![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four functions of the digestive system?
|
Ingest food
Digest food Absorb nutrients Eliminate indigestible waste |
|
|
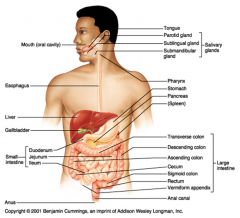
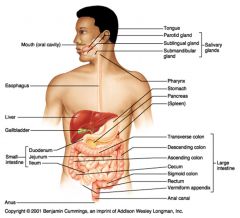
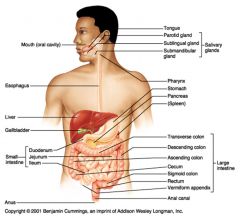
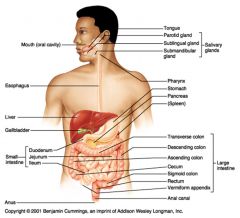
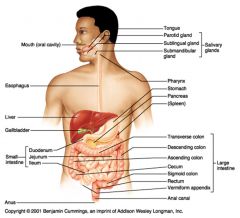
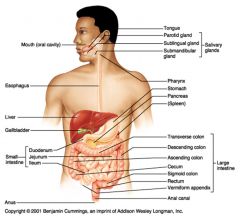
What seven organs are considered to be part of the alimentary canal?
|
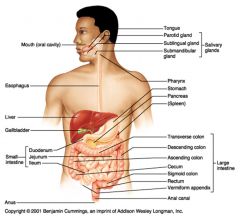
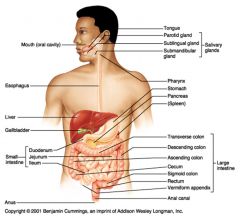
Mouth
Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Anus |
|
|
What six organs are considered to be accessory organs in the digestive system?
|
Teeth
Tongue Salivary glands Gall bladder Liver Pancreas |
|
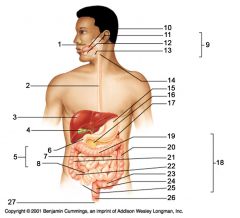
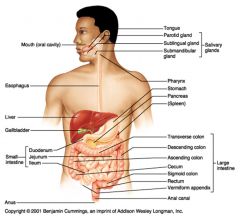
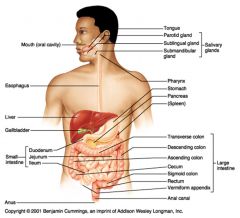
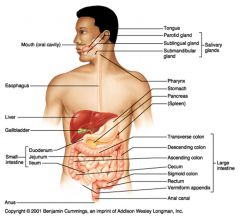
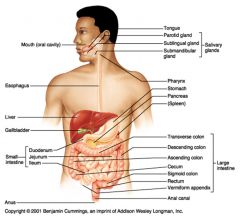
Identify 3
|
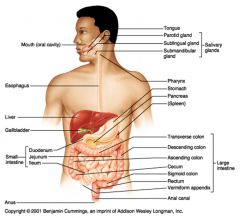
Liver
|
|
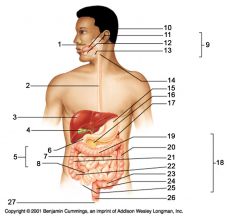
Identify 4
|
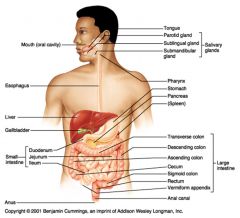
Gallbladder
|
|
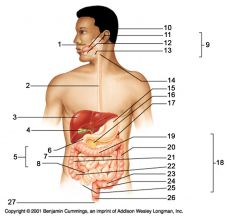
Identify 5
|
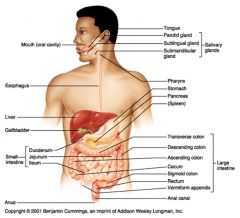
Small intestine
|
|
