![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
215 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the electrolyte disturbances that occur in beer potomania?
|
large alcohol consumption → dietary sodium and protein insufficiency → dilutional hyponatremia
|
|
|
|
What should you order to assess ventilation?
|
PFTs
|
|
|
|
What are the electrolyte disturbances that occur in aldosteronsim?
|
hypernatremia
hypokalemia increased bicarb |
|
|
|
List categories of tests to think about when evaluating the liver.
|
1. synthetic liver function
2. excretory liver function and cholestasis 3. hepatocellular injury 4. detoxifying liver function and serum ammonia 5. specific diseases |
|
|
|
What are the electrolyte disturbances that occur in diabetes insipidus?
|
diabetes insipidus → dehydration → hypernatremia
|
|
|
|
What should you order to assess oxygenation?
|
pulse oximetry
ABG |
|
|
|
What is aldosteronism?
|
oversecretion of aldosterone from adrenal glands independent of renin
aldosterone causes increased sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion |
|
|
|
What is the normal pH of the vagina?
|
3.5-4.0
|
Current OB/Gyn
|
|
|
What are the normal and critical values for serum calcium?
|
NORMAL:
8.5-10.5 mg/dL CRITICAL: <6.5 mg/dL >13.5 mg/dL |
|
|
|
What does ABG stand for?
|
arterial blood gas
|
|
|
|
What are the normal and critical values for serum magnesium?
|
NORMAL:
1.8-3.0 mg/dL CRITICAL: <0.5 mg/dL >4.5 mg/dL |
|
|
|
What is included in an LFT panel?
|
ALT
AST bilirubin alkaline phosphatase albumin |
|
|
|
What are the normal and critical values for serum phosphate?
|
NORMAL:
2.5-4.5 mg/dL CRITICAL: <1.0 mg/dL |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering an ABG?
|
dyspnea, tachypnea
suspected respiratory, renal, metabolic, or acid-base disorder |
|
|
|
What is serum fructosamine?
|
formed by glycosylation of serum proteins (primarily albumin)
test evaluates glucose control in last 1-3 weeks (average lifespan of plasma proteins) fingerstick or venipuncture used to monitor DM instead of A1C when: recent change in diet recent change in tx pregnancy blood loss hemolytic anemia abnormal hemoglobin (sickle cell disease etc) results depend on albumin normally 200–285 mcmol/L when the serum albumin level is 5 g/dL results will be lower if abnormally low albumin d/t hepatic or renal disease correlates with A1C HbA1c = 0.017 x serum fructosamine level (mcmol/L) + 1.61 serum fructosamine 317, 375, and 435 mcmol/L = A1C 7%, 8%, and 9% respectively |
|
|
|
PKU is highly sensitive when testing infants at least _ hours old?
|
24
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
What are the components of an ABG?
|
1. arterial pH
2. plasma oxygen (PO2) 3. plasma carbon dioxide (CO2) 4. plasma bicarbonate (HCO3−) 5. base excess/deficit 6. anion gap |
|
|
|
What does AST stand for?
|
aspartate aminotransferase
|
|
|
|
What is the procedure for performing an ABG?
|
1. perform Allen test
2. if patient on O2 → turn off O2 for 20-30 minutes before performing ABG for room air test or document amount of O2 being taken 2. draw blood from radial artery into syringe 3. place syringe on ice 4. deliver to lab immediately |
|
|
|
List the 4 criteria for diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis.
|
1. thin white/yellow homogenous discharge
2. pH > 4.5 3. clue cells 4. fishy odor (after adding KOH) *3 of 4 must be present for diagnosis |
|
|
|
Why must an ABG be transported on ice?
|
to prevent continued in vitro changes in PaO2, PaCO2, and pH
|
Lab Data p.6
|
|
|
What does ALT stand for?
|
alanine aminotransferase
|
|
|
|
What is the normal range for blood pH?
|
7.34-7.45
|
|
|
|
What conditions cause cholesterol to be temporarily elevated?
|
pregnancy
wait 6 weeks after giving birth to check cholesterol |
http://tiny.cc/chol
|
|
|
If pH is ≤7.35, what is this called?
|
acidemia
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p179
|
|
|
What liver tests are used to evaluate plasma protein synthesis?
|
albumin
prealbumin PT/INR (clotting proteins) |
|
|
|
If pH is ≥7.45, what is this called?
|
alkalemia
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p179
|
|
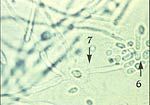
What does this wet mount slide indicate?
