![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
504 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
SW2 is a nonroot switch with a 100-Mbps STP root port. A BPDU received on this port contains a root cost of 38. If SW2 advertises to another switch, what will the root cost be in the BPDU SW2 advertises? a)19 b)57 c)42 d)38 e)None
|
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. Objective: Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1D) |
|
|
An engineer first confirms that a router's interface Fa0/0 is up and working. He then configures that interface with the ip address 10.101.101.101 255.255.255.128 command. The engineer leaves configuration mode, and issues the show ip route command. Which of the following masks will be listed in the output that describes the connected route that exists as a result of this new ip address command? a)/23 b)None of the other answers are correct, because the ip address command will be rejected c)/25 d)/22 e)/26 |
Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
On your lunch break, you discuss networking theory to help yourself prepare for the ICND1 exam. A co-worker makes the following bold statement: "Routers need to only think about Layer 3 when forwarding packets; switches need to think about only Layer 2 when forwarding frames." Which of the following statements are accurate clarifications of or additions to this statement?
|
Answer options D, E , and C are correct. |
|
|
The status of a LAN switch interface shows err-disabled. Which of the following would have caused this status?
|
d
Answer option D is correct.
|
|
|
A user in an Enterprise network sits at her PC and connects to a web server inside the Enterprise by entering the URL http://www.example.com/payroll.html into the browser's window and pressing Enter. Which of the following answers are true about the actions taken by the user's PC? a) if any packets sent by the server are lost in transit, HTTP causes the server to resend the lost data. b) The PC uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to get the files that comprise the requested web page. d) All the text after the // in the URL (in the question) is considered to be the server's hostname and is used in the DNS request to find the server's IP address. |
Answer options B and C are correct. |
|
|
You have received a new Cisco 2960 switch, removed it from the box, and mounted it into a cabinet. You then connect your devices to various ports on the switch and power on the switch. Which of the following answers best describes what will occur? |
a The Cisco 2960 switch comes with all the interfaces ready to go out of the box. There is no need to purchase any power supplies or to activate any products. |
|
|
An aspiring CCNA buys two Cisco routers, along with serial DCE and DTE V.35 cables. She connects a serial interface on each router to one of the two serial cables and connects the two cables. Which of the following commands must she add to the configuration before the serial link will run at 64 Kbps? |
a The clock rate command sets the clock rate on the router with the DCE cable, with the units in bits per second. The bandwidth command sets an administrative value that is used for many purposes, but it does not affect the speeds at which the bits are encoded on the link. The csu-speedcommand does not exist on a router. |
|
|
Two switches are connected using a crossover cable. Using the combinations of configurations listed here (one on each end of the crossover cable on each switch), which of the following are accurate? |
Answer options B and E are correct. |
|
|
On which switch would you always find a root port? |
Answer option D is correct. Chapter: Spanning Tree Protocol Concepts |
|
|
A user at a router CLI interface configuration mode command prompt issues the command ip address 10.1.1.22 255.255.255.0. When does the command take effect? a)After the user exits configuration mode b)As soon as the configuration is saved c)After the user presses Enter d)After the command apply is entered |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
Your organization’s security manager informs you that a station with the MAC address of 00-10-DC-56-EC-96 is causing a broadcast storm. How can you locate this station on your Cisco 2960 switch? a) Issue the show mac address 0010.DC56.DC96 command b) Issue the show address 0010.DC56.EC96 command c) Issue the show mac address-table dynamic address 0010.DC56.EC96 command d) Issue the show mac address-dynamic 0010.DC56.DC96 command |
c |
|
|
DSL operates at which of the following OSI layers? Physical Data link Network Transport Session Application |
ab |
|
|
Bridges and switches help decrease Ethernet congestion by using which two of the following methods? a)Increasing bandwidth b)Separating broadcast domains c)Decreasing logical address space d)Separating collision domains |
DA Segmenting Ethernet networks with a bridge or switch reduces collisions. In addition, each port of a bridge or switch is its own Ethernet segment and does not share bandwidth with the other segments, increasing the bandwidth available across the network. |
|
|
Which of the following are reserved private IP addresses, according to RFC 1918? a) 192.168.10.1 b) 172.29.42.167 c) 169.254.128.222 d) 127.10.172.192 e) 10.127.255.37 |
Answer options E, B , and A are correct. |
|
|
Which of the following is not considered a security benefit of using Internet VPNs? a) Anti-replay b) Data integrity c) Accounting d) Authentication e) Privacy |
c) Accounting |
|
|
What is true about the command switchport nonegotiate? a) Using this command prevents a switchport from being a trunk port. b) When used, if a connected switch is using dynamic desirable or dynamic auto, it will not form a trunk. c) This is on by default. d) This will cause DTP packets to be sent, preventing a trunk from being negotiated. e) It is used on a router to prevent VLAN hopping. |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the FCS field in an HDLC frame? a) Used to indicate to the receiving device that a new frame is arriving b) Used for identifying the type of L3 payload being carried in the frame c) Specifies the destination IP address for the frame d) Used for error detection e) Identifies the destination L2 address for the frame |
Explanation: Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
IP functions at what layer of the OSI Reference Model? a) Transport b) Network c) Physical d) Session |
b |
|
|
Which layer of the OSI Reference Model defines end-to-end delivery of packets? a)The Network layer b)The Session layer c)The Transport layer d)The Link layer e)The Ozone layer |
a Network layer
The Session layer is responsible for starting, controlling, and ending sessions. |
|
|
Which of the following describe a MAC address? a) Layer 1 address b) Layer 2 address c) Layer 3 address d) 32 bits e) 48 bits f) 128 bits |
Explanation: Answer options B and E are correct. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the FCS field in an HDLC frame? A) Identifies the destination L2 address for the frame B) Used for error detection C) Specifies the destination IP address for the frame D) Used for identifying the type of L3 payload being carried in the frame E) Used to indicate to the receiving device that a new frame is arriving |
Answer option B is correct. |
|
|
When PC1 on an Ethernet network sends a packet to a remote PC2 that is on another Ethernet network, and the packet is routed by exactly two routers, connected by an HDLC WAN connection, how many Layer 2 headers will be used in the forwarding of the packet from PC1 to PC2? A)1 B)2 C)3 D)4 E)None. HDLC doesn’t use Ethernet headers. |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
How does the receiver of an HDLC frame know what has been encapsulated within that frame? a) HDLC only encapsulates IPv4 b) Based on the FCS field c) From the IP address (IPv4, IPv6, and so on) d) The Type field in the header e) Based on the Flag field |
Explanation: Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are examples of common Internet access links? a)Leased line b)HDLC c)DSL d)Cable e)PPP |
Answer options A, C , and D are correct. |
|
|
Which protocol finds an unknown Layer 2 address from a known IP address? a)DNS b)ARP c)ICMP d)DHCP |
b |
|
|
Q: What is the correct sequence for TCP connection establishment? a)(1) SYN (2) SYN ACK (3) b)ACK (1) ACK (2) SYN ACK (3) SYN c)There is no sequence because TCP is a connectionless protocol. d)(1) SYN (2) ACK (3) SYN |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct.
|
|
|
Which of the following are characteristics of UDP? |
Answer options A, C , D , E , and F are correct. |
|
|
A user sits at her PC at her desk inside an Enterprise network. She opens a web browser and connects to a website that sits on the Internet. Which of the following answers is most true about the applications and functions used as a result of this user's actions? |
Explanation: Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
An internetwork supports traditional data applications such as web, file transfer, and chat, as well as Voice over IP (VoIP) and Video over IP. Which of the following two statements are most accurate about the impact of these applications on the internetwork? b) A single VoIP call tends to take less bandwidth than a single videoconference or a single person using a web browser to actively browse websites. c) Chat typically requires lower delay than video over IP. d) VoIP traffic needs low delay and low jitter but can tolerate more packet loss than web applications. |
Explanation: Answer options A and B are correct. VoIP traffic typically requires low bandwidth but requires low delay and low jitter (variation in delay) and prefers little or no packet loss. Two-way video has the same requirements, but it generates much more traffic. Web applications use HTTP, which uses TCP, which in turn can recover from lost packets. |
|
|
A user in an Enterprise network sits at her PC and connects to a web server inside the Enterprise by entering the URL http://www.example.com/payroll.html into the browser's window and pressing Enter. Which of the following answers are true about the actions taken by the user's PC? |
Answer options A and D are correct. |
|
|
A switch receives a frame whose source MAC address has not been seen by the switch since the switch was most recently powered on. What is the first thing a switch does in reaction to this frame? |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
Which type of switch processing checks the first 64 bytes of a frame to ensure that a collision has not occurred before forwarding the frame? |
Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Bridges and switches help decrease Ethernet congestion by using which two of the following methods? |
Answer options A and B are correct. |
|
|
A network engineer has logged into router R1, entered enable mode, and entered the following commands in succession: configure terminal After which command does R1 start using 10.1.1.1 as its Fa0/0 IP address? a) After the user enters the first exit command and presses Enter |
b
Answer option B is correct. |
|
|
When you use the banner motd # command on a router or switch, what is the # character used for? |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Two new Cisco 2960 switches are removed from their cardboard boxes. The two switches have been placed into a rack and power applied, but no Ethernet cables are connected yet. Which of the following answers describes the method to get the two switches to communicate using an 802.1Q trunk which requires the least number of steps? |
Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are characteristics of 802.1Q? |
Explanation: Answer options B, C, E , and F are correct. |
|
|
Your customer is having a connectivity problem with his Cisco network and has asked for your assistance. He provided a topology diagram and has given you user mode access through an SSH connection. What could be used to verify that the topology diagram provided is accurate? |
b
Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) can be used to either confirm or fix the documentation shown in a network diagram. Confirming that the network is actually cabled to match the network diagram is a good idea before troubleshooting. |
|
|
Which of the following commands list at least three lines of output per neighbor that describe information about a neighboring Cisco device? |
Answer options C and D are correct. |
|
|
Which command displays the Frame Relay LMI standard in use? |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Given the show ip protocols command output in the exhibit, how many ospf neighbors does this router have?
HICKORY#show ip protocols Routing Protocol is "ospf 1" Sending updates every 0 seconds Invalid after 0 seconds, hold down 0, flushed after 0 Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is Redistributing: ospf 1 Routing for Networks: 0.0.0.0 Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 10.255.255.1 110 00:07:52 Distance: (default is 110)
a)0 b)1 c)2 d)3 |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following IP addresses could be assigned to a host?
|
For 12.150.146.96/27, the number is the subnet number, with a range of valid IP addresses 12.150.146.97 through 12.150.146.126. For 225.16.102.232, the first octet means that the address is a multicast (Class D) address and cannot be assigned to an interface as a unicast IP address. For address 0.102.62.1, the first octet is 0, which is a reserved value. 150.159.216.202/24 is a valid address, with its subnet having a range of valid addresses 150.159.216.1 through 150.159.216.254. 214.122.127.76/26 is also a valid address, in subnet 214.122.127.64, whose range of valid addresses is 214.122.127.65 through 214.122.127.126. |
|
|
When originally designed, a branch office needed only 6 IP addresses, and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.248 was used. Two more devices need IP addresses on that LAN. Thankfully VLSM was properly and carefully implemented and there are several more subnets available to accommodate this new growth. Which of the following answers would work for adding these two new hosts to the LAN? |
Explanation: Answer options B and C are correct. |
|
|
When using static routes, you type in ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0, two options are available to specify the next hop as the next parameters in the command. Select the two valid choices. |
Answer options A and B are correct. |
|
|
You would like to limit telnet connection into your router to a range of IP address. You have created the access list numbered 99, how do you apply this ACL to limit telnet connections? |
Answer option A is correct. The correct command to apply an ACL to VTY interfaces is access-class under the VTY interfaces. |
|
|
NAT translates a private address 192.168.1.1 to a public IP address 12.150.146.100. How would 192.168.1.1 be described? |
Answer options B and C are correct. |
|
|
For a particular NAT implementation, a private address 192.168.1.1 should always be translated with a 1:1 mapping to IP address 12.150.146.100. Which command accomplishes this? |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
PC1 and PC2 reside on the same VLAN. Both hosts use IPv6. When PC1 pings PC2’s IPv6 address, PC1 does not know PC2’s MAC address. How does PC1 learn PC2’s MAC address? |
Explanation: Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
Your organization’s security manager informs you that a station with the MAC address of 00-10-DC-56-EC-96 is causing a broadcast storm. How can you locate this station on your Cisco 2960 switch? |
Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are functions provided by Spanning Tree Protocol?
|
Explanation: Answer options A, C, and E are correct. By blocking on specific ports that would otherwise be parallel Layer 2 paths, STP prevents Layer 2 loops, thus preventing broadcast storms, preventing MAC table instability due to the a single-source Layer 2 address showing up on multiple different ports, and preventing multiple copies of a single frame from being forwarded (because spanning tree is blocking on enough ports to stop the forwarding of frames on parallel paths). STP does not use any TTL mechanism in a frame header (there is not one there); that is why it must do blocking on Layer 2 ports where an otherwise parallel path would be. STP performs blocking on Layer 2 ports, not Layer 3 ports. |
|
|
If two nonroot switches were connected together in a three-switch topology, the connection between the two switches would result in a parallel path. Which of the following would occur in STP?
|
Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
If spanning tree is disabled, what are the potential issues with a redundant Layer 2 network design? b) TTL expiring c) MAC database instability d) Duplicate IP addresses e) Multiple (duplicate) frames being seen |
Answer options A, C, and E are correct. |
|
|
Which of the following ways could remove the need for spanning tree?
|
Answer options A and C are correct. |
|
|
When configuring interfaces to be part of the same EtherChannel, which of the following should you configure identically?
|
Answer options A, B, C, and D are correct. |
|
|
When a computer issues a ping request, and gets a ping reply, which protocol is being used to communicate the reachability information? |
Explanation: Answer option E is correct. Ping uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). Ping uses ICMP, not TCP, UDP, ARP, or HTTP. |
|
|
What is one of the main drawbacks to using autosummarization? b) Autosummarization uses requires a high powered router c) Autosummarization only works when using two or more protocols d) Autosummarization requires networks to be contiguous |
Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following represents the total cost between the device forwarding a BPDU and the switch in STP that has the lowest BID? b) Sender’s bridge ID c) Sender’s root cost d) Hello timer e) Forward delay |
Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
PortFast enables you to set ports on your switch to be placed in a forwarding state once the host device is plugged in. What Cisco feature enables you to detect switches or any other networking devices that could cause problems on links with PortFast enabled?
|
Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
When configuring a serial interface, what is the purpose of the bandwidth command? A)It tells the router how fast to physically encode bits out the serial interface. b)It defines the bandwidth setting that the router advertises in CDP updates sent out that interface. c)Its only purpose is to document the link's speed. d)It is used in EIGRP to calculate metrics. |
Answer option D is correct. |
|
|
What is the correct order for the spanning-tree algorithm? A: Elect a designated port for each segment. |
Answer option E is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are valid types of STP?
