![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Why should myelomeningocele defects be repaired in the early postnatal period? |
The major indication to repair a myelomeningocele defect in the early postnatal period is to prevent infection and bacterial meningitis. Great care is taken to keep the sac sterile and hydrated. |
|
|
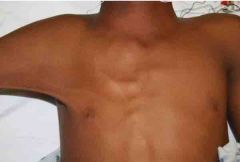
Syndrome? |
Poland syndrome with unusual axillary web. |
|
|
|
A 65-year-old man is prescribed leuprolide acetate for prostate cancer. Which of the following is the most likely effect the drug will have on this patient's breasts? A) Darkening of the nipple-areola complex B) Decrease in size C) Galactorrhea D) Mastodynia E) Petechiae
|
The correct response is Option D. Mastodynia. Gynecomastia and breast tenderness are known side effects of leuprolide treatment for prostate cancer. |
|
|
|
Per rectus muscle, approximately __ cm can be gained at the epigastric and suprapubic areas; __ cm can be advanced at the waist |
Per rectus muscle, approximately 4 cm can be gained at the epigastric and suprapubic areas; 10 cm can be advanced at the waist |
|
|
|
Component separation: The procedure calls for a release of the _____, which allows for medialization of the rectus abdominis and underlying lateral musculature for primary approximation. |
The procedure calls for a release of the external oblique aponeurosis 1 cm lateral to the linea semilunaris, which allows for medialization of the rectus abdominis and underlying lateral musculature for primary approximation. |
|
|
|
A 24-year-old man is evaluated because of a 15-month history of painful idiopathic gynecomastia. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment? Which is the most effective medically? A) Anastrozole B) Radiation therapy C) Spironolactone D) Surgical resection E) Tamoxifen
|
The correct response is Option D. Surgical treatment if painful gynecomastia has been present > 1 year. Spironolactone causes gynecomastia. Tamoxifen can be used for treatment. |
Which medication causes it? |
|
|
Define each of the following: - Dead-space volume - Functional capacity - Residual volume - Tidal volume - Vital capacity |
Tidal volume (VT) is the volume of air that is moved into or out of the lungs during quiet breathing. Tidal volume can be measured directly through spirometry or estimated based on a patient’s ideal body mass. It is a key parameter in mechanical ventilation to allow adequate ventilation without causing barotrauma to the lungs.
Vital capacity (VC) is the volume of air expired after deepest inspiration.
Functional capacity is a physiologic description of an individual’s ability to complete activities of daily living. It can be estimated through exercise treadmill testing and reported in metabolic equivalents (METs).
Residual volume (RV) is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after maximal exhalation.
Dead-space volume is the volume of air inhaled that does not take part in gas exchange. This volume can include both gas that remains in conducting airways (e.g., trachea, bronchi) during respiration and gas that reaches nonfunctional alveoli (e.g., nonperfused lung parenchyma following pulmonary embolism). |
|
|
|
Which flaps should be used to reconstruct posterior defects of the vaginal vault, especially in the setting of XrT? |
For posterior defects of the vaginal vault, abdominal-based flaps are usually preferable. They can provide a large amount of vascularized tissue that rotates easily into the defect. |
|
|
|
Repair with rectus advancement and polypropylene mesh is planned. Placement of mesh between which planes is most likely to decrease this patient’s risk of hernia recurrence? |
Rectus & posterior sheath |
|
|
|
Rigid chest wall Reconstruction: 1. How many ribs? 2. Size of defect? |
Generally, reconstruction of the lateral bony chest wall seems necessary if four or more consecutive ribs are resected or if the diameter of the total defect is larger than 5 cm. |
|
|
|
Which of the following represents the lateral border of the breast footprint? A) Anterior axillary line B) Anterior edge of the latissimus dorsi muscle C) Lateral clavicle D) Midaxillary line E) Posterior axillary line |
A) anterior axillary line |
|
|
|
Development of breast tissue in men, a condition called gynecomastia, may arise because of increased conversion of testosterone to ______ by the enzyme aromatase. |
Development of breast tissue in men, a condition called gynecomastia (which is usually caused by high levels of circulating estradiol), may arise because of increased conversion of testosterone to estradiol by the enzyme aromatase. |
|
|
|
Which syndrome is associated with gynecomastia? |
Klinefelter syndrome |
|
|
|
Which vessel gives rise to the SIEA? |
The femoral vessels give rise to the superficial inferior epigastric artery and vein, which perfuse the skin and subcutaneous fat of the inferior lateral abdomen. |
|
|
|
A 55-year-old woman with recurrent rectal cancer comes to the office for preoperative consultation for pelvic exenteration, which will include total vaginal resection and reconstruction with a vertical rectus musculocutaneous flap. Which of the following long-term complications is most likely in this patient?
A) Abdominal hernia B) Pelvic abscess C) Rectovaginal fistula D) Small-bowel obstruction E) Vaginal stenosis |
Vaginal stenosis |
|
|
|
A 25-year-old man is scheduled to undergo soft-tissue coverage and nerve grafting using a seventh intercostal space nerve graft after he sustained a gunshot wound just above the left clavicle. eBetween which of the following structures is the thoracic intercostal nerve located?
A) External intercostal and pectoralis major muscles B) Innermost intercostal and internal intercostal muscles C) Internal and external intercostal muscles D) Parietal pleura and transverse thoracis muscle E) Transverse thoracis innermost intercostal muscles |
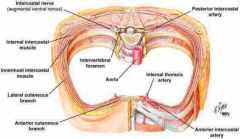
Innermost intercostal and internal intercostal muscles |
|
|
|
In FTM bottom surgeries, which nerve should be used for erogenous sensation? |
pudendal nerve, which terminates in the dorsal nerve of the clitoris |
|
|
|
To maintain innervated muscle flaps during abdominal component separation, what is the most appropriate plane of dissection? |
The plane below the external oblique and above the internal oblique is an avascular plane that will allow for medial advancement of the rectus muscle flaps while protecting the intercostal nerves that run under the internal oblique. |
|
|
|
Bilateral sensate posterior thigh flaps are used for vaginal reconstruction. Which nerve must be included in this procedure? |
Posterior femoral cutaneous |
|
|
|
On analysis of serum and urinary electrolytes, which of the following values is expected to be normal with intrinsic renal failure in this patient? A) BUN:serum creatinine ratio B) Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) C) Urinalysis D) Urinary sodium concentration E) Urine osmolality
|
A) BUN:serum creatinine ratio |
|
|
|
Where are the incisions made for anterior & posterior component separation? |
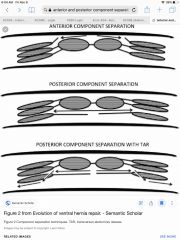
Anterior made lateral to linea semilunaris & posterior is made medial to linea semilunaris. |
|
|

Why would VRaM be used to reconstruct this defect? |
Latissimus and pectoralis flaps in any form are less reliable in their ability to fully cover inferior third sternectomy defects. |
|
|
|
A bilateral component separation technique with incision of the external oblique fascia and muscle lateral to the linea semilunaris and dissection in the plane between the external and internal oblique muscles, and separation of the rectus muscle off of the posterior rectus fascia is performed. At which level can the least amount of advancement of the medial fascial edges be expected? |
Subcostal margin |
|
|
|
During fetal development, failure of the mammary pit to elevate above the skin level results in which deformity? |
Nipple inversion |
|

