![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ovaries
|
are the primary female reproductive organ.
|
|
|
An ovary contains many tiny saclike structures called ________ __________.
|
ovarian follicles
|
|
|
Each follicle consists of an immature egg, called an ________.
|
oocyte
|
|
|
As a developing egg within a follicle begins to ripen or mature, the follicle is now called a ________, or _________ follicle, and the developing egg is ready to be ejected from the ovary, an event called _________.
|
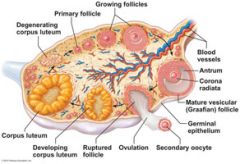
vesicular / Graafian
ovulation Ovulation generally occurs every 28 days. |
|
|
The _______ , or ________ form the initial part of the duct system.
|
uterine / fallopian tubes
hey receive the ovulated oocyte and provide a site where fertilization can occur. Each of the uterine tubes is about 4 inches long and extends medially from an ovary to empty into the superior region of the uterus. |
|
|
The distal end of each uterine tube has projections called _________ that partially surround the ovary.
|
fimbriae
As an oocyte is expelled from an ovary during ovulation, the waving fimbriae create fluid currents that act to carry the oocyte into the uterine tube, where it begins its journey toward the uterus. The oocyte is carried toward the uterus by a combination of peristalsis and the rhythmic beating of cilia. |
|
|
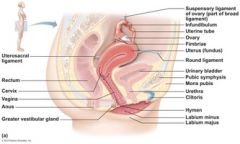
The ________ is a hollow organ that functions to receive, retain, and nourish a fertilized egg.
|
uterus
|
|
|
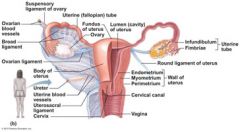
The major portion of the uterus is referred to as the _____. Its superior rounded region above the entrance of the uterine tubes is the _____, and its narrow outlet, which protrudes into the vagina below, is the ______.
|
body
fundus cervix |
|
|
The wall of the uterus is thick and composed of three layers. The inner layer or mucosa is the __________.
|
endometrium
If fertilization occurs, the fertilized egg burrows into the endometrium and resides there for the rest of its development (implantation). When a woman is not pregnant, the endometrial lining sloughs off periodically in response to changes in the levels of ovarian hormones in the blood called menstruation. |
|
|
The __________ is the bulky middle layer of the uterus.
|
myometrium
The myometrium contracts rhythmically during labor to force the baby out. |
|
|
The outermost serous layer of the uterus is the __________.
|
perimetrium
|
|
|
The _______ is a thin-walled tube that provides a passageway for the delivery of an infant and for the menstrual flow to leave the body.
|
vagina
Because it receives the penis and semen during intercourse, it is the female organ of copulation. |
|
|
The female reproductive structures that are located external to the vagina are the external genitalia, also called the ______.
|
vulva
|
|
|
The ___________ is a fatty, rounded area overlying the _____________.
|
mons pubis
pubic symphysis |
|
|
Running posteriorly from the __________ are two enlongated skin folds, the ___________, which enclose two delicate, folds, the _____________.
|
mons pubis
labia majora labia minora |
|
|
The labia majora enclose a region called the ________, which contains the external openings of the ________, followed posteriorly by that of the vagina.
|
vestibule
urethra |
|
|
Two mucus-producing glands, also known as the _____________________, flank or surround the vagina, one on each side.
|
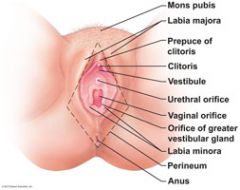
greater vestibular glands
Their secretion lubricates the distal end of the vagina during intercourse. |
|
|
Anterior to the vestibule is the ________ which is composed of sensitive erectile tissue that becomes swollen with blood during sexual excitement.
|
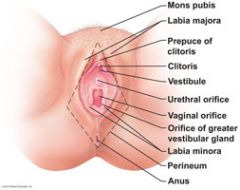
clitoris
|
|
|
Meiosis occurs in the ovaries of a developing female, producing ova, or female gametes, in a process called ___________.
|
oogenesis
|
|
|
At puberty the anterior pituitary gland begins to release ___________________________, which stimulates a small number of primary follicles to grow and mature each month, and ovulation begins to occur.
|
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
|
|
|
These cyclic changes that occur monthly in the ovary constitute the _____________.
|
ovarian cycle
|
|
|
The first meiotic division produces two cells that are very dissimilar in size. The larger cell is a ___________ and the other, very tiny cell body is a ____________.
|
secondary oocyte
polar body |
|
|
Ovulation occurs in response to the release of a second anterior pituitary hormone, _____________________.