|
Answer options B, C, D, and E are correct. |
|
|
Your security manager has asked you to implement a policy that will tell your switch to only accept frames sent from MAC address 0010.DC56.EC96 on a particular switch port. Which of the following command(s) on a 2960 switch will be part of the correct configuration? b) switchport port-security 0010.DC56.EC96 c) port-security mac-address 0010.DC56.EC96 d) port-security 0010.DC56.EC96 |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following is true about PortFast and BPDU Guard? b) PortFast enables fast transition to the “root port” state, in the event of a topology change. c) If a BPDU is seen on a port, PortFast quickly shuts down that port. d) If a BPDU is seen on a port, BPDU Guard filters that packet from entering the switch and continues to allow normal transit traffic. e) BPDU Guard shuts down a port if a BPDU is seen on that port. |
Answer option E is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following would be in a forwarding state in STP? a) All the root ports on the root switch |
Answer options B, C, and D are correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are LACP modes that you can use with EtherChannel configuration? b) On c) Desirable d) Active e) Passive |
Explanation: Answer options D and E are correct. |
|
|
Which of the following are true? b) Trunks carry traffic for multiple VLANs only if those VLANs exist on the switch and are allowed on the trunked interfaces. c) It is a recommended practice to allow DTP to dynamically negotiate trunks. d) A native VLAN mismatch will be automatically adjusted when DTP is used. e) Multiple Layer 2 interfaces can be bound together to increase the overall throughput. |
Explanation: Answer options B and E are correct. Trunks carry traffic for multiple VLANs only if those VLANs exist on the switch and are allowed on the trunked interfaces. EtherChannel allows the bonding of multiple interfaces together for one larger logical interface. A VLAN is a Layer 2 broadcast domain, although normally a single IP (Layer 3) subnet is associated with each Layer 2 VLAN. DTP is dangerous because it could allow an attacker to dynamically negotiate a trunk with a switch, and as therefore it is recommended that it be turned off. A VLAN mismatch is not automatically adjusted by DTP and should be the same on both ends of a trunk. |
|
|
Which of the following answers list either a component or function that is typically required for a high-speed Internet connection, using a cable company, from a home or small office?
|
Explanation: Answer options A, B, and D are correct. Most high-speed Internet connections from the home include a router and either a cable or DSL modem, often contained in a single device. Most connections use Network Address Translation and a LAN switch to allow multiple devices to connect to the home network. Most home office Internet connections do not use a router with a serial interface; these interfaces typically connect Enterprise routers to serial links or Frame Relay access links. |
|
|
Which of the following protocols are examples of TCP/IP transport layer protocols? (Choose |
fd |
|
|
Which of the following protocols are examples of TCP/IP data link layer protocols? (Choose
|
ag |
|
|
The process of HTTP asking TCP to send some data and making sure that it is received |
b |
|
|
The process of TCP on one computer marking a TCP segment as segment 1, and the receiving
|
b |
|
|
The process of a web server adding a TCP header to the contents of a web page, followed by a. Data encapsulation |
a |
|
|
Which of the following terms is used specifically to identify the entity created when |
d |
|
|
Which OSI layer defines the functions of logical network-wide addressing and routing? |
c |
|
|
Which OSI layer defines the standards for cabling and connectors? |
a |
|
|
Which of the following terms are not valid terms for the names of the seven OSI layers? |
ce |
|
|
TCP/IP application layer protocols provide |
TCP/IP application layer protocols provide services to the application software running on a computer. The application layer does not define the application itself, but it defines services that applications need. |
|
|
Who and when created the first browser? |
HTTP did not exist until Tim Berners-Lee created the first web browser and web server in the early 1990s |
|
|
TCP/IP Transport Layer
protocols and usage |
TCP/IP transport layer includes a smaller number of protocols. The two most commonly used transport layer protocols are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). |
|
|
TCP/IP update |
Application Transport Network Data Link Physical
|
|
|
same-layer interaction on different computers |
the two computers use a protocol (an agreed-to set of rules) to communicate with the same layer on another computer. The protocol defined by each layer uses a header that is transmitted between the computers to communicate what each computer wants to do. Header information added by a layer of the sending computer is processed by the same layer of the receiving computer |
|
|
Adjacent-layer interaction on the same computer |
On a single computer, one layer provides a service to a higher layer. The software or hardware that implements the higher later requests that the next lower layer perform the needed function. |
|
|
NDP |
Active Virtual Gateway (AVG) GLBP elects one AVG (Active Virtual Gateway) for each group.
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) acts as a replacement for several IPv4 protocols, including ARP, as well as providing several new functions for IPv6. ARP does not exist in IPv6. |
|
|
TCP/IP Network Layer
Protocols and purpose |
The application layer includes many protocols. The transport layer includes fewer, most notably, TCP and UDP. The TCP/IP network layer includes a small number of protocols, but only one major protocol: the Internet Protocol (IP). In fact, the name TCP/IP is simply the names of the two most common protocols (TCP and IP) separated by a /. |
|
|
TCP/IP Link Layer (Data Link Plus Physical)
Protocols and purpose |
The TCP/IP model’s original link layer defines the protocols and hardware required to deliver data across some physical network. The term link refers to the physical connections, or links, between two devices and the protocols used to control those links. Host or router then uses link-layer details to send that packet to the next host/router. |
|
|
segment, packet, and frame and their layers |
segment for the transport layer, packet for the network layer, and frame for the data link layer |
|
|
osi vs tcp/ip |
OSI 7.Application 6.Presentation 5.Session 4.Transport 3.Network 2.Data Link 1.Physical
TCP/IP 5-7.Application 4.Transport 3.Internet 1-2 Link (Data Link & Physical) |
|
|
Which term refers to the headers and possibly trailers defined by the TCP/IP data link layer, and the data encapsulated following that header? a)Bits b)Frame c)Packet d)Segment |
b |
|
|
Which of the following terms is used specifically to identify the entity created when encapsulating data inside data link layer headers and trailers? B. Segment C. Chunk D. Data E. Packet |
a |
|
|
The OSI Layer 3, the network layer, provides the following? B. This layer defines three main features: logical addressing, routing (forwarding), and path determination. C. The rules that determine when a device can send data over a particular medium. D. Focuses on issues related to data delivery to another computer (for example, error recovery and flow control). |
c Layer 3 of the OSI model deals primarily with IP addressing and routing. |
|
|
Each answer lists two types of devices used in a 100BASE-T network. If these devices were connected with UTP Ethernet cables, which pairs of devices would require a straight-through cable? (Choose three answers.) A. Hub and switch B. Router and hub C. Wireless access point (Ethernet port) and switch D. PC and router E. PC and switch |
cbe Routers, wireless access point Ethernet ports, and PC NICs all send using pins 1 and 2, whereas hubs and LAN switches transmit on pins 3 and 6. Straight-through cables connect devices that use opposite pin pairs for sending, because the cable does not need to cross the pairs. |
|
|
Which of the following is not true of DSL technology? B. Replaces leased lines C. Relatively short physical link D. Uses single-pair telephone line |
c |
|
|
Encapsulation happens differently when using EoMPLS. B. TRUE |
B |
|
|
Which of the following Internet access links are used by many businesses? A. DSL B. Leased line C. Ethernet D. Cable |
b |
|
|
Which of the following is not true of DSL technology? B. Uses single-pair telephone line C. Relatively short physical link D. Replaces leased lines |
d |
|
|
Which of the following are functions of OSI Layer 3 protocols? (Choose two answers.) B. Arbitration C. Error recovery D. Logical addressing E. Physical addressing |
Answer options D and A are correct. |
|
|
Imagine a network with two routers that are connected with a point-to-point HDLC serial link. Each router has an Ethernet, with PC1 sharing the Ethernet with Router1 and PC2 sharing the Ethernet with Router2. When PC1 sends data to PC2, which of the following is true? B. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, never to be used again. C. Router1 encapsulates the Ethernet frame inside an HDLC header and sends the frame to Router2, which extracts the Ethernet frame for forwarding to PC2. D. Router1 strips the Ethernet header and trailer off the frame received from PC1, which is exactly re-created by Router2 before forwarding data to PC2. |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. |
|
|
PC1 and PC2 are on two different Ethernet LANs that are separated by an IP router. PC1’s IP address is 10.1.1.1, and no subnetting is used. Which of the following addresses could be used for PC2? (Choose two answers.) b) 10.200.200.1 c) 10.2.2.2 d) 10.1.1.2 e) 1.1.1.1 f) 225.1.1.1 |
Answer options A and E are correct. |
|
|
The address ranges for usable IP network addresses for Class C are 192 - 224. b) FALSE |
b |
|
|
What are the correct steps of router forwarding logic? b) Compares the IP packet's destination address to the IP routing table c) Uses the FCS field to check for errors d) Encapsulates the IP packet inside the data-link header and trailer |
Explanation: Answer options B, C, D, and A are correct. These are the steps to routing logic. |
|
|
Which of the following does not use UDP? B. DNS |
Answer option A is correct. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a part of a URL?
|
Answer option B is correct.
|
|
|
Which of the following flag fields are used in connection establishment headers? (Select all that apply.) |
Explanation: Answer options D and A are correct.
|
|
|
An engineer had formerly configured a Cisco 2960 switch to allow Telnet access so that the switch expected a password of mypassword from the Telnet user. The engineer then changed the configuration to support Secure Shell. Which of the following commands could have been part of the new configuration? (Choose two answers.) |
BC SSH requires the use of usernames in addition to a password. Using the username global command would be one way to define usernames (and matching passwords) to support SSH. The vty lines would also need to be configured to require the use of usernames, with the login local vty subcommand being one such option. The transport input ssh command could be part of a meaningful configuration, but it is not a global configuration command (as claimed in one wrong answer). Likewise, one answer refers to theusername command as a command in vty config mode, which is also the wrong mode. |
|
|
An engineer’s desktop PC connects to a switch at the main site. A router at the main site connects to each branch office through a serial link, with one small router and switch at each branch. Which of the following commands must be configured on the branch office switches, in the listed configuration mode, to allow the engineer to telnet to the branch office switches? (Choose three answers.) |
ADF To allow access through Telnet, the switch must have password security enabled, at a minimum using the password vty line configuration subcommand. Additionally, the switch needs an IP address (configured under one VLAN interface) and a default gateway when the switch needs to communicate with hosts in a different subnet. |
|
|
Which of the following describes a way to disable IEEE standard autonegotiation on a 10/100 port on a Cisco switch? |
Answer option F is correct. |
|
|
Straight-through cable |
10BASE-T and 100BASE-T use two pair of wires in a UTP cable. A straight-through cable works correctly when the nodes use opposite pairs for transmitting. 1 to 1 2 to 2 3 to 3 6 to 6 |
|
|
Crossover Cable Pinout |
The crossover cable pinout crosses the pair at the transmit pins on each device to the receive pins on the opposite device. 1 to 3 2 to 6 3 to 1 6 to 2 |
|
|
Choosing the Right Cable Pinouts |
Crossover cable: If the endpoints transmit on the same pin pair
|
|
|
PC NICs, Routers and WAPs transmit on pairs |
1,2 |
|
|
Hubs and Switches transmit on pair |
3,6 |
|
|
Gigabit Ethernet crossover calbe |
cable crosses 1 to 3 2 to 6 but it also crosses 4 to 7 5 to 8 |
|
|
Ethernet Frame Format |
Preamble - 7 (synchronization) SFD - 1 (signifies that the next byte begins the destination MAC address field) Destination - 6 Source - 6 Type - 2 - (defines the type of protocol listed inside the frame) Data and Pad - 46/1500 - (holds L3PDU) FCS - 4 - (provide a method for the receiving NIC to determine whether the frame experienced transmission error) |
|
|
HDLC header field |
HDLC - Ethernet equivalent Flag - Preamble Address - Destination Address Type - Type FCS - FCS |
|
|
show port-security interface fastEthernet 0/1 (scr) |
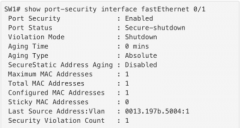
the cmd shows that the interface is in a secured-shutdown state which means that the interface has been disabled because of port security. |
|
|
What is the longest copper cable length supported by the IEEE 802.3u FastEthernet standard? |
100 Meters |
|
|
What is the physical rate of transmission of a T1 leased line? |
d) |
|
|
Which of the following commands might you see associated with the router CLI, but not with |
a |
|
|
Cut-through switching |
Cut-through switching One of three options for internal processing on some models of Cisco LAN switches in which the frame is forwarded as soon as enough of the Ethernet header has been received for the switch to make a forwarding decision, including forwarding the first bits of the frame before the whole frame is received. |
|
|
Fragment-free switching |
Fragment-free switching One of three internal processing options on some Cisco LAN switches in which the first bits of the frame can be forwarded before the entire frame is received, but not until the first 64 bytes of the frame are received, in which case, in a well-designed LAN, collision fragments should not occur as a result of this forwarding logic. |
|
|
Store-and-forward switching
|
Store-and-forward switching One of three internal processing options on some Cisco LAN switches in which the Ethernet frame must be completely received before the switch can begin forwarding the first bit of the frame. |
|
|
Which of the following devices would be in the same broadcast domain as PC1? (Choose three answers.)
|
ABD
|
|
|
Which of the following devices would be in the same collision domain as PC1? |
c |
|
|
A Cisco LAN switch connects to three PCs (PC1, PC2, and PC3), each directly using a cable that supports Ethernet UTP speeds up through 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps). PC1 uses a NIC that supports only 10BASE-T, while PC2 has a 10/100 NIC, and PC3 has a 10/100/1000 NIC. Assuming that the PCs and switch use IEEE autonegotiation, which PCs will use half-duplex? |
c |
|
|
Which of the following statements best describes what a switch does with a frame destined for an unknown unicast address?
|
|
|
|
Which of the following comparisons does a switch make when deciding whether a new MAC address should be added to its MAC address table? |
D
|
|
|
|
B
|
|
|
PC1, with MAC address 1111.1111.1111, is connected to Switch SW1’s Fa0/1 interface. PC2, with MAC address 2222.2222.2222, is connected to SW1’s Fa0/2 interface. PC3, with MAC address 3333.3333.3333, connects to SW1’s Fa0/3 interface. The switch begins with no dynamically learned MAC addresses, followed by PC1 sending a frame with a destination address of 2222.2222.2222. If the next frame to reach the switch is a frame sent by PC3, destined for PC2’s MAC address of 2222.2222.2222, which of the following are true? (Choose two answers.) |
CD
|
|
|
Which of the following statements describes part of the process of how a LAN switch decides to forward a frame destined for a broadcast MAC address? |
E A switch floods broadcast frames, multicast frames (if no multicast optimizations are enabled), and unknown unicast destination frames (frames whose destination MAC address is not in the MAC address table).