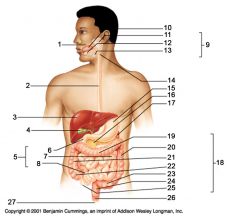
Identify 6
|
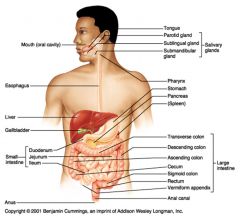
Duodenum
|
|
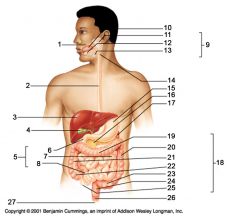
Identify 7
|
Jejunum
|
|
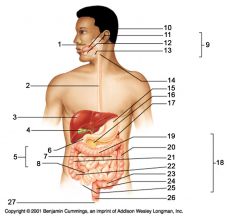
Identify 8
|
Ileum
|
|
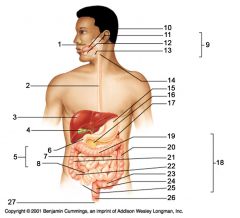
Identify 15
|
Stomach
|
|
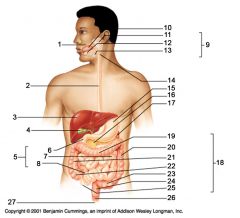
Identify 16
|
Pancreas
|
|
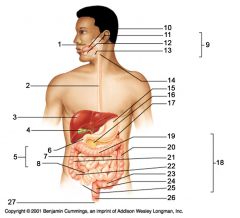
Identify 17
|
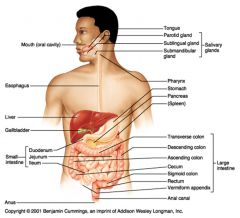
Spleen
|
|
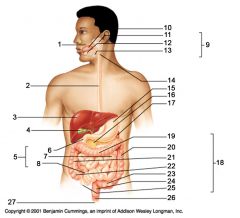
Identify 18
|
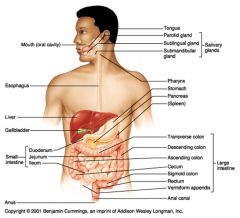
Large intestine
|
|
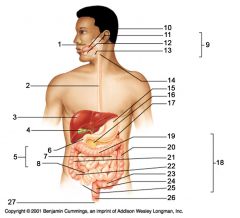
Identify 19
|
Transverse colon
|
|
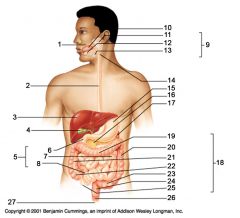
Identify 20
|
Descending colon
|
|
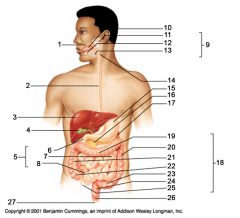
Identify 21
|
Ascending colon
|
|
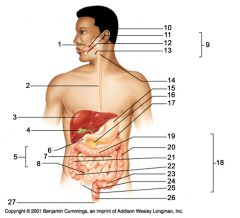
Identify 22
|
Cecum
|
|
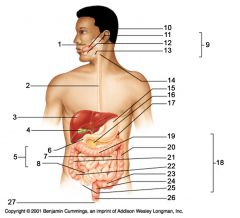
Identify 23
|
Sigmoid colon
|
|
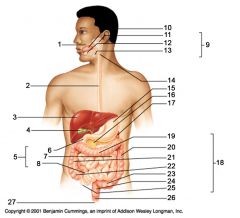
Identify 24
|
Rectum
|
|
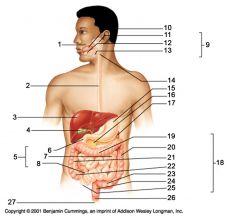
Identify 25
|
appendix
|
|
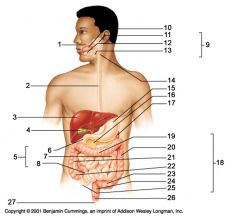
Identify 26
|
Anal canal
|
|
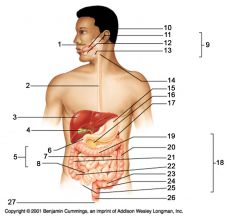
Identify 27
|
Anus
|
|
|
Name the portions of the small intestine, in the order that food would encounter them.