|
budding yeast (6) and pseudohyphae (7) of candida → vulvovaginal candidiasis
|
|
|
|
Is CO2 an acid or base?
|
acid
|
|
|
|
What liver tests are used to evaluate hepatocellular injury?
|
AST
ALT |
|
|
|
True or false, obstructive pulmonary diseases decrease air flow and volume?
|
false, only decrease air flow
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p192
|
|
|
At what age should repeat PKU testing be performed?
|
10-14 days
|
|
|
|
True or false, restrictive pulmonary diseases decrease air flow and volume?
|
true
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p192
|
|
|
What liver test is used to evaluate detoxification?
|
ammonia
|
|
|
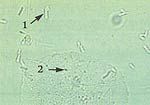
What does this wet mount slide indicate?
|
lactobacilli (1) and epithelial cells (2) → normal wet mount
|
|
|
|
What liver tests are used to evaluate cholestasis?
|
bilirubin
alkaline phosphatase |
|
|
|
What conditions cause cholesterol to be temporarily decreased?
|
acute illness
post-MI stress (like from accident or surgery) wait 6 weeks after illness to check cholesterol |
http://tiny.cc/chol
|
|
|
Is HCO3 an acid or a base?
|
base
|
|
|
|
What is albumin?
|
major plasma protein
|
|
|
|
What is the normal range for PCO2?
|
35-45 torr
|
|
|
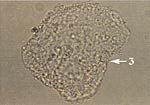
What does this wet mount slide indicate?
|
clue cell (3) → bacterial vaginosis
|
|
|
|
How would you describe the results of an ABG?
|
acidosis or alkalosis?
respiratory or metabolic? compensated or uncompensated? |
|
|
|
What are the functions of albumin?
|
maintain oncotic pressure
bind and transport anions, FAs, hormones, and drugs |
|
|
|
What patient population should not be given O2?
|
COPD patients
|
|
|
|
What tests are in PKU for Washington state?
|
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Hemoglobinopathy Biotinidase Galactosemia CH(Thyroid) Cystic Fibrosis Amino Acid Organic Acid Fatty Acid |
Antrim
|
|
|
Why are serum album levels often normal in acute viral hepatitis or drug-related hepatotoxicity?
|
serum albumin half-life = 20 days
complete cessation of albumin synthesis results in only 25% decrease in serum concentration after 8 days thus serum albumin concentrations are slow to fall following injury |
|
|
|
What radiographic views should be ordered for suspected pneumothorax?
|
PA view
expiratory view |
|
|
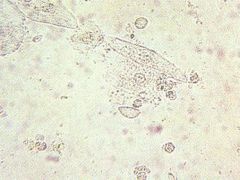
What does this wet mount slide indicate?
|
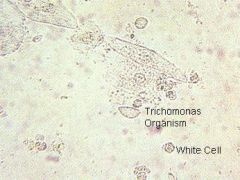
trichomonas and WBCs → trichomoniasis
|
|
|
|
What radiographic views should be ordered for suspected pleural effusion?
|
PA view
lateral decubitus view |
|
|
|
Why are the indications for ordering albumin?
|
measure of protein synthetic function
|
|
|
|
What drugs increase cholesterol?
|
vitamin D
oral contraceptives b-blockers epinephrine anabolic steroids |
http://tiny.cc/chol
|
|
|
What are Kerley B lines?
|
small linear opacities in periphery of lung
|
|
|
|
What is the normal range of albumin?
|
3.5-5.5 grams/dL
|
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of Kerley B lines?
|
1-2cm
water density extend to pleura perpendicular to pleura represent increased fluid density in interlobar septa |
|
|
|
Describe the procedure for collecting a pap smear using a broom and liquid vial.
|
1. insert central bristles of broom into endocervical canal
2. allow shorter bristles of broom to contact ectocervix 2. push gently and rotate broom clockwise 5 times 3. remove broom 4. push broom into bottom of vial 10 times 5. swirl broom vigorously in vial 6. discard broom or deposit in vial |
Mosbys p602
|
|
|
What do Kerley B lines usually indicate?
|
↑ pulmonary venous pressure + pulmonary edema
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of a decreased albumin level?
|
LIVER DYSFUNCTION:
viral hepatitis hepatic cirrhosis toxin ingestion NON-LIVER: malnutrition malabsorption protein loss from gut (nephrotic syndrome) protein loss from kidney (protein-losing enteropathy) protein loss from skin (burns) inflammation (negative acute phase reactant) volume overload (IV fluids) |
|
|
|
What is the ddx for Kerley B lines?