|
|
|
Which of the following Ethernet standards support a maximum cable length of longer than 100 meters? (Choose two answers.) |
Answer options C and A are correct. The IEEE Ethernet standards support 100-meter links when using UTP cabling. Most standards that use fiber-optic cabling, like the standards in the two correct answers, use lengths longer than 100 meters. |
|
|
show port-security interface fastEthernet 0/2
(up and running) |
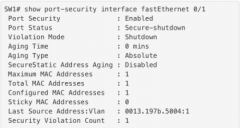
|
|
|
show port-security violation { protect | restrict | shutdown } |
switch can be configure to sue one of three actions when a violation occurs. All 3 cause the switch to discard the offending frame
Protect - discard traffic, no SNMP log, no disabling of interface Restrict - discard traffic, restrict, sends SNMP log message, no disabling of interface Shutdown - discard traffic, restrict, sends SNMP log message, disables of interface |
|
|
cmd to prevent VLAN trunking by making a port a nontrunking interface |
switchport mode access |
|
|
cmd to assign port o an unused VLAN |
switchport access vlan |
|
|
cmd to set the native VLAN to not be VLAN 1, but to instead be an unused VLAN |
switchport trunk native vlan |
|
|
interface configuration basics (scr) |
|
|
|
interface range command |
the interface range FastEthernet
Emma# configure terminal |
|
|
Configuring Port Security (steps) |
Step 1. Make the switch interface either a static access or trunk interface, using the switchport Step 6. (Optional) Tell the switch to “sticky learn” dynamically learned MAC addresses with the switchport port-security mac-address sticky interface subcommand. |
|
|
SW1# show running-config
(Variations on Port Security Configuration) |
(Lines omitted for brevity) |
|
Q: As a Network Administrator for uCertify Inc, you have made the basic configurations on routers. You need to configure each router with the OSPF protocol. Run the appropriate commands. (Priority no. = 2, Area = 0)
|
Explanation: Run the following set of commands to configure the OSPF protocol on each router: R1
R2
|
|
|
Informal IEEE Standard Name 10Base-T 100Base-T 1000Base-LX 1000Base-T 10GBase-T What are the formal IEEE standard names |
10Base-T - 802.3 100Base-T - 802.3u 1000Base-LX - 802.3an 1000Base-T - 802.3z 10GBase-T - 802.3ab |
|
|
port security sequence of commands |
switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access switchport port-security switchport port-security violation restrict switchport port-security mac-address 0090.ABCD.EF10 |
|
|
show interface fa0/1 (for interface that has shutdown issued on it). |
FastEthernet0/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down (disabled)
|
|
|
No speed / No duplex (scr) |
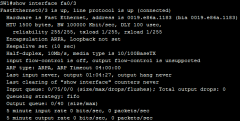
|
|
|
show interface description (scr) |
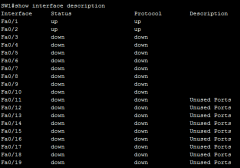
|
|
|
Show vlan (scr) |
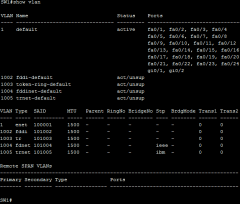
|
|
|
show ip route (scr) |
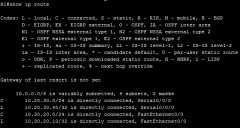
|
|
|
show inteface brief (scr) |
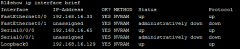
|
|
|
Configure the global command that tells the router to not attempt to ask a DNS for name resolution. What command did you enter? |
no ip domain-lookup |
|
|
show ip route
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
What are the two numbers in brackets? |
The output lists [1/0], where 1 is the administrative distance and 0 is the metric. |
|
|
show ip route (scr) |
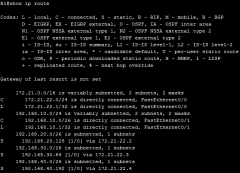
|
|
|
show ip route static |
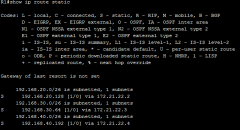
|
|
|
show cdp neighbor |
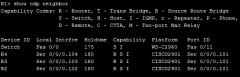
|
|
|
show ip route connected |
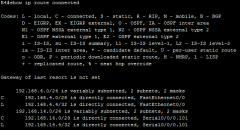
|
|
|
name access list |
ip access-list extended BlockUDP |
|
|
In what modes can you execute the command show mac address-table? a)User mode b)Enable mode c)global configuration mode d)interface configuration mode
|
ab |
|
|
Currently, besides the ports assigned to VLAN 2 and VLAN 3, the rest of the switch is in its default configuration. What would be the result of assigning ports Fa0/13 through Fa0/24 on this switch to a new VLAN 4?
|
Answer option C is correct. On a new switch, creating and assigning existing ports to a new VLAN, results in a single new broadcast domain (VLAN) on that switch.Each VLAN is a separate broadcast domain, so when we add one VLAN, we get one new Layer 2 broadcast domain. The 12 ports already existed on the switch as 12 collision domains before the new VLAN and assignment of any ports to the VLAN. |
|
|
When a router first powers on, which of the following four steps is performed first? B. The router performs a power-on self-test (POST) to discover the hardware components and verify that all components work properly. C. If the bootstrap program loaded the IOS, IOS finds the configuration file (typically the startup config file in NVRAM) and loads it into RAM as the running config file. D. The router copies a bootstrap program from ROM into RAM, and runs the bootstrap program. |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. If the router fails the POST, it will stop the boot process until the cause of failure has been repaired. |
|
|
The shutdown option actually puts the interface in an error disabled (err-disabled) state, making it unusable. An interface in the err-disabled state requires that someone _____. A. enter the shutdown command B. enter the shutdown command followed by the no shutdown command C. do nothing. The port will automatically become usable again after 30 seconds. D. enter the no shutdown command |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct. The error state can only be resolved by manually shutting the interface down and then bringing it back up again.
|
|
|
Which statement is correct for Cisco Layer 2 access switch interfaces by default? B. VLANs must be configured before devices can be connected to the switch. C. All interfaces are assigned to the one VLAN. D. There are no VLANs configured on the switch. |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct. By default, a Cisco switch has all its interfaces in the same broadcast domain, known as VLAN 1. |
|
|
The banner login command is shown when? |
The login banner is designed to be the permanent banner, as opposed to the MOTD (Message of the Day). |
|
|
Switch ports are in full duplex by default. |
FALSE
Switch ports are by default in the autonegotiate state. |
|
|
The encryption type used by the service password-encryption command, as noted with the "7" in the password command, refers to one of several underlying password encryption algorithms. Type 7, the only type used by the service password encryption command, is a weak encryption algorithm, and the passwords can be easily decrypted. |
TRUE It provides low-level encryption. |
|
|
steps required to enable the switchport security |
router>enable router>config terminal router(config)#interface router(config-if)#switchport port-security |
|
|
add VLANs to the list of allowed VLANs on a virtual Ethernet interface trunk port |
switch# configure terminal switch(config)# interface vethernet 1 switch(config-if)# switchport trunk allowed vlan 5-15 switch(config-if)# |
|
|
what command will you use to encrypt the password |
If you have the service password-encryption command enabled, the password you enter is encrypted. When you display it with the more system:running-config command, it is displayed in encrypted form. If you specify an encryption type, you must provide an encrypted password—an encrypted password you copy from another router configuration The service password-encryption command does not provide a high level of network security |
|
|
To create a new privilege level and associate commands with that privilege level, use the following commands in beginning in global configuration mode: |
Router(config)# privilege modelevel level command-string Router(config)# enable secret level level {0 |5} password-string Router(config)# exit ------------------------- Configures the specified privilege level to allow access to the specified command
Sets the password for the specified privilege level. This is the password users will enter after entering the enable level command to access the specified level. •0 indicates an unencrypted password string follows; 5 indicates an encrypted password string follows.
Exists global configuration mode and returns to EXEC mode.
(Optional) Saves the configuration to the startup configuration file in NVRAM. Note The do keyword allows execution of EXEC commands in configuration mode. |
|
|
steps required to enable the switchport security feature on an interface |
router>enable router#configure terminal router(config)#interface interface router(config-if)#switchport port-security
1. Enter privileged mode 2. Enter global configuration mode 3. Enter interface configuration mode 4. Enable the switchport security feature |
|
|
c(default : 1)router(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum valueonfigure the maximum number of MAC addresses allowed on a switchport Configure the switchport violation mode (default : shutdown)router(config-if)#switchport port-security violation {protect | restrict | shutdown} |
router(config-if)#switchport port-security maximum value
router(config-if)#switchport port-security violation {protect | restrict | shutdown} |
|
|
steps required to configure a static MAC address: |
router#configure terminal router(config)#interface interface router(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address mac-address |
|
|
steps required to enable the use of sticky learning on a switchport: |
router#configure terminal router(config)#interface interface router(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky |
|
|
enable the use of the switchport security feature on ports f0/1 and f0/2, statically configure the 0000.1111.2222 MAC address on the f0/1 switchport and enable sticky learning on the f0/2 switchport. |
router#configure terminal router(config)#interface f0/1 router(config-if)#switchport port-security router(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address 0000.1111.2222 router(config)#interface f0/2 router(config-if)#switchport port-security router(config-if)#switchport port-security mac-address sticky |
|
|
show spanning-tree vlan 2 (scr) |
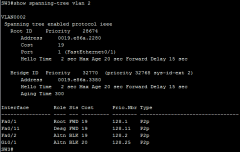
|
|
|
Configure interfaces into Etherchannel group 1 by issuing the |
channel-group 1 mode on |
|
|
how etherchannel 1 summary (scr)
|
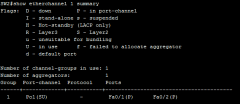
|
|
|
show spanning-tree bridge |
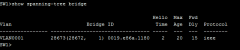
|
|
|
Lower cost of a spanning tree protocol on an interface |
spanning-tree vlan 2 cost 1 |
|
|
configuration of the PortFast feature of ports connected to some of the hosts.
|
configure terminal interface fa0/11 spanning-tree portfas |
|
|
show interface trunk |
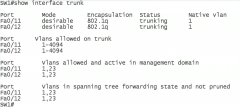
|
|
|
Change the cost of this interface by issuing |
ip ospf cost 14 |
|
|
designated port |
Many switches can attach to the same Ethernet segment, but in modern networks, normally two switches connect to each link. The switch with the lowest root cost, as compared with the other switches attached to the same link, is placed in forwarding state. That switch is the designated switch, and that switch’s interface, attached to that segment, is called the designated port (DP). |
|
|
the default priority for switches in STP is |
32768 |
|
|
The switch that has the lowest STP cost will become the __________ switch for a specific segment. 1. Root 2. Designated 3. Primary 4. Forwarding |
4 |
|
|
Which Cisco IOS command is used to display all switch interfaces, their current statuses, and the current operating mode? 1. show interfaces status 2. show interfaces 3. show ip interface brief 4. show vlan |
a |
|
|
What is the only way an engineer can alter the value of the bridge ID? 1. Modify the main switch MAC address. 2. Configure the bridge ID under STP configuration mode. 3. Swap out the main switch network interface card. 4. Configure the STP priority |
4 |
|
|
What is the default base STP priority used on a Cisco switch? 1. 8192 2. 16,384 3. 32,768 4. 1024 |
3 |
|
|
Which Cisco IOS command would be used on a switch to identify all the interfaces that are enabled with port security? 1. show switchport port-security 2. show port security 3. show interfaces 4. show port-security |
4 |
|
|
Which Cisco IOS command specifically lists each VLAN and all interfaces assigned to that VLAN, not including VLAN trunks? 1. show interface all switchport 2. show mac address-table dynamic 3. show vlan all 4. show vlan 5. show interfaces vlan 6. show cam dynamic
|
4 |
|
|
You are troubleshooting IP connectivity. After pinging from a host computer, you realize you can ping some hosts and not others on the same subnet. What is a potential cause? 1. ICMP redirects are disabled. 2. IP ACLs are preventing it. 3. The default gateway is not functioning. 4. The subnet mask is misconfigured. 5. None of the above. |
2 |
|
|
When diagnosing a problem where a host can't reach a remote host, you find that you can't ping the first router in the path, and the first router can't ping the host initiating the connection. Which is not part of a reasonable plan for first-step diagnostics? 1. Investigate Layer 1 issues with the LAN: cabling, powered-off device, and so on. 2. Investigate any Layer 2 issues: VLAN configuration, trunk mismatches, and so on. 3. Check the IP configuration on both the host the and router. 4. Use a host on a remote subnet and use a tracert to determine the path. 5. Ensure that the router's interface is in an up/up state. |
4 |
|
|
What is the most likely problem if a ping fails when using a device's hostname but not when using the device's IP address?
1. ARP |
2 |
|
|
show flash |

|
|
|
Which term refers to the headers and possibly trailers defined by the TCP/IP transport layer, and the data encapsulated following that header? 1) bits 2) segment 3) packet 4) frame |
2 |
|
|
What protocols are controlled by the TCP/IP link layer (choose 2)? 1) Ethernet 2) HTTP 3) IP 4) PPP |
1,4 |
|
|
Q: Which of the following flag fields are used in connection establishment headers? (Select all that apply.)
