![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Similar to charged surfaces, ions are surrounded by an |

Ion atmosphere |
|
|
|
Mu i_(elec) is |
The deviation from ideality of a solution caused by epectrostatic interactions of ions with surroundings. |
|
|
|
What is the activity coefficient gamma and mu (elec) in terms of gamma? |
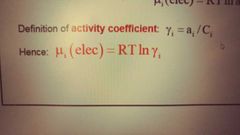
|
|
|
|
What is the work done in the process of charging an ion that is initiallly uncharged up to its actual charge zi e. |

|
|
|
|
How was the equation for gamma derived using the guoy chapman theory? |

|
|
|
|
Gamma coefficients cannot be |
Measured from experiment |
|
|
|
How are single ion activities related to mean ion activities? |

|
|
|
|
Abs(z1v1) = |
Abs(z2v2) |
|
|
|
Common equations for ln gamma look like |

|
|
|
|
For 1:1 2:2 3:3 1:2 electrolytes etc. The mean ionic concentration equals |

C=C C=2C C=3C C =4^(1/3)C |
|
|
|
The nernst equation can also be written as and how would you find E nought and gamma values? |

|

|
|
|
What is the experimental procedure for measuring ionic strengths using square root of I |

|
|
|
|
When a solvent is in equillibrium with its vapor, muA(chemical potential of solvent) is equal to |

MuA(vapor) |
|
|
|
From the Gibbs- deluhem equation: 0 = VdP - SdT + sum(nidmui) so |

At constant T and P sum(nidmui) = 0 |
|
|
|
Look at this wild equation for when hydration layers are taken into account beyond th edehye huckel theory |

|
|
|
|
Mean activity coefficients can vary from |
0.2 to > 2 |
|
|
|
Read these take home messages |

|
|

