![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the diagnostic, surgical, and adjunctive treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects involving both the functional and the aesthetic aspects of the hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial regions |
oral and maxillofacial surgery |
|
|
act of breaking or condition of being broken into small fragments |
comminution |
|
|
a hemorrhagic spot, larger than a petechia, in the skin or mucous membrane caused by extravasation of blood; forms a nonelevated, rounded, or irregular purplish patch |
ecchymosis |
|
|
branch of dentistry dealing with the surgical removal of teeth |
exodontics |
|
|
benign new growth projecting from the surface of bone |
exostosis |
|
|
fixation of the maxilla in occlusion with the mandible held in place by means of wires and elastic bands; the healing parts are stabilized following fracture or surgery |
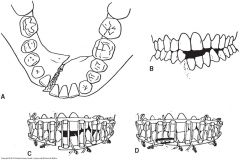
intermaxillary fixation |
|
|
pertaining to the jaws and the face |
maxillofacial |
|
|
the branch of prosthodontics concerned with the restoration of the mouth and jaws and associated facial structures that have been affected by disease, injury, surgery, or a congenital defect |
maxillofacial prosthetics |
|
|
surgery to alter relationships of the dental arches and/or supporting bone; usually coordinated with orthodontic therapy |
orthognathic surgery |
|
|
science dealing with the causes and treatment of malposition of the bones of the jaws |
orthognathics |
|
|
internal fixation of a fracture by mechanical means, such as metal plates, pins, or screws |
osteosynthesis |
|
|
a method of internal fixation of mandibular fractures utilizing miniaturized metal plates and screws formerly made of titanium or stainless steel and currently made primarily of biodegradable or resorbable synthetic materials |
miniplate osteosynthesis |
|
|
motor disturbance of the trigeminal nerve with spasm of masticatory muscles and difficulty in opening the mouth (lockjaw) |
trismus |
|
|
What are the objectives for patient preparation prior to oral and maxillofacial surgery? |
|
|
|
What are some personal factors that may need to be addressed prior to maxillofacial surgery? |
Apprehensive and Fearful Resigned Discouraged |
|
|
What are two causes of fractured jaws? |
Traumatic and Predisposing |
|
|
A fracture is classified by using a combination of descriptive words for its.... |
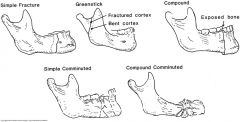
Location Direction Nature Severity |
|
|
has no communication with outside |
simple fracture |
|
|
has communication with outside |
compound fracture |
|
|
shattered |
comminuted fracture |
|
|
fracture has one side of bone broken and the other side bent; occurs in incompletely calcified bones |
incomplete (greenstick) |
|
|
classification used widely to identify the three general levels of maxillary fractures |
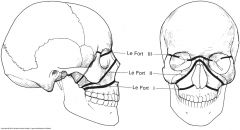
Le Fort |
|
|
a horizontal fracture line that extends above the roots of the teeth, above the palate, across the maxillary sinus, below the zygomatic process, and across the pterygoid plates |
Le Fort I |
|
|
the midface fracture extends over the middle of the nose, down the medial wall of the orbits, across the infraorbital rims, and posteriorly, across the pterygoid plates |
Le Fort II |
|
|
the high-level craniofacial fracture extends transversely across the bridge of the nose, across the orbits and the zygomatic arches, and across the pterygoid plates |
Le Fort III |
|
|
On average, how long does it take a maxillary fracture to heal without complications? |
4 to 6 weeks |
|
|
On average, how long does it take a mandibular fracture to heal without complications? |
6 weeks |
|
|
What is the major cause of complications with fractured jaws? |
infection |
|
|
the positioning of the parts on either side of the fracture so they are in apposition for healing and restoration of function |
reduction |
|
|
refers to the use of a surgical flap procedure to expose the fracture ends and bring them together for healing |
open reduction |
|
|
accomplished by manipulation of the parts without surgery |
closed reduction |
|
|
two special bone screws are placed via skin incisions on either side of the fracture; an acrylic bar is molded and, while still pliable, is pressed over the threads of the bone screws and locked into position with the screw nuts |
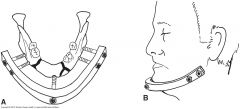
external skeletal fixation |