1)SYN 2)FIN 3)ACK 4)TCP |
1,2 |
|
|
1000Base-LX 1000Base-ZX |
1000Base-LX Single-mode 5km 1000Base-ZX 70 km lengh |
|
|
EoMPLS
MPLS
DSLAM |
Ethernet over MPLS
Multiprotocol Label Switching
DSL Access Multiplexer |
|
|
application layer |
this layer provides an interface between the communications software and any application that needs to communicate outside the computer on which the application resides. It also define process for user authentication. |
|
|
Presentation layer. |
define and negotiate data formats. Encryption is defined here |
|
|
Session layer. |
defines how to start, control, and end conversations. Includes control and management of multiple bidirectional messages so that the application can be notified if only some of a series of messages are completed |
|
|
Transport layer. |
Multiplexing using ports Error recovery Flow control using windowing Connection establishment and termination Ordered data transfer and data segmentation |
|
|
Network layer. |
logical addressing routing path determination |
|
|
Data link layer |
Defines the rules that determine when a device can send data over a particular medium. Data link protocols also define the format of a header and trailer that allows devices attached to the medium to successfully send and receive data. |
|
|
Physical layer. |
Defines standards from otehr organization |
|
|
Merge replication
Merging two companies
|
1) Starts with a snapshot of the two companies (starts with a snapshot of the publisher)
2) Than continues with triggers to track changes (changes are tracked with triggers)
3) sudden surprise at the subscriber are pushed to view during the merger (Changes at the subscriber are synced to the publisher)
4) yes multi merge is allowed
(Multiple subscribers are allowed)
5) when conflicts occur they must be resolved (conflicts may occur and when they do you need the ability to detect and resolve them) |
|
|
Limitations when reverting a database from a DB snapshot
Single person dating - Start To Yield and Update Filestream
|
1) single
(only a single DB snapshot can exist for source DB)
2) total access to all catalogs of people (full text catalogs on the source DB must be dropped and then re-created after the revert completes)
3) yesterday's log is useless
(Because the transaction log is rebuild transaction log chain is broken)
4) unaccessible are all swinger clubs
(Both the source DB and the DB snapshot are offline during the revert)
5) file stream
(The source DB cannot be set up with Filestream)
|
|
|
Cut-through processing |
The switch starts sending the frame out the output port as soon as possible |
|
|
Fragment-free processing |
waits to receive the first 64 bytes of a frame and then sends is forward |
|
|
Which of the following is true about the Ethernet FCS field? 1)it is 2 bytes long 2)Ethernet uses FCS for error recovery 3)It is used for encryption 4)It resides in the Ethernet trailer, not the Ethernet header |
4 |
|
|
In the cabling for a leased line, which of the following typically connects to a four-wire line provided by a telco? 1)CSU/DSU 2)Router serial interface with internal transceiver 3)Switch serial interface 4)Router serial interface without internal CSU/DSU |
1) |
|
|
which of the following is not true of DSL technology 1)Replaces leased lines 2)Creates high-speed WAN links 3)Uses single-pair telephone line 4)relatively short physical line |
1 |
|
|
the CSU/DSU device is used in ______ 1) WAN connectivity 2)LAN and WAN connectivity 3)None of the above 4)LAN connectivity |
2 |
|
|
What is the purpose of ARP? 1) Request MAC address for known IP address 2) None of the above 3) Request IP address for known MAC address 4) test for connectivity |
1 |
|
|
Which of the following is not a goal of a routing protocol? 1) To notice when routes in the table are no longer valid 2) To dynamically learn notes 3) To place the fist route in the routing table 4) To prevent routing loops |
3 |
|
|
Which of the following is not a function of the transport layer? 1) flow control 2) connection establishment 3) multiplexing 4) data fragmentation |
4 |
|
|
Which of the following are typical functions of TCP (choose 4)? 1) Flow control (windowing) 2) Error recovery 3) Multiplexing using port numbers 4) Eouting 5) Encryption 6) Ordered data transfer |
1 2 3 6 |
|
|
A switch is cabled to a router whose host name is Hannah. Which of the following CDP cmd could identify Hannah's model and hardware? 1) show neighboor Hannah 2) show cdp 3) show cdp interface 4) shid cdp neighboors 5) show cdp entry Hannah 6) show neighboors |
4,5
The show cdp neighbors cmd lists one line of output per neighbor. However, it does list the platform information of the neighbor, which typically includes the hardware model number.
show cdp entry hannah commands lists a group of messages about the neighboring router, including more detail about the hardware model and the IOS version |
|
|
show cdp neighbor (def) |
show cdp neighbor
this cmd lists one line of output per neighbor. However, it does list the platform information of the neighbor, which typically includes the hardware model number |
|
|
show cdp entry Hannah (def) |
show cdp entry hannah
this cmd lists a group of messages about the neighboring router, including more detail about the hardware model and the IOS version |
|
|
On a cisco catalyst switch, you issue a show mac-address-table cmd. Which of the following answers list information you would likely see in most lines of output? (2) 1) A Vlan ID 2) An IP address 3) A MAC address 4) Type |
1,3 |
|
|
show mac address-table (cmd def) |
show mac address-table cmd
Lists all entries in the siwtch's MAC address table, including dynamically learned and statically defined addresses. |
|
|
Which of the following cmds list the MAC address table entries for MAC addresses configure by port security (2) 1) show mac address-table 2) show mac address-table static 3) show mac address-table port-security 4) show mac address-table dynamic |
1,2 |
|
|
Imagine that a switch connects through an Ethernet cable to a router, and the router’s host name is Hannah. Which of the following commands could tell you information about the IOS version on Hannah without establishing a Telnet connection to Hannah? (Choose two answers.) 1) show cdp entry Hannah 2) show cdp neighbors Hannah 3) show cdp neighbors 4) show cdp 5) show neighbors Hannah 6) show cdp neighbors detail |
1, 6 |
|
|
If you ping across a serial line and it fails, and you follow it up with a show interface commands and get a Line Status up, Protocol up, most likely. 1) its a layer 3 problem 2) the interface is shut down 3) it is a Layer 1 problem 4) it is a Layer 2 problem |
1
if both line and protocol are up and you still cannot ping, it is probably an IP address issues. |
|
|
Which of the following commands list both access and trunk ports for the VLAN? 1) show vlan id num 2) show vlan brief 3) show mac address-table 4) show interfaces type number swithcport |
3
Show vlan brief / show vlan lists each VLAN and all interfaces assigned to that VLAN.
|
|
|
If you do a ping across a serail link and it fails, and you follow it up with a show interface cmd and get a Line Status up, Protocol status down, most likely 1) it is a layer 1 problem 2) it is a layer 2 problem 3) it is a layer 3 problem 4) the interface is shut down |
2
Protocol status down is most likely a Layer 2 issue |
|
|
Which of the following is a piece of information gathered by CPD? (3) 1) Platform 2) Address list 3) Local port identified 4) Device identifier |
1,2,4
CDP reveals the interface on the remore router or switch on the other end of the link that sent the CDP advertisement |
|
|
Which cmd identifies the interface's access VLAN, voice VLAN, plus the configure and operational mode? 1) show interface type number switchport 2) show vlan id num 3) show vlan brief 4) show mac address-table |
1 |
|
|
Which of the following cmd identify switch interfaces as being trunking interfaces: interfaces that currently operate as VLAN trunks? (2) 1) show interface 2) show trunk 3) show interfaces trunk 4) show interfaces switchport |
3,4
show interface switchport cmd
lists both the administrative and operational status of each port, When a switch considers a port to be trunking, the cmd lists an operational trunking state of "trunk"
|
|
|
show interface switchport cmd |
show interface switchport cmd
lists both the administrative and operational status of each port, When a switch considers a port to be trunking, the cmd lists an operational trunking state of "trunk" |
|
|
show interfaces trunk cmd |
show interfaces trunk cmd
This cmd lists a set of interfaces: the interfaces that are currently operating as trunks |
|
|
How can switch Fast Ethernet port fa0/2 be removed from VLAN 2 and assigned to VLAN 3?
1) Enter the switchport access vlan 3 command in interface configuration mode
2) Enter the no vlan 2 and the vlan 3 commands in global configuration mode
3) Shut down Fast Ethernet port fa0/2 and then configure the port for VLAN 3
4) Rename Fast Ethernet port fa0/2 to Fast Ethernet port fa0/3
|
1
Each access port of a switch can only be a member of one VLAN. VLAN membership can therefore be reassigned by simply issuing the switchport mode access vlan vlan-id command on the port. |
|
|
A network tech accidentally deletes VLAN from a switch when port fa0/14 through fa0/24 are assigned to VLAN 22. What happens to the ports that were assigned to VLAN 22? 1) Devices connected to the VLAN 22 member ports will be unable to communicate 2) By default, the ports will automatically become members of the native VLAN 3) By default, the ports will automatically become members of VLAN 1. 4) All ports will remain assigned to VLAN 22 becuase it cannot be deleted if any ports are currently assigned to it |
1
if a VLAN with member ports is deleted, those ports are isolated and connected devices cannot communicate until the ports are assigned to an existing VLAN. |
|
|
Which of the following is true of routers that are routing between VLANs?
1. The router has a trunk port that links to the switch.
2. None of the answers are correct.
3. Layer 2 switches forward data between 2 VLANs.
4. The router has an access port that links to the switch.
|
1
Routers use VLAN trunking instead of a separate link for each VLAN through the port connected to the switch. |
|
|
What are the three modes available to be configured on Cisco LAN switches in a VTP domain?
1. client
2. root
3. transparent
4. server
5. bridge
|
1,3,4
Cisco LAN switches can be configured to server (default), client, or transparent VTP mode. They can also be set to off mode. |
|
|
Which of the following is/are not a reason to prevent VLAN traffic from crossing the trunk?
1. Not seen using the show vlan command 2. Removed from the allowed list 3. Does not exist and shutdown 4. All options are reasons to prevent traffic. |
4 |
|
|
show vlan brief |
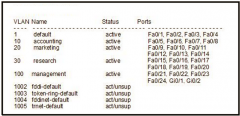
|
|
|
Considering the differences between NAT and PAT, which is the most accurate description? 1) PAT translates many IP addresses into a few or even one IP address 2) NAT allows for multiple protocols across a single IP address 3) NAT translates many IP addresses into a few or even one IP address 4) PAT allows for multiple protocols across multiple IP address |
1)
Both NAT and PAT can support multiple protocols for each of their translations. PAT translates multiple inside local addresses into a single global address. PAT is also used with pools when there are more inside devices than addresses in the pool and the keyword overload has been used in the configuration.
NAT is a one-to-one translation of IP to IP |
|
|
Which cmd enables you to view summary of NetFlow statistics of protocols on a Cisco IOS router? 1) show ip flow export 2) show ip interface 3) show flow 4) show ip flow cache 5) show ip cache flow |
5
The show ip cache flow cmd displays a summary of NetFlow statistics, including which protocols are in use |
|
|
show frame pvc summary |

|
|
|
show frame-relay pvc 110 |
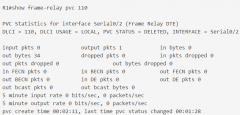
|
|
|
Which if the following technologies match with their use? 1) digital signature for authentication 2) AES for data integrity 3) SHA1 for confidentiality 4) 3DES for encryption 5) MD5 for encryption |
1,4
Digital signatures can be used for authenticating the VPN peer on the other side of the tunnel, and 3DES is an encryption algorithm that can be used for encryption.MD5 and SHA-1 are a hashing algorithm used for data integrity. AES is an encryption algorithm used for privacy of data. |
|
|
show log (scr) |
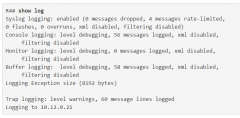
|
|
|
What cmd enables you to see information about current Cisco IOS software licenses that are on the device? 1) show version 2) show start 3) show run 4) license-info 5) show licenses |
1,5
show license cmd provides info on the current licenses active on the device
show version cmd does provide some of the details about licensing near the end of the output |
|
|
The newer console port |
type-B usb console
the older is RJ-45 |
|
|
Class A determine via binary
Class B determine via binary
Class C determine via binary |
Class A determine via binary 00000000 = 0 01111111 = 127
Class B determine via binary 10 000000 = 128 11 000000 = 192
Class C determine via binary 110 00000 = 192 111 00000 = 223
|
|
|
Cmds to administratively shut down vlan |
1) shutdown vlan vlan-id (global config)
2) shutdown (vlan config) |
|
|
engineer can limit the VLANs allowed on the trunk by using the following interface subcmd: |
switchport trunk allowed vlan { add | all | except | remove } vlan-list
this cmd provides a way to easily add and remove VLANs from the list |
|
|
Cisco has supported two ifferent trunking protocols over the years: |
Inter-Switch Link (ISL) (proprietary) IEEE 802.1Q |
|
|
Cisco switches break the range of VLAN IDs (1-4094) into ____________ ranges |
two
the normal range and the extended range
All switches can use normal-range VLANs with values from 1 to 1005. Only some siwtches can use extended -range VLANs 1005 to 4094 |
|
|
Steps to config vlan |
1. From config mode, use the vlan vlan-id global config cmd to create the VLAN and to move the user into VLAN config mode 2. (Optional) use the name name VLAN subcmd to list a name for the VLAN 3. For desirable interfaces enter interface config mode 4. Use the switchport access vlan id-number interface subcmd to specify the VLAN number associated with that interface 5. (Optional) disable trunking on that same interface, so that the interface does not negotiate to become a trunk, use the switchport mode access interface subcmd |
|
|
VTP |
VTP VLAN Trunking Protocl
Cisco-proprietary protocol and tool used to advertise each VLAN configure in one switch so that all the other switches in the network |
|
|
CMD to set VTP to transparent mode |
vtp mode transparent global cmd
or
vtp mode off
to check the VTP status use vtp mode off |
|
|
VTP modes |
server client transparent (standard construct template) |
|
|
switches that support both type of trunking (ISL and 802.1Q) use __________________ interface subvmd to either configure the type or allow DTP to negotiate the type |
switchport trunk encapsulation {dot1q | isl | negotiate } |
|
|
configure basic password and host name
cmd sequence
|
s#configure terminal s(config)# enable secret cisco s(config)# hostname ema ema(config)#line console 0 ema(config-line)#password faith ema(config-line)# login ema(config-line)# exit ema(config)#line vty 0 15 ema(config-line)# password love ema(config-line)# login ema(config-line)# end ema# |
|
|
Switches can control their support of Telnet and/or SSH on the vty lines using what cmd? |
transport input { all | none | telnet | ssh } |
|
|
what cmds store the password in clear text |
the console and vty lines with the password cmd username password |
|
|
To prevent password vulnerability in a printed version of the config file, or in a backup copy of the config file stored on a server you can encrypt some passwords using |
service password-encryption
global config cmd
it affects has password cmd in both console and vty modes and username password global cmd |
|
|
this cmd show two very important details related to switch IO addressing |
lists the interface status of the VLAN 1 lists the interface IP address |
|
|
CDP discovers several useful details from the neighboring Cisco device |
Device identifier - typically the hostname Address list - network and data-link address Port identifier - the interface on the remote router or switch
|
|
|
auxiliary port def |
auxiliary port is similar to console port. The main difference with an auxiliary port is that it also allows you to config modem cmd so that modem can be connected to the router |
|
|
Access list configuration mode prompt |
s#config t s(config)# ip access-list standard Tod s(config-std-nacl)# |
|
|
Routing protocol config mode prompt |
s(config)# ip routing s(config)# router rip s(config-router)# |
|
|
user exec mode
privileged exec mode
global configuration mode |
user exec mode - limited to basic monitoring cmd
privileged exec mode - provides access to all other router cmd
global configuration mode - cmd that affect the entire system |
|
|
specific config mode
setup mode |
specific config mode - cmd that affect interface/process only
setup mode - interactive config mode |
|
|
Cmd sequence to configure auxiliary password on a router |
t#config t t(config)#line aux 0 t(config-line)#login t(config-line)#password aux t(config-line)#login
|
|
|
Manually encrypting your password |
t#config t t(config)#service password-encryption t(config)#exit t#run |
|
|
using the pipe |
sh run | ?