|
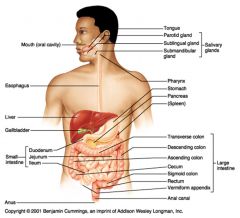
Enters the small intestine from the stomach through the pyloric sphincter:
Duodenum > Jejunum > Ileum Exits from the small intestine to the large intestine through the ileocecal sphincter |
|
|
Name the portions of the areas of the large intestine, in the order that food would encounter them.
|
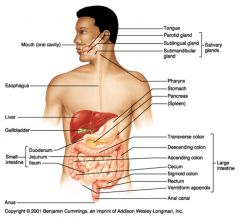
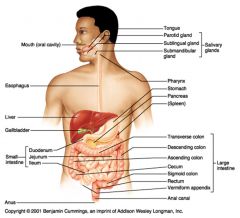
Enters from the small intestine to the large intestine through the ileocecal sphincter
Cecum (passing, but not entering the Vermiform appendix) > Ascending colon (along right side of body) > Transverse colon (from right to left side of body) > Descending colon (along left side of body) > Sigmoid colon > Rectum Exits the large intestine through the two anal sphincters and out of the body via the anus |
|
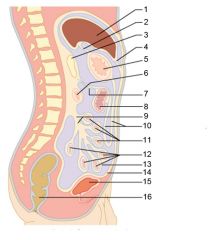
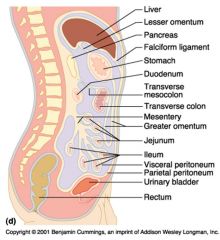
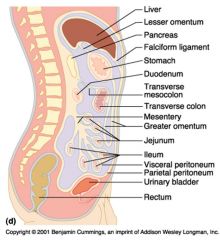
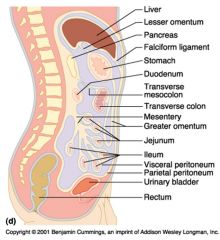
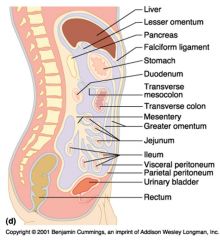
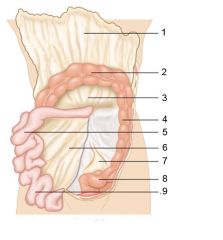
Identify 5
|
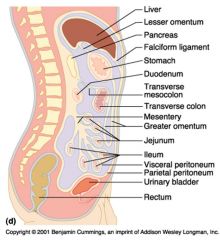
Stomach
|
|
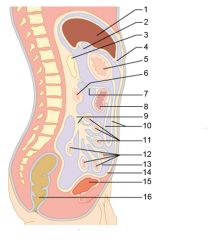
Identify 6
|
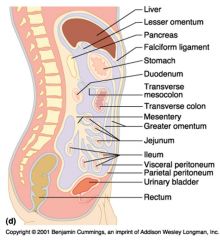
Duodenum
|
|
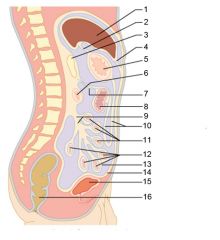
Identify 7
|
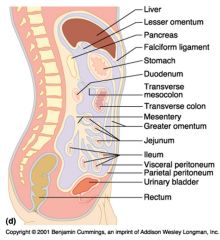
Transverse mesocolon
|
|
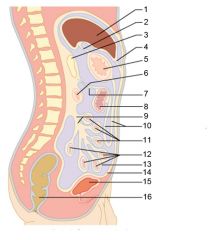
Identify 8
|
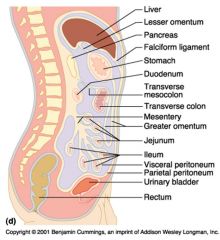
Transverse colon
|
|
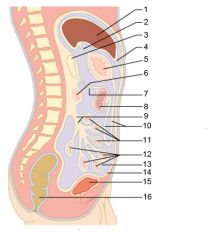
Identify 9
|
Mesentery
|
|