|
luteinizing hormone (LH)
In addition to triggering ovulation, LH also causes the ruptured follicle to change into a very different glandular structure, the corpus luteum. |
|
|
If the secondary oocyte is penetrated by a sperm in one of the uterine tubes, the oocyte undergoes the second meiotic division that produces another polar body and the _______.
|
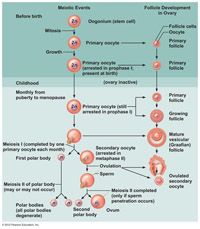
ovum
|
|
|
The events of the uterine, or menstrual, cycle are the cyclic changes that the _________, or mucosa of the uterus, goes through month after month as it responds to changes in the levels of ovarian hormones in the blood.
|
endometrium
|
|
|
Both female cycles are about ____ long. Ovulation typically occurs about day___.
|
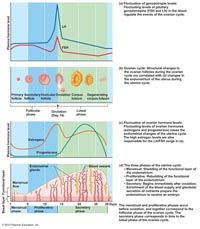
28 days
14 |
|
|
The menstrual cycle has three stages. The first stage occurs during days 1-5, and is called the _________ phase.
|
menstrual
During this interval, the superficial functional layer of the thick endometrial lining of the uterus is sloughing off or detaching from the uterine wall. This is accompanied by bleeding for 3 to 5 days. The detached tissues and blood pass through the vagina as the menstrual flow. |
|
|
The second stage occurs during days 6-14 and is called the ____________ phase.
|
proliferative
Stimulated by rising estrogen levels produced by the growing follicles of the ovaries, the basal layer of the endometrium regenerates the functional layer and the endometrial blood supply increases. The endometrium once again becomes thick and well vascularized. Ovulation occurs at the end of this stage. |
|
|
The third stage occurs during days 15‒28 and is called the ___________.
|
secretory phase
Rising levels of progesterone production by the corpus luteum of the ovary act on the estrogen-primed endometrium and increase its blood supply even more. Progesterone also causes the endometrial glands to increase in size and to begin secreting nutrients into the uterine cavity. These nutrients will sustain a developing embryo until it has implanted. If fertilization does occur, the embryo produces a hormone very similar to LH that causes the corpus luteum to continue producing its hormones. If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum begins to degenerate toward the end of this period as LH blood levels decline. Lack of ovarian hormones in the blood causes the blood vessels supplying the functional layer of the endometrium to go into spasms and kink. When deprived of oxygen and nutrients, those endometrial cells begin to die, which sets the stage for menses to begin again on day 28. |
|
|
As the ovaries become active at puberty and start to produce ova, they also begin to produce ovarian hormones. The follicle cells of the growing and mature follicles produce _________, which cause the appearance of secondary sex characteristics in the young woman.
|
estrogens
Such changes include: enlargement of the accessory organs of the female reproductive system (uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, external genitals); development of the breasts; appearance of axillary and pubic hair; increased deposits of fat beneath the skin in general, and particularly in the hips and breasts; widening and lightening of the pelvis; and onset of menses, or the menstrual cycle. |
|
|
_________ also has metabolic effects including helping to maintain low total blood cholesterol levels and facilitates calcium uptake, which sustains bone density.
|
Estrogen
|
|
|
The second ovarian hormone, ___________, is produced by the glandular corpus luteum.
|
progesterone
As long as LH is present in the blood the corpus luteum produces progesterone, approximately 10 to 14 days. Progesterone also helps maintain pregnancy by inhibiting contraction of the myometrium of the uterus, and helps prepare the breasts for milk production. |
|
|
The ________ are present in both sexes, but they normally function only in women.
|
mammary glands
Because the biological role of the mammary glands is to produce milk to nourish a newborn baby, they are important only when reproduction has been accomplished. |
|
|
Slightly below the center of each breast is a pigmented area, the ______, which surrounds a central protruding _______.
|
areola
nipple |
|
|
Internally each mammary gland consists of ______ lobes that radiate around the nipple. Within each lobe are smaller chambers called _______, which contain clusters of ________________ that produce the milk when a woman is lactating.
|
15 to 25
lobules alveolar glands |
|
|
The alveolar glands of each lobule pass the milk into the _______________, which open to the outside at the nipple.
|
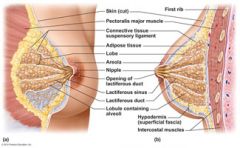
lactiferous ducts
|
|
|
Just deep to the areola, each duct has a dilated region called a _________________ where milk accumulates during nursing.
|
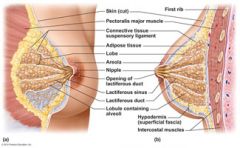
lactiferous sinus
|