sh run | begin interface |
|
|
You can see if a router's serial interface has a DCE cable connected with the __________________ |
show controllers int
router#sh controllers s0/0/0 Interface Serial0/0/0 Hardware is GT96K DTE V.35idb at 0x4342FCB0, driver data structure 0x434373D4 |
|
|
How to see if an interface is DCE connection |
router#sh controllers s0/2/0 Interface Serial0/2/0 Hardware is GT96K DCE V.35, clock rate 10000000 |
|
|
show ip route eigrp |
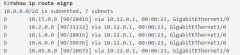
|
|
|
show ip eigrp topology |
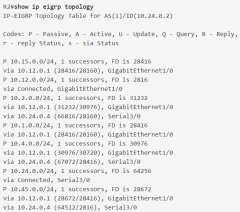
|
|
|
Setting up SSH |
router(config)#hostname todd todd(config)#ip domain-name lamle.com todd(config)#username todd password lamle todd(config)#crypto key generate rsa todd(config)#ip ssh version 2 todd(config)#line vty 0 15 todd(config)#transport input ssh telnet |
|
|
access interface |
access interface is a LAN network design term that refers to a switch interface connected to end-user devices, configured so that it does not use VLAN trunking |
|
|
trunk interface def |
trunk interface
A switch interface configured so that it operate using VLAN trunking |
|
|
Trunking administrative mode |
Trunking administrative mode
The configured trunking setting on a Cisco switch interface, as configured with the switchport mode command |
|
|
Trunking operational mode |
Trunking operational mode
The current behavior of a Cisco switch interface for VLAN trunking |
|
|
VTP transparent mode |
One of three VTP operational modes. Switches in transparent mode can configure VLANs, but they do no tell other switches about the changes, and they do not learn about VLAN changes from other switches |
|
|
trunking administrative mode options with the switchport mode cmd |
access - always act as an access port
trunk - always act as trunk port
dynamic desirable - initiates negotiation messages and responds to negotiation messages to dynamically choose whether to start using trunking
dynamic auto - passively waits to receive trunk negotiation messages, at which point the switch will respond and negotiate whether to use trunking |
|
|
switchport mode dynamic desirable cmd |
asks the switch to both negotiate as well as to beign the negotiation process, rather than waiting on the other device |
|
|
show interfaces trunk |
this cmd lists information about all interfaces that currently operationally tunk |
|
|
Display OSPF info (ospf) |
show ip ospf
show ipv6 ospf |
|
|
Display all source of routing information (ospf) |
show ip protocol
show ipv6 protocol |
|
|
Displays details about ospf-enabled interfaces (ospf) |
show ip ospf interface
show ipv6 ospf interface
|
|
|
Display concise details about ospf enable interfaces (ospf) |
show ip ospf interface brief
show ipv6 ospf interface brief
|
|
|
List of neighbors (ospf) |
show ip ospf neighbors
show ipv6 ospf neighbors |
|
|
summary of lsdb (ospf) |
show ip ospf database
show ipv6 ospf database |
|
|
show ospf learned routes |
show ip route ospf
show ipv6 route ospf |
|
|
The engineer can configure the interface as OSPFv3 passive interface telling the route to do the following |
Quite sending OSPF hellos on the interface Ignore received Hellos on the interface Do not form neighbor relationships over the interfaces continue to advertise about any subnet connect to the interface |
|
|
how to configure an interface to be passive for OSPFv3 |
passive-interface gigabitethernet0/0 |
|
|
CEF |
CEF Cisco Express Forwarding
A method of internal processing on Cisco routers, meant to make the routing process very efficient, doing so by caching IP routes in a table that can be searched very quickly, and by remembering data link headers rather than building them for every packet that is forwarded. |
|
|
Connected route |
Connected route
On a router, an IP route added to the routing table when the router interfaces is both up and has an IP address configured. The route is for the subnet that can be calculated based on the configured IP address and mask. |
|
|
Static route |
Static route
An IP route on a router created by the user configuring the details of the route on the local router. |
|
|
ABR |
ABR Are Border Router
A router using OSPF in which the router has interfaces in multiple OSPF areas
|
|
|
Convergence |
Convergence
The time required to react to changes in the network, removing and adding new, better routes so that the current best routes are in all the routers' routing table |
|
|
Distance vector |
Distance vector
The logic behind the behavior of some interior routing protocols, such as RIP. Distance vector routing algorithms call for each router to send its entire routing table in each update but only to its neighbors. distance vector routing algorithms can be prone to routing loops but are computationally simple than line-state routing algorithms. |
|
|
Link-state def |
A classification of the underlying algorithm used in some routing protocols. Link-state protocols build a detailed database that lists link (subnet) and their state (up, down), from which the best routes can then be calculated. |
|
|
Link-state advertisement (LSA) |
In OSPF, the name of the data structure that resides inside the LSDB and describes in detail the various components in a network, including routers and links |
|
|
LSDB (def and abbr) |
LSDB
Link-state database
In OSPF, the data structure in RAM of router that holds the various LSAs, wth the collective LSAs representing the entire topology of the network |
|
|
SPF |
SPF - Shortest path first
The name of the algorithm used by link-state routing protocol to analyze the LSDB and find the least-cost router to each subnet. |
|
|
standard access list |
a list of IOS global configuration commands that can match only a packet's source IP address, for the purpose of deciding which packets to discard and which to allow through the router |
|
|
extended access list |
A list of IOS access-list global configuration commands that can match multiple parts of an IP packet, including the source and destination IP address and TCP/UDP ports, for the purpose of deciding which packets to discard and which to allow through the router |
|
|
named access list |
an ACL that identifies the various statements in the ACL based on a name, rather that a number |
|
|
inside global |
for packets sen to and from a host that resides inside the trusted part of a network that uses NAT, a term referring to the IP address used in the headers of those when those packets traverse the global internet |
|
|
inside local |
for packets sent to and from a host that resides inside the trusted part of a network that uses NAT, a term referring to the IP address used in the headers of those packets traverse the enterprise (private) part of the network |
|
|
PAT |
port address translation
a NAT feature in which one inside global IP address support over 60K concurrent TCP and UDP connection |
|
|
NAT |
NAT - Network Address Translation
A mechanism for reducing the need for globally unique IP addresses. NAT allows an organization with addresses that are not globally unique to connect to the Internet, by translating those addresses into public addresses in the globally routable address space. |
|
|
Global routing prefix |
An IPv6 prefix that defines an IPv6 address block made up of global unicast address, assigned to one organization, so that the organization has a block of globally uniques IPv6 addresses to use in its network |
|
|
Global unicast address |
A type of unicast IPv6 address that has been allocated from a range of public globally uniques IP addresses, as registered through IANA/ICANN, its member agencies, and other registries or IPSs |
|
|
Unicast local address |
A type of IPv6 unicast address meant as a replacement for IPv4 private addresses |
|
|
All-nodes multicast addres |
A specific IPv6 multicast address, FF02::1, with link-local scope, used to send packets to all devices on the link that support IPv6 |
|
|
All-routers multicast address |
All-routers multicast address
A specific IPv6 multicast address, FF02::2, with link-local scope, used to send packets to all devices that act as IPv6 routers on the local link |
|
|
EUI-64 |
Literally, a standard for an extended unique identifier that is 64 bits long. Specifically for IPv6, a set of rules for forming a 64-bit identifier, used as the interface ID in IPv6 addresses, by starting with a 48-bit MAC address, inserting FFE (hex) in the middle, and inverting the seventh bit |
|
|
Link-local address |
A type of unicast IPv6 address that represents an interface on a single data link. Packets sent to a link-local address cross only that particular link and are never forwarded to other subnets by a router. Used for communication that do not need to leave the local link/ |
|
|
Link-local scope |
With IPv6 multicasts, a term that refers to the parts of the network to which a multicast packet can flow, with link-local referring to the fact that the packet stays on the subnet in which it originated |
|
|
Solicited-nodemulticast address |
A term used in IPv6 to refer to how hosts first check whether another host is using a unicast address before the first host uses that address |
|
|
Neighbor Advertisement (NA) |
A message defined by the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP), used to declare to other neighbors a host's MAC address. Sometimes sent in response to a previously received NDP Neighbor Solicitation (NS) messages. |
|
|
Neighbor Solicitation (NS) |
NS
A message defined by the IPv6 NDP, used to ask a neighbor to reply with a Neighbor Advertisement which lists the neighbor's MAC address. |
|
|
Router Advertisement (RA) |
RA
A message defined by the IPv6 NDP, used by routers to announce their willingness to act as an IPv6 router on a link. These can be sent in response to a previously received NDP Router Solicitation (RS) message |
|
|
Router Solicitation (RS) |
A message defined by the IPv6 Neighbor Discover Protocol, used to ask any routers on the link to reply, identifying the router, plus other configuration settings |
|
|
Stateful DHCP |
A term used in IPv6 to contrast with stateless DHCP. Stateful DHCP keeps track of which clients have been assigned which IPv6 addresses |
|
|
SLAAC |
SLAAC - Stateless Address Auto-configuration
a feature of IPV6 in which a host or router can be assigned an IPv6 unicast address without the need for a stateful DHCP server |
|
|
Stateless DHCP |
A term used in IPv6 to contrast with stateful DHCP. Stateless DHCP servers don't lease IPv6 addresses to clients. Instead, they supply other useful information, such as DNS server IP address, but with no need to track information about the clients. |
|
|
Before class B network 172.16.0.0 is subnetted by a network engineer, what parts of the structure of the IP address in this network already exist, with a specific size? (2) A) host B) broadcast C) network d) subnet |
A and C
An unsubnetted Class A, B, or C network has two parts: the network and host parts. |
|
|
A Class B network needs to be subnetted such that it supports 100 subnets and 100 hosts/subnet. Which of the following answers list a workable combination for the number of network, subnet, and host bits? (Select two answers.) a) Network = 16, subnet = 9, host = 7 b) Network = 16, subnet = 8, host = 8 c) Network = 16, subnet = 7, host = 7 d) Network = 8, subnet = 7, host = 17 |
ab
The number of network, subnet, and host bits must total 32 bits |
|
|
Which of the following installation steps are typically required on a Cisco router, but not typically required on a Cisco switch? (Choose two answers.) a) Turn the on/off switch to "on" b) Connect the power cable c) Connect to the console port d) Connect serial cables |
Explanation: Answer options D and A are correct.
Cisco routers have an on/off switch, but Cisco switches generally do not. |
|
|
You just bought two Cisco routers for use in a lab, connecting each router to a different LAN switch with their Fa0/0 interfaces. You also connected the two routers’ serial interfaces using a back-to-back cable. Which of the following steps are not required to be able to forward IPv4 packets on both routers’ interfaces? (Choose two answers.) a) Configuring the bandwidth command on one router's serial interface b) Configuring an IP address on each router's Fast Ethernet and serial interfaces c) Setting the interface description on both the Fast Ethernet and serial interface of each router d) Configuring the clock rate command on one router's serial interface |
Answer options A and C are correct.
To route packets, a router interface must have an IP address assigned and be in an “up and up” interface state. For a serial link created in a lab, without using CSU/DSUs, one router must be configured with a clock rate command to the speed of the link. The bandwidth and description commands are not required to make a link operational. |
|
|
Which of the following commands do not list the IP address and mask of at least one interface? (Choose two answers.) a) show version b) show interfaces c) show ip interface brief e) show protocols type number f) show running-config |
Answer options C and A are correct.
The show ip interface brief command lists all the interface IPv4 addresses but none of the masks. The show version command lists none of the IP addresses and none of the masks. The other three commands list both the address and mask. |
|
|
A router is configured with the no ip subnet-zero global configuration command. Which of the following interface subcommands would not be accepted by this router?
a) ip address 10.0.0.5 255.255.255.252 b) ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 c) ip address 10.0.0.129 255.255.255.128 d) ip address 10.1.2.2 255.254.0.0 |
Explanation: Answer option D is correct.
With the no ip subnet-zero command configured, the router will not allow any interfaces to be configured with an IP address in the zero subnet. Of the listed answers, subnet 10.0.0.0 255.254.0.0 is a zero subnet, with a range of addresses from 10.0.0.1 to 10.1.255.254. The ip address 10.1.2.2 255.254.0.0 command would be rejected. |
|
|
Router R1 lists a route in its routing table. Which of the following answers list a fact from a route, that the router then compares to the packet’s destination address? (Choose 2 answers.)
a) Next-hop router b) Mask c) Outgoing interface d) Subnet ID |
Explanation: Answer options B and D are correct.
The route defines the group of addresses represented by the route using the subnet ID and mask. The router can use those numbers to find the range of addresses that should be matched by this route. The other two answers list facts useful when forwarding packets that happen to match the route. Lesson: Configuring IPv4 Addresses and Routes |
|
|
Router 1 has a Fast Ethernet interface 0/0 with IP address 10.1.1.1. The interface is connected to a switch. This connection is then migrated to use 802.1Q trunking. Which of the following commands could be part of a valid configuration for Router 1’s Fa0/0 interface? (Choose two answers.) a) trunking enable 4 b) trunking enable c) dot1q enable 4 d) dot1q enable e) interface fastethernet 0/0.4 f) encapsulation dot1q 4 |
Explanation: Answer options E and F are correct.
Of all the commands listed, only the two correct answers are syntactically correct router configuration commands. The command to enable 802.1Q trunking is encapsulation dot1q vlan_id. |
|
|
Which of the following commands correctly configures a static route? a) ip route 10.1.3.0 /24 10.1.130.253 b) ip route 10.1.3.0 serial 0 c) ip route 10.1.3.0 255.255.255.0 10.1.130.253 d) ip route 10.1.3.0 /24 serial 0 |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct. |
|
|
A PC opens a command prompt and uses the ipconfig command to see that the PC’s IP address and mask are 192.168.4.77 and 255.255.255.224. The user then runs a test using the ping 192.168.4.117 command. Which of the following answers is the most likely to happen?
a) The PC sends an ARP looking for the MAC address of the DHCP server. b) The PC sends a DNS query for 192.168.4.117. c) The PC sends packets to its default gateway. d) The PC sends packets directly to the host with address 192.168.4.117. |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct.
PCs use two-option logic: send local packets (destined for hosts in the same subnet) directly, and send remote packets (destined for hosts in other subnets) to the default gateway/router. In this case, the PC’s own IP address is 192.168.5.77, with mask 255.255.224.0, so it is in subnet 192.168.4.64/27. This subnet has a range of addresses from 192.168.4.64 to 192.168.4.95, including the subnet and broadcast address. As a result, the PC sends the packet to its default gateway. As for the other incorrect answers, if the ping command had used a host name, it would have first asked a DNS server to resolve the name. Also, the PC already has an IP address, so DHCP would not be needed. Lesson: Configuring IPv4 Addresses and Routes |
|
|
A Layer 3 switch has been configured to route IP packets between VLANs 1, 2, and 3, which connect to subnets 172.20.1.0/25, 172.20.2.0/25, and 172.20.3.0/25, respectively. The engineer issues a show ip route command on the Layer 3 switch, listing the connected routes. Which of the following answers lists a piece of information that should be in at least one of the routes? a) Next-hop router 172.20.4.1 b) Interface VLAN 2 c) Mask 255.255.255.0 d) Interface Gigabit Ethernet 0/0.3 |
Explanation: Answer option B is correct.