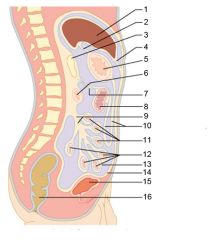
Identify 10
|
Greater omentum
|
|
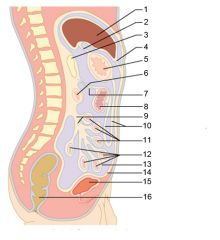
Identify 11
|
Jejunum
|
|
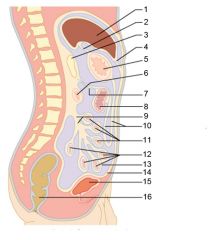
Identify 12
|
Ileum
|
|
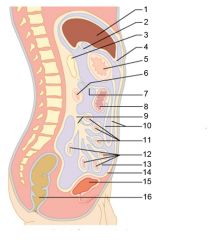
Identify 15
|
Urinary bladder
|
|
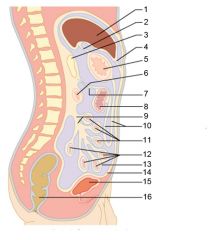
Identify 16
|
Rectum
|
|
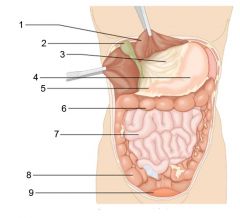
Identify 1
|
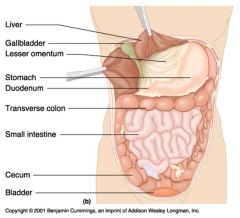
Liver
|
|
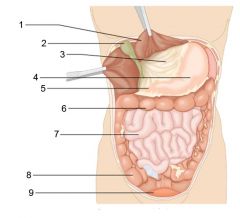
Identify 2
|
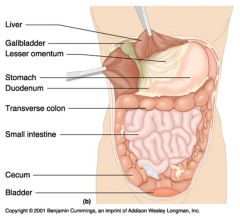
Gallbladder
|
|
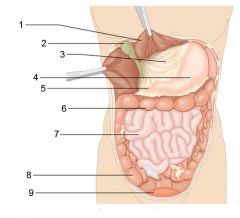
Identify 3
|
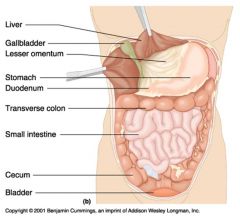
Lesser omentum
|
|
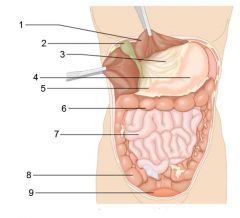
Identify 4
|
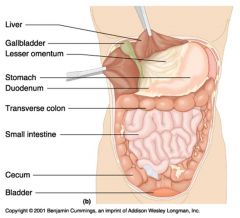
Stomach
|
|
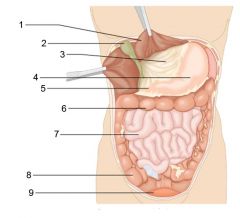
Identify 5
|
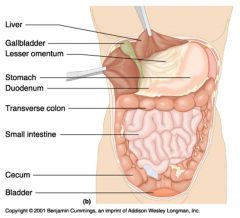
Duodenum
|
|
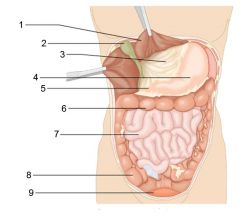
Identify 6
|
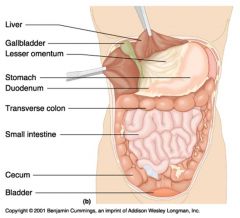
Transverse colon
|
|
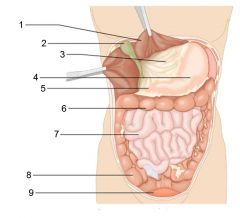
Identify 7
|
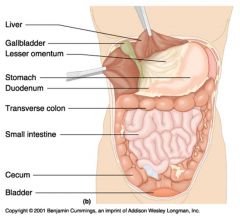
Small intestine
|
|
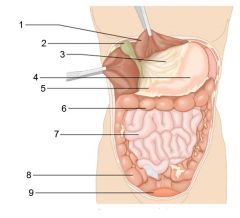
Identify 8
|
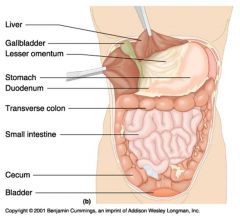
Cecum
|
|
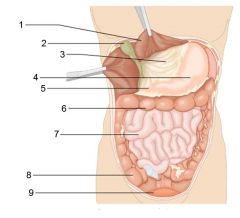
Identify 9
|
Bladder
|
|
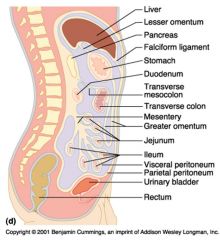
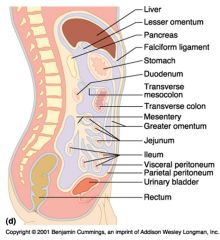
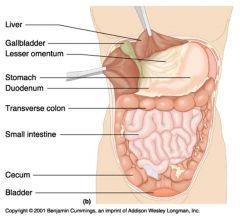
Identify 1
|
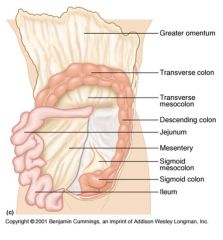
Greater omentum
|
|
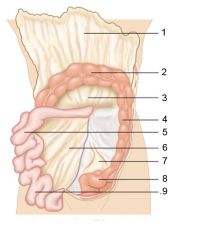
Identify 2
|
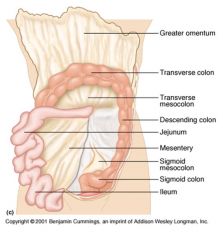
