![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Trigeminal Nerve
|
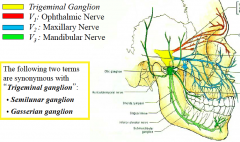
(V1, V2 and V3 carry sensory information; V3 also has a motor component)
Trigeminal Ganglion V1: Ophthalmic Nerve V2 : Maxillary Nerve V3 : Mandibular Nerve |
|
|
Nuclei of the Trigeminal nerve (general)
|
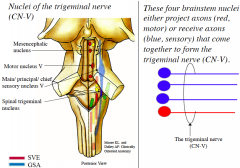
|
|
|
4 Nuclei of the Trigeminal nerve (3 sensory, 1 motor)
|

|
|
|
Describe the course of CN- V from the point that it emerges from the brainstem to where V1, V2 and V3 leave the cranial cavity
|
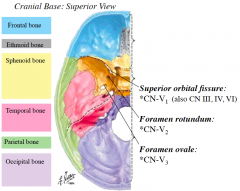
-When the trigeminal nerve emerges from the brainstem, it courses anteriorly through the middle cranial fossa
-From the trigeminal ganglion, located on the floor of the middle cranial fossa, emerges V1, V2 and V3 -V1, V2 and V3 leave the cranial cavity via openings in the middle cranial fossa |
|
|
supraorbital
|
skin of middle of superior eyelid; skin of the anterolateral forehead and scalp to vertex.
|
|
|
supratrochlear
|
Skin of the medial aspect of superior eyelid; skin of anteromedial forehead
|
|
|
Lacrimal
|
small area of skin of lateral part of superior eyelid
|
|
|
Infratrochlear
|
Skin lateral to root of nose; skin of eyelids adjacent to medial canthus, lacrimal sac, and lacrimal caruncle
|
|
|
External nasal
|
Skin of nasal ala, vestibule, and dorsum of nose, including apex
|
|
|
Infraorbital
|
Skin of inferior eyelid; skin of cheek, lateral nose, and anteroinferior nasal septum; skin of superior lip
|
|
|
Zygomaticofacial
|
Skin on prominence of cheek
|
|
|
Zygomaticotemporal
|
Hairless skin anterior part of temporal fossa
|
|
|
Aurioculotemporal
|
Skin anterior to auricle and posterior two thirds of temporal region; skin of tragus and adjacent helix of auricle; skin of roof of external acoustic meatus; skin of superior tympanic membrane
|
|
|
Buccal
|
Skin of cheek (over-lying and deep to anterior part of buccinator)
|
|
|
Mental
|
Skin of chin
|
|
|
Organization of the Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus (Subdivisions)
|
1. Pars Oralis (Oral Nucleus): located most rostral, this nucleus extends from the main sensory nucleus (mid pons) to the pontomedullary junction.
2. Pars Interpolaris (Interpolar Nucleus): located in middle position, this nucleus extends from the pontomedullary junction to the level of the obex (the obex marks the caudal end of the fourth ventricle). 3. Pars Caudalis (Caudal Nucleus): located caudally, this nucleus extends from the obex to spinal cord (C2-C3). |
|
|
Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus facial representation
|
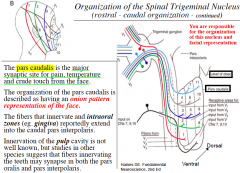
|