The configuration of the Layer 3 switch’s routing feature uses VLAN interfaces, with the interface number matching the VLAN ID. The matching connected routes, like all connected IP routes, will list the interfaces but not a next-hop IP address. The three connected routes will list the VLAN interfaces 1, 2, and 3, respectively. |
|
|
Which of the following network commands, following the command router ospf 1, tells this router to start using OSPF on interfaces whose IP addresses are 10.1.1.1, 10.1.100.1, and 10.1.120.1? a) network 10.0.0.1 0.0.255.255 area 0 b) network 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.255 area 0 c) network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 d) network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0 |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct.
The network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 command works, because it matches all interfaces whose first octet is 10. The rest of the commands match as follows: all addresses that end with 0.0.0 (wildcard mask 255.0.0.0); all addresses that begin with 10.0.0 (wildcard mask 0.0.0.255); and all addresses that begin 10.0 (wildcard mask 0.0.255.255). |
|
|
Which of the following commands list the OSPF neighbors off interface serial 0/0? (Choose two answers.) a) show ip ospf interface brief b) show ip neighbor c) show ip interface d) show ip ospf neighbor serial 0/0 e) show ip ospf neighbor |
Explanation: Answer options E and D are correct.
Of the three wrong answers, two are real commands that simply do not happen to list the OSPF neighbors. show ip ospf interface brief lists interfaces on which OSPF is enabled, but does not list neighbors. show ip interface lists IPv4 details about interfaces, but none related to OSPF. One incorrect answer, show ip neighbor, is not a valid IOS command. |
|
|
Which of the following is true about how a router using a link-state routing protocol chooses the best route to reach a subnet? a) The router uses the path that has the lowest hop count. b) The router compares the metrics listed for that subnet in the updates received from each neighbor and picks the best (lowest) metric route. c) The router calculates the best route by running the SPF algorithm against the information in the link-state database. d) The router finds the best route in the link-state database. |
Explanation: Answer option C is correct.
Link-state protocols do not exchange data that lists routes. They do list metric information, but it is per-interface information, and it is not tied to a subnet. Link-state protocols do require the SPF algorithm to take the varied pieces of information and create routes based on that information.
|
|
|
Which of the following routing protocols use a metric that is, by default, at least partially affected by link bandwidth? (Choose two answers.)
a) RIP-2 b) EIGRP c) OSPF d) RIP-1 |
Explanation: Answer options B and C are correct.
Both versions of RIP use the same hop-count metric. |
|
|
Which of the following commands, following the command router ospf 1, tells this router to start using OSPF on interfaces whose IP addresses are 10.1.1.1, 10.1.100.1, and 10.1.120.1?
a) network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0 b) network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.0 area 0 c) network 10.1.1.0 0.x.1x.0 area 0 d) network 10.1.1.0 255.0.0.0 area 0 e) network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0 |
Explanation: Answer option A is correct.
The network 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.255 area 0 command matches all IP addresses as a result of the 255.255.255.255 wildcard mask, so this command enables OSPF in Area 0 on all interfaces. The answer with wildcard mask 0.255.255.0 is illegal, because it represents more than one string of binary 0s separated by binary 1s. The answer with x’s is syntactically incorrect. The answer with wildcard mask 255.0.0.0 means “Match all addresses whose last three octets are 0.0.0,” so none of the three interfaces are matched.
|
|
|
link state protocols |
in link-state protocols, also called SPF protocols, the routers each create three separate tables. One for tracking directly attached neighbors One to determine the topology of the entire internetwork One used as the routing table
|
|
|
Cmd to verify DHCP server |
#show ip dhcp binding
|
|
|
CMD to show dhcp pool and lease |

show ip dhcp pool SF_LAN |
|
|
Bootstrap |
Stored in the microcode of the ROM
The bootstrap is used to bring a router up during initialization. It boots the router and then loads the IOS
|
|
|
POST def |
Stored in the ROM,
The POST is used to check the basic functionality of the router hardware and determines which interfaces are present |
|
|
Mini IOS |
ROM - Called RXBOOR or boot loader by Cisco,
a small IOS in ROM that can be used to bring up an interface and load a Cisco IOS into flash memory. The mini-IOS can also perform a few other maintenance operations. |
|
|
RAM |
Used to hold packet buffers, ARP cache, routing tables, and also the software and data structures that allow the router to function. Running-config is stored in RAM, and most routers expand the IOS from flash into RAM upon boot. |
|
|
Packet buffer
Routing table |
Packet buffer - RAM
Routing table - RAM |
|
|
ROM monitor |
Stored in ROM
The ROM monitor is used for manufacturing, testing, and trouble-shooting, as well as running a mini-IOS when the IOS in flash fails to load. |
|
|
ROM def |
Used to start and maintain the router. Holds the POST and the bootstrap program as well as the mini-IOS |
|
|
Flash memory def |
Stores the Cisco OPS by default. Flash memory is not erased when the router is reloaded. It is EEPROM created by Intel. |
|
|
NVRAM |
Used to hold the router and switch configuration. NVRAM is not erased when the router or switch is reloaded. Does not store an IPS. The configuration register is stored in NVRAM. |
|
|
Configuration register |
Used to control how the router boots up.
This value can be found as the last line of the show version command output and by default is set to 0x2012, which tells the router to load the IOS from flash memory as well as to load the configuration from NVRAM. |
|
|
Show processes |
Show processes |
|
|
If you have a DNS server on your network, you will need to add a few commands to make the DNS name resolution work |
#config t (config)#ip domain-lookup (config)#ip name-server 4.4.4.4 (config)#ip domain-name lamle.com |
|
|
By default CDP transmits every 60 seconds and will hold packets from a neighbor in the CDP table for 180 seconds. What global cmds can be used... |
cdp holdime length of time that receiver must keep the packets it receives from neighboring devices
cdp time - rate at which CDP packets are sent on all active interfaces |
|
|
IF someone statically configures an IP address on a LAN and the DHCP server hands out that same address, you will end up with a duplicate address. What cmd can can help |
show ip dhcp server statistics |
|
|
List DHCP server statistics |
show ip dhcp server statistics |
|
|
A syslog server save copies of console messages and can time-stamp them so you can view them at a later time. What cmds are used to do this? |
(config)#logging host 172.16.10.1 (config)#service timestamps log datetime msec |
|
|
Config an interface on a router to accept the DHCP client requests and forward them to the DHCP server with the following cmd |
#config ter (config)#interface fa0/0 (config-if)#ip helper-address 10.10.10.254 |
|
|
Cmd to list the state information about each IP address currently leased to a client |
show ip address bindings |
|
|
DHCP Relay |
If you need to provide address from a DHCP server to hosts that aren't on the same LAN as the DHCP server, you can configure your router interface to relay or forward the DHCP client request |
|
|
show cdp |
Router#show cdp Global CDP information: Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled |
|
|
show cdp entry device.cisco.com |
The following is sample output from the show cdp entry command with no limits. Information about the neighbor device.cisco.com is displayed, including device ID, address and protocol, platform, interface, hold time, and version. outer# show cdp entry device.cisco.com-------------------------Device ID: device.cisco.comEntry address(es): IP address: 192.168.68.18 CLNS address: 490001.1111.1111.1111.00 DECnet address: 10.1Platform: cisco 4500, Capabilities: RouterInterface: Ethernet0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): Ethernet0Holdtime : 125 secVersion :Cisco IOS SoftwareCisco IOS (tm) 4500 Software (C4500-J-M), Version 12.1(2)Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Mon 07-Apr-00 19:51 by joeuser |
|
|
show cdp entry protocol |
show cdp entry protocol command. Only information about the protocols enabled on device.cisco.com is displayed. Router# show cdp entry device.cisco.com protocol
Protocol information for device.cisco.com: IP address: 192.168.68.18 CLNS address: 490001.1111.1111.1111.00
DECnet address: 10.1 |
|
|
show cdp interface |
how cdp interface
Serial0 is up, line protocol is up, encapsulation is SMDS Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds Ethernet0 is up, line protocol is up, encapsulation is ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds
Holdtime is 180 seconds |
|
|
show cdp entry protocol (scr) |
The following is sample output from the show cdp entry protocol command. Only information about the protocols enabled on device.cisco.com is displayed. Router# show cdp entry device.cisco.com protocol
Protocol information for device.cisco.com: IP address: 192.168.68.18 CLNS address: 490001.1111.1111.1111.00 DECnet address: 10.1 |
|
|
show cdp entry device.cisco.com (scr) |
Router# show cdp entry device.cisco.com
------------------------- Device ID: device.cisco.com Entry address(es): IP address: 192.168.68.18 CLNS address: 490001.1111.1111.1111.00 DECnet address: 10.1 Platform: cisco 4500, Capabilities: Router Interface: Ethernet0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): Ethernet0 Holdtime : 125 sec
Version : Cisco IOS Software Cisco IOS (tm) 4500 Software (C4500-J-M), Version 12.1(2) Copyright (c) 1986-2000 by cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Mon 07-Apr-00 19:51 by joeuser |
|
|
Show cdp (scr) |
Router#show cdp Global CDP information: Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled |
|
|
you can add the RIP routing protocol by using this two cmd |
router rip network
#config t (config)#router rip (config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 (config-router)#network 192.168.10.2 (config-router)#version 2 (config-router)#no auto-summary |
|
|
redistribution def |
translating from one type of routing protocol to another.
The means that you can support old routers using RIP but then use some newer routers as well |
|
|
preventing an interface for sending and receiving RIP advertisements |
#config t (config)#router rip (config-router)#passive-interface FA0/0 |
|
|
3. Which of the following statements are true regarding the command ip route 172.16.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.2? (Choose two.) A. The command is used to establish a static route. B. The default administrative distance is used. C. The command is used to configure the default route. D. The subnet mask for the source address is 255.255.255.0. E. The command is used to establish a stub network. |
3. A, B. Although option D almost seems right, it is not; the mask is the mask used on the remote network, not the source network. Since there is no number at the end of the static route, it is using the default administrative distance of 1. |
|
|
17. Which of the following is an EGP? A. RIPv2 B. EIGRP C. BGP D. RIP |
C. BGP |
|
|
18. Which of the following is an advantage of static routing? A. Less overhead on the router CPU B. No bandwidth usage between routers C. Adds security D. Recovers automatically from lost routes |
18. D. Recovery from a lost route requires manual intervention by a human to replace the lost route. The advantages are less overhead on the router and network, as well as more security. |
|
|
Inside local def |
An address used for a host inside an enterprise. It is the actual IP address assigned to a host in the private enterprise network |
|
|
Inside global def |
pAn address used for a host inside an enterprise. NAT uses an inside global address to re[resent the inside host as the packet is sent through the outside network (Internet).
A NAT router changes the src IP address of a packet sent by an inside host from an inside local address to an inside global address as the packet goes from the inside to the outside network |
|
|
Outside global def |
An address used for a host outside an enterprise. Outside global address is the actual IP address assigned to a host that resides in the outside network, typically the internet |
|
|
Outside local def |
An outside IP address is the IP address that represent the host outside the enterprise network |
|
|
Dynamic NAT |
The NAT router creates a one-to-one mapping between an inside local and inside global address, and change the IP address in packets as they exit and enter the network. The mapping of an inside local address to an inside global address happens dynamically |
|
|
Does OSPF support auto-summatization? |
No |
|
|
OSPF link def |
Link is a network or router interface assigned to any given network. When an interface is added to the OSPF process it's considered to be a lin |
|
|
OPSF Router ID def |
The router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify router. Cisco chooses the router by using the highest IP address of all configure loopback interface.
If no loopback interfaces are configured with address, OSFP will choose the highest IP address out of all active physical interface |
|
|
OSPF Neighbor def |
Two or more routers that have an interface on a common network, such as two router connected on a PPP serial link. OSPF neighbors must have a number of common configuration details in order to be able to establish neighbor relationship Area ID Sub are flag Hello and dead intervals |
|
|
OSPF Adjacency |
it is a relationship between two OSPF router that permits the direct exchange of router update. |
|
|
OSPF designated router def |
a DR is elected whenever OSPF routers are connected to the same broadcast network to minimize the number of adjacency formed and to publicize received routing info to and from the remaining routers on the broadcast network or link |
|
|
OSPF Hello protocol def |
OSPF Hello protocol provides dynamic neighbor discovery and maintains neighbor relationships. Hello packets and LSA (link state advertisements) build and maintain the topological database |
|
|
OSPF neighborship database def |
neighborship database is a list of all OSPF routers for which Hello packets have been seen. |
|
|
OSPF Topological database def |
topological database contains info from all of the LSA packets that have been received for an area. The router uses the information from the topology database as input to the Dijkstra algorithm that computes the shortest path on the network |
|
|
OSPF LSA def |
LSA is an OSPF data packet containing link-state and routing info that is shared among OSPF routers |
|
|
OSPF areas def |
OSPF area is a neighboring of contiguous networks and routers. All routers in the same are share a common area ID. |
|
|
OSPF operation is basically divided into these three categories: |
Neighbor and adjacency initialization LSA flooding SPF tree calculation |
|
|
What address is used by OSPF to send Hello packets |
224.0.0.5 |
|
|
LSA flooding |
LSA flooding is the method OSPF uses to share routing information. Via LSU packets, LSA information containing the link-state data is shared with all OSPF routers within an area. |
|
|
CMD for enabling OSFP |
router ospf |
|
|
Configuring OSPF Areas |
Router#config t Router(config)#router ospf 1 Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0 |
|
|
Configuring Loopback Interfaces OSPF |
Corp(config)#int loopback 0 *Mar 22 01:23:14.206: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up Corp(config-if)#ip address 172.31.1.1 255.255.255.255 |
|
|
show ip ospf Command |
Corp#sh ip ospf Routing Process "ospf 1" with ID 223.255.255.254 Start time: 00:08:41.724, Time elapsed: 2d16h Supports only single TOS(TOS0) routes Supports opaque LSA Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Supports area transit capability Router is not originating router-LSAs with maximum metric Initial SPF schedule delay 5000 msecs Minimum hold time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs Maximum wait time between two consecutive SPFs 10000 msecs Incremental-SPF disabled Minimum LSA interval 5 secs Minimum LSA arrival 1000 msecs LSA group pacing timer 240 secs Interface flood pacing timer 33 msecs Retransmission pacing timer 66 msecs Number of external LSA 0. Checksum Sum 0x000000 |
|
|
show ip ospf database Command |
Corp#sh ip ospf database OSPF Router with ID (223.255.255.254) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.2 966 0x80000001 0x007162 1 172.31.1.4 172.31.1.4 885 0x80000002 0x00D27E 1 192.168.10.1 192.168.10.1 886 0x8000007A 0x00BC95 3 192.168.20.1 192.168.20.1 1133 0x8000007A 0x00E348 3 223.255.255.254 223.255.255.254 925 0x8000004D 0x000B90 5 Net Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum 10.10.10.1 223.255.255.254 884 0x80000002 0x008CFE |
|
|
show ip ospf interface Command |
Corp#sh ip ospf int f0/0 FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 |
|
|
show ip ospf neighbor Command |
Corp#sh ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 |
|
|
show ip protocols Command |
Corp#sh ip protocols Routing Protocol is "ospf 1" Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Router ID 223.255.255.254 Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 172.16.10.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 172.16.10.5 0.0.0.0 area 0 Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 192.168.10.1 110 00:21:53 192.168.20.1 110 00:21:53 Distance: (default is 110) Distance: (default is 110) |
|
|
1. There are three possible routes for a router to reach a destination network. The first route is from OSPF with a metric of 782. The second route is from RIPv2 with a metric of 4. The third is from EIGRP with a composite metric of 20514560. Which route will be installed by the router in its routing table? A. RIPv2 B. EIGRP C. OSPF D. All three |
B. Only the EIGRP routes will be placed in the routing table because it has the lowest administrative distance (AD), and that is always used before metrics. |
|
|
3. Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two.) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C. It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database. D. It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router. E. All routes in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information. |
A, C. The process ID for OSPF on a router is only locally significant and you can use the same number on each router, or each router can have a different number—it just doesn’t matter. The numbers you can use are from 1 to 65,535. Don’t get this confused with area numbers, which can be from 0 to 4.2 billion. |
|
|
4. All of the following must match for two OSPF routers to become neighbors except which? A. Area ID B. Router ID C. Stub area flag D. Authentication password if using one |
B. The router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router. It need not and should not match. |
|
|
7. Which of the following statements is true with regard to the output shown? Corp#sh ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 A. There is no DR on the link to 192.168.20.1. B. The Corp router is the BDR on the link to 172.31.1.4. C. The Corp router is the DR on the link to 192.168.20.1. D. The link to 192.168.10.1 is Active. |
A. A dash (-) in the State column indicates no DR election, because they are not required on a point-to-point link such as a serial connection. |
|
|
8. What is the administrative distance of OSPF? A. 90 B. 100 C. 120 D. 110 |
D. By default the administrative distance of OSPF is 110. |
|
|
In OSPF, Hellos are sent to what IP address? A. 224.0.0.5 B. 224.0.0.9 C. 224.0.0.10 D. 224.0.0.1 |