|
pulmonary edema 2° to CHF
pulmonary fibrosis lymphangitis carinomatosis |
|
|
|
What is phenylketonuria?
|
autosomal recessive genetic disorder of amino acid metabolism
characterized by an inability to breakdown the amino acid phenylalanine into tyrosine d/t absence/deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase phenylalaline and related substances accumulate and result in mental retardation treated with diet low in phenylalanine |
|
|
|
What does it mean that albumin is a negative acute phase reactant?
|
in setting of inflammation, liver produces less albumin
|
|
|
|
Describe the procedure for collecting a wet mount.
|
1. insert sterile cotton swab into vagina
2. swab vaginal secretions 3. remove swab 4. insert swab into saline solution |
Mosbys p603
|
|
|
When does hypoalbuminemia produce symptoms?
|
not until albumin really low (<2-2.5g/dL)
|
|
|
|
What is the range for OPTIMAL TRIGLYCERIDES?
|
<150 mg/dL
|
http://tiny.cc/lipid |
|
|
What are the symptoms of hypoalbuminemia?
|
peripheral edema
pulmonary edema ascites |
|
|
|
For suspected ovarian cancer, which tumor marker would you order?
|
CA 125
|
|
|
|
What is the significance of hyperalbuminemia?
|
anabolic steroids
FALSELY ELEVATED: marked dehydration ampicillin heparin |
|
|
|
What is galactosemia?
|
autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by an inability to breakdown galactose d/t a deficiency in either:
1. galactose-1 phosphate uridyl transferase (classic) 2. galactose kinase 3. galactose-6-phosphate epimerase galactose builds up and may result in eye, liver, kidney and brain damage treatment is to avoid milk and other foods containing galactose + calcium supplementation |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for prealbumin?
|
19.5-35.8 mg/dL
|
|
|
|
Do yeast form hyphae or pseudohyphae?
|
pseudohyphae
*yeast are unicellular and therefore cannot form hyphae, but yeast can form pseudohyphae if incomplete budding occurs and cells remain intact after division |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a prealbumin?
|
evaluation of protein nutrition
especially to monitor IV or tube feeding |
|
|
|
What is a lordotic view?
|
CXR while patient leaning backwards
|
|
|
|
What are 8 reasons to order laboratory testing?
|
screening
confirm suspected diagnosis differentiate among several diagnoses determine stage, activity, or severity of disease monitor disease progression detect disease recurrence guide treatment monitor treatment |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1, p5
|
|
|
Compare albumin and prealbumin.
|
both synthesized by liver
both bind and transport solutes prealbumin → short half life (2 days), levels respond quickly to disease, high % of tryptophan and amino acids albumin → long half life (20 days), levels respond slowly to disease |
|
|
|
When is the clinical accuracy of pulse oximetry decreased?
|
1. severe anemia <5g/dL
2. abnormal hemoglobin moieties → carboxyhemoglobin, methemoglobin, fetal hemoglobin 3. intravascular dyes 4. motion artifact 5. lack of pulsatile arterial flow → hypotension, hypothermia, cardiac arrest, simultaneous use of BP cuff *pulse oximetry measures percent of bound hemoglobin but cannot distinguish the molecule that is actually bound (i.e. hemoglobin could be bound with carboxyhemoglobin following carbon monoxide poisoning and SaO2 would still be normal) |
|
|
|
A wet mount with a fishy odor (positive whiff test) is indicative of?
|
bacterial vaginosis or trichomoniasis
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of PKU?
|
hyperactivity
light complexion, eczema seizures, mental retardation |
|
|
|
What are clue cells and what are they indicative of?
|
epithelial cells coated in bacteria that are indicative of bacterial vaginosis
|
|
|
|
What are the VQ scan results for high probability of PE?
|
reduced perfusion + normal ventilation
|
|
|
|
What is a false negative?
|
failure to identify an abnormality that is present
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a VQ scan?
|
medium or high probability of PE
COPD pre- and post-lobectomy |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a DDQ?
|
DVT
PE (only order if low probability of PE, if high probability of PE just order VQ scan) DIC |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for vaginal pH?
|
3.8-4.2
|
|
|
|
What is a DDQ?
|
fibrin degradation product formed after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentatio of galactosemia?
|
if given lactose → vomiting, jaundice (indirect and direct), hepatomegaly, liver insufficiency
if untreated → cataracts (reversible if treated), hepatic cirrhosis, renal Fanconi syndrome, death within a month (usually d/t sepsis with E. coli) even if treated → often delayed apraxic speech (can’t say what want to say), ovarian failure; less often developmental delay, tremor, ataxia (gross lack of motor coordination), mental retardation |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ordering a chloride sweat test?