Transverse colon
|
|
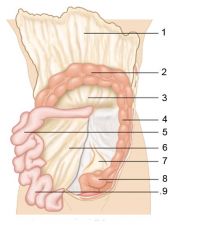
Identify 3
|
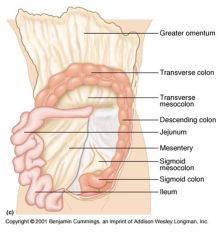
Transverse mesocolon
|
|
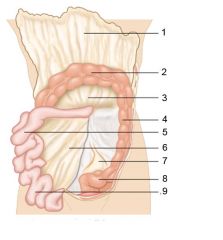
Identify 4
|
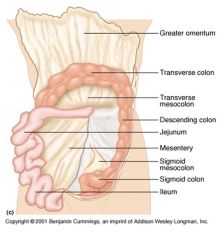
Descending colon
|
|
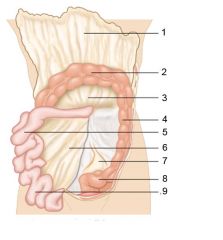
Identify 5
|
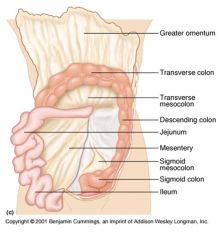
Jejunum
|
|
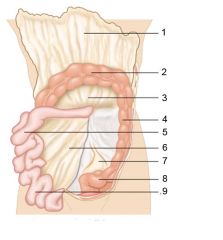
Identify 6
|
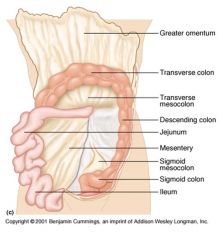
Mesentery
|
|
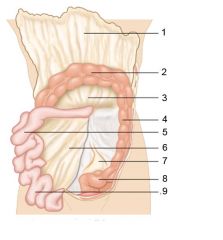
Identify 7
|
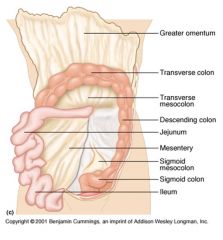
Sigmoid mesocolon
|
|
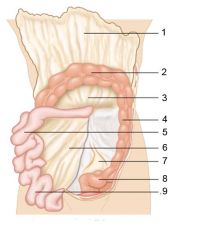
Identify 8
|
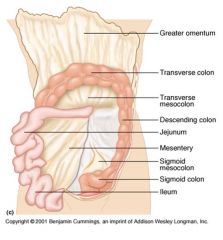
Sigmoid colon
|
|
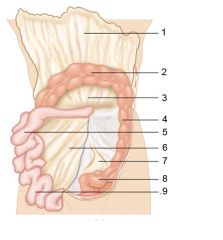
Identify 9
|
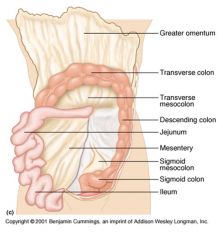
Ileum
|
|
|
When a substance is added to Lugol's solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for starch. The solution turns blue/black in the presence of starch.
|
|
|
When a substance is added to Benedict's solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for sugar. The solution (originally blue) will turn green, yellow, or red, depending on the amount of sugar present, or remain blue if none is present.
|
|
|
When a substance is added to a BAPNA solution, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing for Tripsyn, which breaks down proteins. The solution will turn yellow if Tripsyn is present.
|
|
|
When you test as substance using litmus blue, what are you testing for? What is a positive indicator?
|