A. Hello packets are addressed to multicast address 224.0.0.5.
|
|
|
10. What command generated the following output? 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 A. show ip ospf neighbor B. show ip ospf database C. show ip route D. show ip ospf interface |
10. A. The show ip ospf neighbor command displays all interface-related neighbor infor-mation. This output shows the DR and BDR (unless your router is the DR or BDR), the RID of all directly connected neighbors and the IP address and name of the directly con-nected interface. |
|
|
11. Updates addressed to 224.0.0.6 are destined for which type of OSPF router? A. DR B. ASBR C. ABR D. All OSPF routers |
11. A. 224.0.0.6 is used on broadcast networks to reach the DR and BDR. |
|
|
14. Type the command that will disable OSPF on the Fa0/1 interface under the routing process. Write only the command and not the prompt. |
14. passive-interface fastEthernet 0/1 The command passive-interface fastEthernet 0/1 will disable OSPF on the specified interface only. |
|
|
15. Which two of the following commands will place network 10.2.3.0/24 into area 0? (Choose two.) A. router eigrp 10 B. router ospf 10 C. router rip D. network 10.0.0.0 E. network 10.2.3.0 255.255.255.0 area 0 F. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area0 G. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 |
15. B, G. To enable OSPF, you must first start OSPF using a process ID. The number is irrelevant; just choose a number from 1 to 65,535 and you’re good to go. After you start the OSPF process, you must configure interfaces on which to activate OSPF using the network command with wildcards and specification of an area. Option F is wrong because there must be a space after the parameter area and before you list the area number. |
|
|
16. Given the following output, which statement or statements can be determined to be true? (Choose all that apply.) RouterA2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.23.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:29 10.24.4.2 FastEthernet1/0 192.168.45.2 2 FULL/BDR 00:00:24 10.1.0.5 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.85.1 1 FULL/- 00:00:33 10.6.4.10 Serial0/1 192.168.90.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:32 10.5.5.2 FastEthernet0/1 192.168.67.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:20 10.4.9.20 FastEthernet0/2 192.168.90.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:23 10.5.5.4 FastEthernet0/1 <> A. The DR for the network connected to Fa0/0 has an interface priority higher than 2. B. This router (A2) is the BDR for subnet 10.1.0.0. C. The DR for the network connected to Fa0/1 has a router ID of 10.5.5.2. D. The DR for the serial subnet is 192.168.85.1. |
16. A. The default OSPF interface priority is 1, and the highest interface priority determines the designated router (DR) for a subnet. The output indicates that the router with a router ID of 192.168.45.2 is currently the backup designated router (BDR) for the seg-ment, which indicates that another router became the DR. It can be then be assumed that the DR router has an interface priority higher than 2. (The router serving the DR func-tion is not present in the truncated sample output.) |
|
|
18. Type the command that produced the following output. Write only the command and not the prompt. FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 172.31.1. Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) |
18. show ip ospf interface The show ip ospf interface command displays all inter-face-related OSPF information. Data is displayed about OSPF information for all OSPF-enabled interfaces or for specified interfaces. |
|
|
Which of the following is the best summarization of the following networks: 192.168.128.0 through 192.168.159.0 A. 192.168.0.0/24 B. 192.168.128.0/16 C. 192.168.128.0/19 D. 192.168.128.0/20 |
20. C. If you start at 192.168.128.0 and go through 192.168.159.0, you can see this is a block of 32 in the third octet. Since the network address is always the first one in the range, the summary address is 192.168.128.0. What mask provides a block of 32 in the third octet? The answer is 255.255.224.0, or /19. |
|
|
Which of the following network addresses correctly summarizes the three networks shown below efficiently? 10.0.0.0/16 10.1.0.0/16 10.2.0.0/16 A. 10.0.0.0/15 B. 10.1.0.0/8 C. 10.0.0.0/14 D. 10.0.0.8/16 |
C. The interesting octet in this example is the second octet, and it is a block size of four starting at 10.0.0.0. By using a 255.252.0.0 mask, we are telling the summary to use a block size of four in the 2nd octet. This will cover 10.0.0.0 through 10.3.255.255. This is the best answer. |
|
|
When a ping to the local host IP address succeeds but a ping to the default gateway IP address fails, what can you rule out? (Choose all that apply.) A. The IP address of the local host is incorrect. B. The IP address of the gateway is incorrect. C. The NIC is not functional. D. The IP stack has failed to initialize. |
10. C, D. If a ping to the local host succeeds, you can rule out IP stack or NIC failure. |
|
|
When a ping to the local host IP address fails, what can you assume? A. The IP address of the local host is incorrect. B. The IP address of the remote host is incorrect. C. The NIC is not functional. D. The IP stack has failed to initialize. |
C. When a ping to the local host IP address fails, you can assume the NIC is not functional. |
|
|
Which two of the following are true regarding the distance-vector and link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.) A. Link state sends its complete routing table out of all active interfaces at periodic time intervals. B. Distance vector sends its complete routing table out of all active interfaces at periodic time intervals. C. Link state sends updates containing the state of its own links to all routers in the internetwork. D. Distance vector sends updates containing the state of its own links to all routers in the internetwork. |
B, C. The distance-vector routing protocol sends its complete routing table out of all active interfaces at periodic time intervals. Link-state routing protocols send updates containing the state of their own links to all routers in the internetwork. |
|
|
Which of the following is an advantage of static routing? A. Less overhead on the router CPU B. No bandwidth usage between routers C. Adds security D. Recovers automatically from lost routes |
D. Recovery from a lost route requires manual intervention by a human to replace the lost route. The advantages are less overhead on the router and network, as well as more security. |
|
|
Which of the following describe the process identifier that is used to run OSPF on a router? (Choose two.) A. It is locally significant. B. It is globally significant. C. It is needed to identify a unique instance of an OSPF database. D. It is an optional parameter required only if multiple OSPF processes are running on the router. E. All routes in the same OSPF area must have the same process ID if they are to exchange routing information. 4. All of the following must match for two |
A, C. The process ID for OSPF on a router is only locally significant and you can use the same number on each router, or each router can have a different number—it just doesn’t matter. The numbers you can use are from 1 to 65,535. Don’t get this confused with area numbers, which can be from 0 to 4.2 billion.
|
|
|
4. All of the following must match for two OSPF routers to become neighbors except which? A. Area ID B. Router ID C. Stub area flag D. Authentication password if using one |
B. The router ID (RID) is an IP address used to identify the router. It need not and should not match. |
|
|
You get a call from a network administrator who tells you that he typed the following into his router: Router(config)#router ospf 1 Router(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 area 0 He tells you he still can’t see any routes in the routing table. What configuration error did the administrator make? A. The wildcard mask is incorrect. B. The OSPF area is wrong. C. The OSPF process ID is incorrect. D. The AS configuration is wrong. |
A. The administrator typed in the wrong wildcard mask configuration. The wildcard should have been 0.0.0.255 or even 0.255.255.255. |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true with regard to the output shown? Corp#sh ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 A. There is no DR on the link to 192.168.20.1. B. The Corp router is the BDR on the link to 172.31.1.4. C. The Corp router is the DR on the link to 192.168.20.1. D. The link to 192.168.10.1 is Active. |
A. A dash (-) in the State column indicates no DR election, because they are not required on a point-to-point link such as a serial connection. |
|
|
What command generated the following output? 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 A. show ip ospf neighbor B. show ip ospf database C. show ip route D. show ip ospf interface |
A. show ip ospf neighbor |
|
|
Updates addressed to 224.0.0.6 are destined for which type of OSPF router? A. DR B. ASBR C. ABR D. All OSPF routers |
A. 224.0.0.6 is used on broadcast networks to reach the DR and BDR. |
|
|
A designated router is elected on ______
Each OSPF router maintains an identical database describing _____.
A Hello protocol provides _________.
A routing table contains ______. |
A designated router is elected on broadcast networks.
Each OSPF router maintains an identical database describing the AS topology.
A Hello protocol provides dynamic neighbor discovery.
A routing table contains only the best routes. |
|
|
Which two of the following commands will place network 10.2.3.0/24 into area 0? (Choose two.) A. router eigrp 10 B. router ospf 10 C. router rip D. network 10.0.0.0 E. network 10.2.3.0 255.255.255.0 area 0 F. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area0 G. network 10.2.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 |
B, G. To enable OSPF, you must first start OSPF using a process ID. The number is irrelevant; just choose a number from 1 to 65,535 and you’re good to go. After you start the OSPF process, you must configure interfaces on which to activate OSPF using the network command with wildcards and specification of an area. Option F is wrong because there must be a space after the parameter area and before you list the area number. |
|
|
Given the following output, which statement or statements can be determined to be true? (Choose all that apply.) RouterA2# show ip ospf neighbor Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 192.168.23.2 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:29 10.24.4.2 FastEthernet1/0 192.168.45.2 2 FULL/BDR 00:00:24 10.1.0.5 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.85.1 1 FULL/- 00:00:33 10.6.4.10 Serial0/1 192.168.90.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:32 10.5.5.2 FastEthernet0/1 192.168.67.3 1 FULL/DR 00:00:20 10.4.9.20 FastEthernet0/2 192.168.90.1 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:23 10.5.5.4 FastEthernet0/1 <> A. The DR for the network connected to Fa0/0 has an interface priority higher than 2. B. This router (A2) is the BDR for subnet 10.1.0.0. C. The DR for the network connected to Fa0/1 has a router ID of 10.5.5.2. D. The DR for the serial subnet is 192.168.85.1. |
A. The default OSPF interface priority is 1, and the highest interface priority determines the designated router (DR) for a subnet. The output indicates that the router with a router ID of 192.168.45.2 is currently the backup designated router (BDR) for the segment, which indicates that another router became the DR. It can be then be assumed that the DR router has an interface priority higher than 2. (The router serving the DR function is not present in the truncated sample output.) |
|
|
What are three reasons for creating OSPF in a hierarchical design? (Choose three.) A. To decrease routing overhead B. To speed up convergence C. To confine network instability to single areas of the network D. To make configuring OSPF easier |
A, B, C. OSPF is created in a hierarchical design, not a flat design like RIP. This decreases routing overhead, speeds up convergence, and confines network instability to a single area of the network. |
|
|
18. Type the command that produced the following output. Write only the command and not the prompt. FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 172.31.1. Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) |
18. Type the command that produced the following output. Write only the command and not the prompt. FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 Last flood scan time is 0 msec, maximum is 0 msec Neighbor Count is 1, Adjacent neighbor count is 1 Adjacent with neighbor 172.31.1. Suppress hello for 0 neighbor(s) |
|
|
config corp router with default route towards interent |
Corp#config t Corp(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 Fa0/0 Corp(config)#router ospf 1 Corp(config-router)#default-information originate |
|
|
Configuring Loopback Interfaces ospf |
SF#config t SF(config)#int loopback 0 *Mar 22 01:25:11.206: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Loopback0, changed state to up SF(config-if)#ip address 172.31.1.2 255.255.255.255 |
|
|
sh ip ospf database |
OSPF Router with ID (223.255.255.254) (Process ID 1) Router Link States (Area 0) Link ID ADV Router Age Seq# Checksum Link count 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.2 966 0x80000001 0x007162 1 172.31.1.4 172.31.1.4 885 0x80000002 0x00D27E 1 192.168.10.1 192.168.10.1 886 0x8000007A 0x00BC95 3 192.168.20.1 192.168.20.1 1133 0x8000007A 0x00E348 3 223.255.255.254 223.255.255.254 925 0x8000004D 0x000B90 5 |
|
|
show ip ospf interface |
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up Internet Address 10.10.10.1/24, Area 0 Process ID 1, Router ID 223.255.255.254, Network Type BROADCAST, Cost: 1 Transmit Delay is 1 sec, State DR, Priority 1 Designated Router (ID) 223.255.255.254, Interface address 10.10.10.1 Backup Designated router (ID) 172.31.1.4, Interface address 10.10.10.2 Timer intervals configured, Hello 10, Dead 40, Wait 40, Retransmit 5 oob-resync timeout 40 Hello due in 00:00:08 Supports Link-local Signaling (LLS) Cisco NSF helper support enabled IETF NSF helper support enabled Index 3/3, flood queue length 0 Next 0x0(0)/0x0(0) Last flood scan length is 1, maximum is 1 |
|
|
show ip ospf neighbor Command |
Neighbor ID Pri State Dead Time Address Interface 172.31.1.4 1 FULL/BDR 00:00:34 10.10.10.2 FastEthernet0/0 192.168.20.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:31 172.16.10.6 Serial0/1 192.168.10.1 0 FULL/ - 00:00:32 172.16.10.2 Serial0/0 |
|
|
show ip protocols Command |
Routing Protocol is "ospf 1" Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set Router ID 223.255.255.254 Number of areas in this router is 1. 1 normal 0 stub 0 nssa Maximum path: 4 Routing for Networks: 10.10.10.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 172.16.10.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 172.16.10.5 0.0.0.0 area 0 Reference bandwidth unit is 100 mbps Routing Information Sources: Gateway Distance Last Update 192.168.10.1 110 00:21:53 192.168.20.1 110 00:21:53 Distance: (default is 110) Distance: (default is 110) |
|
|
Voice access ports |
Nowadays, most switches will allow you to add a second VLAN to an access port on a switch port for your voice traffic, called the voice VLAN. The voice VLAN used to be called the auxiliary VLAN, which allowed it to be overlaid on top of the data VLAN, enabling both types of traffic to travel through the same port. Even though this is technically considered to be a different type of link, it’s still just an access port that can be configured for both data and voice VLANs. This allows you to connect both a phone and a PC device to one switch port but still have each device in a separate VLAN. |
|
|
Trunk ports |
Believe it or not, the term trunk port was inspired by the telephone system trunks, which carry multiple telephone conversations at a time. So it follows that trunk ports can similarly carry multiple VLANs at a time as well |
|
|
ISL def |
Inter-Switch Link (ISL)
proprietary to Cisco encapsulates the frame |
|
|
802.1q |
inserts a field into the frame to identify the VLAN |
|
|
using unassigned VLANs |
Remember that a created VLAN is unused until it is assigned to a switch port or ports and that all ports are always assigned in VLAN 1 unless set otherwise. |
|
|
show vlan |
VLAN Name Status Ports ---- ------------------------- --------- ------------------------------- 1 default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4 Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8 Fa0/9, Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/12 Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/19, Fa0/20 Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Gi0/1 Gi0/2 2 Sales active 3 Marketing active 4 Accounting active [output cut] |
|
|
change, delete, or rename VLAN 1 |
You can’t change, delete, or rename VLAN 1 because it’s the default VLAN and you just can’t change it |
|
|
DTP |
Dynamic Trunk Protocol - Cisco proprietary
if there is a compatible switch connected, they will start trunking automatically, which is precisely where my four ports are
is used for negotiating trunking on a link between two devices as well as negotiating the encapsulation type of either 802.1q or ISL. I use the nonegotiate command when I want dedicated trunk ports; no questions asked.
