of the appropriate enzymes |
|
|
Which statement is true concerning the relationship between FAD and FADH2? |
FADH2 is the reduced form of FAD |
|
|
The reaction in which ATP is converted to ADP with release of 7.3 kcal is a(an) _ reaction |
hydrolysis |
|
|
The fourth stage of metabolism, in which the high energy molecules from stage three are oxidized to produce ATP is referred to as |
the electron transport chain |
|
|
The energy released by GTP hydrolysis is (more than, less than or the same) as ATP hydrolysis |
the same |
|
|
In the TCA or citric acid cycle, α-Ketoglutaric acid reacts with co-enzyme A to yield |
succinyl-SCoA |
|
|
In the TCA or citric acid cycle, the reactions at steps 3, 4, 6 and 8 are catalyzed by |
NAD+ and FAD |
|
|
_ is the common intermediate of all food groups |
pyruvate? |
|
|
In the 1st stage of metabolism, the catabolic process is facilitated by _ |
amylase |
|
|
The pH difference in the mitochondria is a result of the overall process of _ |
metabolism |
|
|
The electron transport chain transfers electrons from _ co-enzymes to oxygen and is coupled to _ production |
reduced; ATP |
|
|
In addition to flavoproteins and the heme protein _, the respiratory chain of mitochondria includes the small molecules _ |
cytochrome; ubiquinones |
|
|
Whereas digestion is _, metabolism is _ |
catabolic; anabolic |
|
|
The citric acid cycle supplies the _ with _, which ultimately generate energy |
electron transport chain; reduced coenzymes |
|
|
A glycosidic bond is |
a bond formed between an anomeric carbon atom and any OR group |
|
|
The linkage joining the two monosaccharides in the dissacharide shown in the structure is a(n) _ glycosidic linkage |
β (1,4) |
|
|
Which is the best description of a carbohydrate? |
A compound that is composed of an aldehyde or ketone and has one or more hydroxyl groups |
|
|
Lactose when hydrolyzed will form |
glucose and galactose |
|
|
Cellulose is a polymer consisting of thousands of |
β-glucose molecules |
|
|
Which substance is a monosaccharide? |
cellulose |
|
|
_ is converted to ketone bodies during starvation, which can provide up to 50% of the ATP needed for homeostasis |
Acetyl-SCoA |
|
|
The metabolic process which produces glucose from _ sources is called _ |
non-carbohydrate; gluconeogenesis |
|
|
In the 1st stage of carbohydrate metabolism the enzyme _ catabolizes _ and _, which are polymeric forms of the carbons that supply the TCA cycle |
α-amylase; starch; glycogen |
|
|
The blood clotting factor heparin, insect exoskeleton chitin and chondroitin found in the fluids of the eyes and joints are all synthesized from _ |
monosaccharides |
|
|
Amylopection and glycogen both have _ and _ glycosidic bonds |
α-1,4; α-1,6 |
|
|
Which is a hemiacetal? |
glucopyranose |
|
|
Lactate formed in muscles can be utilized through |
glucose-alanine cycle |
|
|
α-glycosidic bond is present in |
maltose, sucrose and lactose |
|
|
compounds having the same structural formula but differing in spatial configuration are known as _ |
optical isomers
|
|
|
In the 1st stage of carbohydrate metabolism the enzyme _ catabolizes _ and _, which is one source of the carbons that supplies the TCA cycle |
amylase; glucose; other sugars |
|
|
Sucrose is a disaccharide of _ and _, linked by a(n) _ bond |
glucose; fructose; ether glycosidic |
|
|
_ is the most abundant polysaccharide in nature |
Cellulose |
|
|
Two sugars which differ from one another only in configuration around the C1 carbon atom are termed _ |
anomers |
|
|
The reducing ability of carbohydrates is due to _ |
carboxyl group |
|
|
The formation of the stable, low energy ring structure in D-glucose requires that _ forms a hemiacetal |
c-1 and c-4 |
|
|
Exergonic reaction picture |

|
|
|
Endergonic reaction picture |
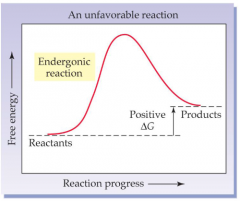
|
|
|
ATP to ADP picture |
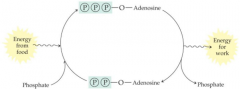
|
|
|
Citric acid cycle picture |

|
|
|
Electron transport chain process picture |
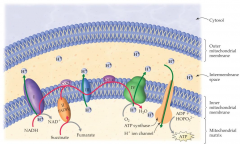
|
|
|
Metabolism picture |
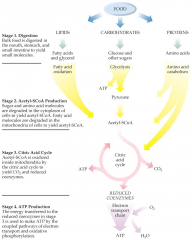
|
|
|
Disaccharide pictures |
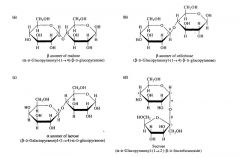
|