You are testing acidity. Litmus blue changes from blue to pink as the tested substance becomes more acidic.
|
|
|
path of food digestion in humans
|
esophagus > stomach > pyloric sphincter > small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) > ileocecal sphincter > large intestine (ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon) > rectum > anus
|
|
|
Stomach
|
temporary food storage, most acidic part of the body (pH 1.5-3), acidic chime exits the stomach through the pyloric sphincter
|
|
|
Duodenum
|
1st section of the small intestine
pancreatic enzyme and bile secretion mixed into the chime, neutralizes stomach acids, Brunner glands |
|
|
jejunum
|
2nd section of the small intestine
majority of digestion and nutrient absorption |
|
|
Ileum
|
3rd section of the small intestine
peyer’s patches, ends at ileocecal junction |
|
|
Large intestines
|
bacteria flora, water removal, fecal compression
Ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid colon Rectum: straight portion ending at anal canal |
|
|
What is the path of food digestion in Aves?
|
Esophagus > Crop > Proventriculus > Gizzard > Small intestines > Large intestines > Cloaca
|
|
|
crop
|
temporary food storage
(Aves) |
|
|
Proventriculus
|
no storage function, mixes food with pepsin, little acid production
(Aves) |
|
|
Gizzard
|
macerates food
(Aves) |
|
|
Cloaca
|
common opening for the gastrointestinal, urinary and genital system
|
|
|
enzymes
|
large protein molecules that function as biological catalysts
increase the rate of reaction without being part of the product |