|
|
|
S1# show interfaces trunk |
S1# show interfaces trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Fa0/15 desirable n-isl trunking 1 Fa0/16 desirable n-isl trunking 1 Fa0/17 desirable n-isl trunking 1 Fa0/18 desirable n-isl trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Fa0/15 1-4094 Fa0/16 1-4094 Fa0/17 1-4094 Fa0/18 1-4094 |
|
|
S1#sh interfaces fastEthernet 0/15 switchport Name: Fa0/15 Switchport: Enabled Administrative Mode: dynamic desirable Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: negotiate Operational Trunking Encapsulation: isl Negotiation of Trunking: On Access Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Administrative Native VLAN tagging: enabled Voice VLAN: none [output cut] |
The highlighted output shows us the administrative mode of dynamic desirable, that the port is a trunk port, and that DTP was used to negotiate the frame tagging method of ISL. It also predictably shows that the native VLAN is the default of 1. |
|
|
configure interface Fa0/3 to VLAN 3. |
S3#config t S3(config)#int fa0/3 S3(config-if)#switchport mode access S3(config-if)#switchport access vlan 3 |
|
|
trunk configuration on interfaces Fa0/15–18 as set to trunk: |
S1(config)#int range f0/15-18 S1(config-if-range)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q S1(config-if-range)#switchport mode trunk |
|
|
switchport mode dynamic auto (expl) |
This mode makes the interface able to convert the link to a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk or desirable mode. The default is dynamic auto on a lot of Cisco switches, but that default trunk method is changing to dynamic desirable on most new models. |
|
|
switchport mode dynamic desirable (expl) |
This one makes the interface actively attempt to convert the link to a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface if the neighboring interface is set to trunk, desirable, or auto mode. I used to see this mode as the default on some switches, but not any longer. This is now the default switch port mode for all Ethernet interfaces on all new Cisco switches. |
|
|
switchport mode trunk (expl) |
Puts the interface into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the neighboring link into a trunk link. The interface becomes a trunk interface even if the neighboring interface isn’t a trunk interface. |
|
|
switchport nonegotiate (expl) |
Prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. You can use this command only when the interface switchport mode is access or trunk. You must manually configure the neighboring interface as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link. |
|
|
configured on S1 port F0/15, causing it to drop all traffic sent and received for VLANs 4, 6, 12, and |
S1(config)#int f0/15 S1(config-if)#switchport trunk allowed vlan 4,6,12,15 |
|
|
change the native VLAN, use the following command |
S1(config)#int f0/15 S1(config-if)#switchport trunk native vlan 4 |
|
|
Standard access lists |
These ACLs use only the source IP address in an IP packet as the condition test. All decisions are made based on the source IP address. This means that standard access lists basically permit or deny an entire suite of protocols. They don’t distinguish between any of the many types of IP traffic such as Web, Telnet, UDP, and so on. |
|
|
Extended access lists |
Extended access lists can evaluate many of the other fields in the layer 3 and layer 4 headers of an IP packet. They can evaluate source and destination IP addresses, the Protocol field in the Network layer header, and the port number at the Transport layer header. This gives extended access lists the ability to make much more granular decisions when controlling traffic. |
|
|
Named access lists |
named access lists are either standard or extended and not actually a distinct type |
|
|
Inbound access lists |
When an access list is applied to inbound packets on an interface, those packets are processed through the access list before being routed to the outbound interface. Any packets that are denied won’t be routed because they’re discarded before the routing process is invoked. |
|
|
Outbound access lists |
When an access list is applied to outbound packets on an interface, packets are routed to the outbound interface and then processed through the access list before being queued. |
|
|
access-list numbers 1–99 or 1300–1999 |
access-list numbers 1–99 or 1300–1999, you’re telling the router that you want to create a standard IP access list, which means you can only filter on source IP address. |
|
|
this cmd tells the list to deny any packets from host 172.16.30.2. |
access-list 10 deny host 172.16.30.2 |
|
|
Corp(config)#access-list 10 deny 172.16.16.0 0.0.7.255 |
This example reveals an access list starting at 172.16.16.0 going up a block size of 8 to 172.16.23.255. |
|
|
When you use a web browser to make an HTTP connection toan IPv6 device, you have to type the address into the browser with brackets around theliteral address.
|
example
http://[2001:0db8:3c4d:0012:0000:0000:1234:56ab]/default.html |
|
|
Global unicast addresses
|
2000::/3
|
|
|
Link-local addresses
|
FE80::/10
|
|
|
Unique local addresses
|
FC00::/7
intended for nonrouting purposesover the Internet, but they are nearly globally unique |
|
|
Multicast
|
FF00::/8
packets addressed to a multicast address aredelivered to all interfaces tuned into the multicast address aka one to many |
|
|
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
|
Equals ::. This is the equivalent of IPv4’s 0.0.0.0 and is typicallythe source address of a host before the host receives an IPaddress when you’re using DHCP-driven stateful configuration.
|
|
|
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1
|
Equals ::1. The equivalent of 127.0.0.1 in IPv4.
|
|
|
0:0:0:0:0:0:192.168.100.1
|
This is how an IPv4 address would be written in a mixed IPv6/IPv4 network environment.
|
|
|
The global unicast address range.
|
2000::/3
|
|
|
The unique local unicast range.
|
FC00::/7
|
|
|
The link-local unicast range.
|
FE80::/10
|
|
|
The multicast range.
|
FF00::/8
|
|
|
3FFF:FFFF::/32
|
Reserved for examples and documentation.
|
|
|
2001:0DB8::/32
|
Also reserved for examples and documentation.
|
|
|
2002::/16
|
Used with 6-to-4 tunneling, which is an IPv4-to-IPv6 transitionsystem. The structure allows IPv6 packets to be transmitted overan IPv4 network without the need to configure explicit tunnels.
|
|
|
ipv6 unicast-routing global configurationcommand:
|
Corp(config)#ipv6 unicast-routing
By default, IPv6 traffic forwarding is disabled, so using this command enables it. Also,as you’ve probably guessed, IPv6 isn’t enabled by default on any interfaces either, so wehave to go to each interface individually and enable it. |
|
|
EUI
|
extendedunique identifier
|
|
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration (eui-64)Autoconfiguration is an especially useful solution because it allows devices on a network toaddress themselves with a link-local unicast address as well as with a global unicast address.
This process happens through first learning the prefix information from the router and thenappending the device’s own interface address as the interface ID. physical MACaddress, which is exactly what’s used for the interface ID. But since the interface ID in anIPv6 address is 64 bits in length and a MAC address is only 48 bits, where do the extra 16bits come from? The MAC address is padded in the middle with the extra bits—it’s paddedwith FFFE.For example, let’s say I have a device with a MAC address that looks like this:0060:d673:1987. After it’s been padded, it would look like this: 0260:d6FF:FE73:1987. |
|
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration example 0090:2716:fd0f
|
MAC address 0090:2716:fd0f
IPv6 EUI-64 address: 2001:0db8:0:1:0290:27ff:fe16:fd0f |
|
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration example MAC address aa12:bcbc:1234
|
MAC address aa12:bcbc:1234
IPv6 EUI-64 address: 2001:0db8:0:1:a812:bcff:febc:1234 |
|
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration example MAC address 0c0c:dede:1234
|
MAC address 0c0c:dede:1234
IPv6 EUI-64 address: 2001:0db8:0:1:0e0c:deff:fede:1234 |
|
|
Stateless Autoconfiguration example MAC address 0b34:ba12:1234
|
MAC address 0b34:ba12:1234
IPv6 EUI-64 address: 2001:0db8:0:1:0934:baff:fe12:1234 |
|
|
To perform autoconfiguration, a host goes through a basic two-step process:
|
1. First, the host needs the prefix information, similar to the network portion of an IPv4address, to configure its interface, so it sends a router solicitation (RS) request for it.This RS is then sent out as a multicast to all routers (FF02::2). The actual informationbeing sent is a type of ICMP message, and like everything in networking, this ICMPmessage has a number that identifies it. The RS message is ICMP type 133.2. The router answers back with the required prefix information via a router advertisement(RA). An RA message also happens to be a multicast packet that’s sent to the all-nodesmulticast address (FF02::1) and is ICMP type 134. RA messages are sent on a periodicbasis, but the host sends the RS for an immediate response so it doesn’t have to wait untilthe next scheduled RA to get what it needs.
|
|
|
The IPv6 equivalent to IPv4 0.0.0.0 |
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or ::. Equivalent to IPv4s 0.0.0.0 and is typically the source address of a host before the host receives an IP address |
|
|
The IPv6 equivalent to 127.0.0.1 |
0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1 |
|
|
How an IPv5 address would be written in a mixed IPv6/IPv6 network environment |
0:0:0:0:0:0:192.168.10.1 |
|
|
The global unicast address range |
2000::/3 |
|
|
The unique local unicast range |
FC00::/7 |
|
|
The link-local unicast range |
FE80::/10 |
|
|
The multicast rane |
FF00::/8 |
|
|
IPv6 Reserved for sample documentation |
3FFF:FFFF::/32 |
|
|
IPv6 range used for 6-to-4 tunneling |
2002::/16 |
|
|
A switch user is currently in console line configuration mode. Which of the following would place the user in enable mode? (Choose two answers.) a) Using the exit command once b) Using the quit command c) Pressing the Ctrl-Z key sequence once d) Using the end command once |
cd Answer options D and C are correct.The exit command moves the user one config mode backward, toward global configuration mode, or if already in global configuration mode, it moves the user back to enable mode. From console mode, it moves the user back to global configuration mode. The end command and the Ctrl-Z key sequence both move the user back to enable mode regardless of the current configuration submode. |
|
|
Fred has just added DSL service at his home, with a separate DSL modem and consumer-grade router with four Ethernet ports. Fred wants to use the same old phone he was using before the installation of DSL. Which is most likely true about the phone cabling and phone used with his new DSL installation? a)The old phone must be replaced with a digital phone.b)He uses the old phone, cabled to one of the router/switch device's Ethernet ports. c)He uses the old phone, cabled to the DSL modem's ports. d)He uses the old phone, cabled to an existing telephone port, and not to any new device. |
Answer option D is correct.With DSL, the requirements on the phone’s wiring are unchanged. The phone can connect to any working telephone jack, as if the DSL modem and router did not exist. |
|
|
Which of the following Internet access technologies, used to connect a site to an ISP, offers asymmetric speeds? (Choose two answers.) a)BGP b)Cable Internet c)DSL d)Leased lines |
Answer options C and B are correct.Leased lines transmit data at the same speed in both directions, making it a symmetric service. DSL and cable Internet offer asymmetric speeds, with a faster downstream speed. BGP is a routing protocol and is not an Internet access technology. |
|
|
Two routers, R1 and R2, connect using an Ethernet over MPLS service. The service provides point-to-point service between these two routers only, as a Layer 2 Ethernet service. Which of the following are the most likely to be true about this WAN? (Choose two answers.) a) R1 will forward data link frames to R2 using an Ethernet header/trailer. b) R1 will connect to a physical Ethernet link, with the other end of the cable connected to R2. c) R1 will connect to a physical Ethernet link, with the other end of the cable connected to a device at the WAN service provider point of presence. d) R1 will forward data link frames to R2 using an HDLC header/trailer. |
Answer options C and A are correct.The physical installation uses a model in which each router uses a physical Ethernet link to connect to some SP device in an SP facility called a point of presence (POP). The Ethernet link does not span from each customer device to the other. From a data link perspective, both routers use the same Ethernet standard header and trailer used on LANs; HDLC does not matter on these Ethernet WAN links. |
|
|
Which of the following fields in an HDLC header is equivalent to Preamble in an Ethernet header? a) FCS b) Flag c) Address d) Type |
Answer option B is correct. The Flag field in an HDLC header is equivalent to Preamble in an Ethernet header. |
|
|
The CSU/DSU device is used in ________ . a)WAN connectivity b)LAN and WAN connectivity c)None of the above d)LAN connectivity |
Answer option B is correct. CSU/DSU is a WAN device that connects LANs to WANs. |
|
|
What Ethernet standard was improved to make it viable as a WAN technology? a) Cable length b) Devices c) Popularity d) Speed |
Answer option A is correct. As the IEEE improved cabling distances for fiber Ethernet links, Ethernet became a reasonable WAN technology. |
|
|
Which of the following is not true when comparing DSL to cable Internet service? a) Cable speeds are faster b) Both are "always on" c) Both support asymmetric speeds d) Cable costs about the same as DSL |
Answer option D is correct. DSL providers charge less to compensate for slower speeds. |
|
|
Which of the following is not a characteristic of leased lines? a) All of the answers are correct. b) Use full-duplex logic c) Deliver bits in both directions d) Have a predetermined speed |
Answer option A is correct. The leased-line service delivers bits in both directions, at a predetermined speed, using full-duplex logic. |

