![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a two hybrid experiment? |
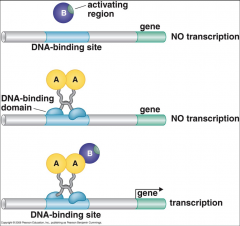
|
|
|
What would be the best technique to ID a specific DNA sequence to which a protein binds? |
ChIP-Seq Assay
|
|
|
Zinc finger domain vs zinc cluster domain |
Finger has three domains that interact with the DNA |
|
|
Leucine Zipper |
Coiled coil region, helices insert into the major groove. They often form heterodimers. |
|
|
Activation domains |
often made up of small units of repeated acidic and hydrophobic amino acids. they usually bind to the mediator complex or the TFIID. |
|
|
Activators brings in nucleator modifiers: examples |
chromatin remodeling complex and histone acetyl transferase |
|
|
What is the purpose of nucleosome anchors? |
They position the nucleosome and facilitate activator binding. |
|
|
What is NELF complex? |
It induces stalling shortly after initiation. The stalling allows for activators to recruit SEC( Super elongation complex). |
|
|
What is an example of an activator that recruits elongation factors? |
Drosophila HSP70 heat shock, causes formation of HSF which replaces H2B allowing Pol II to leave. It also recruits P-TEFb which phosphorylates; |
|
|
Mixed lineage leukemia |
Is related to the stalling problem. you need more detail on this guy. Basically what happens is there is a fusion between protein complexes. The most common is theAFF1 |
|
|
Purpose of insulators
|
If there is an insulator betweenthe enhancer and the promoter, expression from that promoter will be turnedoff. They also insulators are a way ofcontrolling which promoter is activated by a distant enhancer.
|
|
|
Locus control region
|
LCRs contain multiple elements –enhancers, insulators and even promoter-like sequences. LCR work in conjunction withother activators for each gene to determine which is expressed when duringdevelopment.
|
|
|
What are the ways activators interact?
|
Cooperative bindingof activators:Four ways that the binding ofone protein to a site on DNA can help thebinding of another to a nearby site. (a)Cooperative binding through direct interac-tion between the two proteins is shown. (b) A similar effect is achievedby both proteins interacting with a commonthird protein. (c,d) Indirect effects in whichbinding of one protein to its site on DNAwithin nucleosomes helps binding of asecond protein. (c) The first protein recruitsa nucleosome remodeler whose actionreveals a binding site for a second protein.(d) The binding of the first protein to its siteon the DNA just where it exits the nucleo-some. By binding there, it unwinds theDNA from the nucleosome a little, revealingthe binding site for the second protein.Each of these mechanisms can explain howone regulator can help others bind or,indeed, how an activator can help the tran-scriptional machinery bind to a promoter.
|
|
|
How does activation of HO endonuclease work?
|
It requires the work of two activators. SWI5 and SBF. SWI5 recruits chromatin remodeling complex (SNF) and histone complex. SBF activates the HO gene.
|