|
suspected CF
|
|
|
|
Describe the procedure for collecting a gonorrhea/chlamydia DNA probe.
|
1. insert discard swab into vagina and remove excess mucus from cervical os and surrounding mucosa
2. discard swab 3. insert DNA probe swab 1.0-1.5cm into endocervical canal avoiding contact with vaginal membranes 4. rotate swab clockwise for 30 sec 5. remove swab avoiding contact with vaginal membranes 6. insert swab into media |
Mosbys p603
http://www.gen-probe.com/pdfs/pi/103267RevJ.1.pdf |
|
|
What chloride sweat test results indicate CF?
|
PEDIATRIC:
≤29mmol/L = unlikely 30-59 mmol/L = possible ≥60 mmol/L = CF ADULT: ≤39 mmol/L = CF 40-59 mmol/L = possible ≥60 mmol/L = CF |
|
|
|
What polysomnography results indicate sleep apnea?
|
results reported using apnea-hypopnea index (AHI)
5-15 = mild sleep apnea 15-30 = moderate sleep apnea >30 = severe sleep apnea |
|
|
|
What is a false positive?
|
identification of an abnormality that is not present
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
How long are pap specimens kept in pathology?
|
21 days
|
|
|
|
What is the anion gap?
|
anion gap = Na+ - (Cl- + HCO3-)
number of unmeasured anions normally exceeds number of unmeasured cations *anion = negative charged *cation = positively charged |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of congenital hypothyroidism?
|
usually appear normal at birth, gain weight normally during first few months of life
may have jaundice, dry skin, large fontanels, thick tongue, hoarseness, umbilical hernia, hypotonia, mental retardation |
|
|
|
What does an increased anion gap indicate?
|
increase in negatively charged weak acids
loss og HCO3- without concurrent increase in Cl- bicarbonate consumed by unmeasured anion resulting in high anion gap increased anion gap indicates certain types of metabolic acidosis anion gap normal if metabolic acidosis caused by HCL production or excessive loss of bicarbonate anion gap elevated if metabolic acidosis caused by diabetic ketoacidosis, methanol intoxication, etc. (metabolic acidosis that leads to excess anions not in anion gap calculation) |
|
|
|
The presence of intermediate or basal cells on wet mount indicates?
|
inflammation of vaginal epithelium
|
|
|
|
What is the base excess/deficit?
|
base excess = amount of strong acid that must be added to blood to return pH to 7.4
|
|
|
|
What is the definition of accuracy?
|
the extent to which the measurement is close to its true value
If accurate, the measurment is close to or the same as its true value |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
What does an abnormal base excess/deficit indicate?
|
abnormally high base excess = metabolic alkalosis
abnormally low base excess (i.e. base deficit) = metabolic acidosis |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for total bilirubin?
|
0.3-1.0 mg/dL
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of congenital hypoglycemia?
|
may be asymptomatic or symptoms may be difficult to detect
lethargy, apathy, limpness, high-pitched crying, refusal to eat, hypothermia, cyanosis, irregular breathing or apnea, tremors, seizures |
|
|
|
What is the normal range for indirect (unconjugated) bilirubin?
|
0.2-0.7 mg/dL
|
|
|
|
What is the definition of precision?
|
the extent to which the measurement is reproducible
If precise, the result is the same each time the test is repeated |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
What is the norma range for direct (conjugated) bilirubin?
|
0.1-0.3 mg/dL
|
|
|
|
Are bound substance active or inactive?
|
inactive
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
What is the significance of the FEV1/FVC ratio?
|
used to estimate presence and amount of airway obstruction
ratio indicates amount of air mobilized in 1 second as a percentage of total amount of movable air normal = 50% in 0.5sec, 80% in 1sec, 98% in 3sec |
|
|
|
Describe bilirubin metabolism.
|
RBC breakdown in spleen → unconjugated bilirubin released, bound to albumin, and transported to liver → unconjugated bilirubin converted to conjugated bilirubin → conjugated bilirubin secreted into bile and excreted in feces
|
|
|
|
Unbound substances elicit the physiological or pharmacological effect, true or false?
|
true
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
At what total bilirubin concentration does jaundice develop?
|
2-4 mg/dL
*normal 0.3-1.0 mg/dL |
|
|
|
What does the MELD score stand for?
|
model for end-stage liver disease score
|
|
|
|
What is an analyte?
|
the substance measured by an assay
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.1
|
|
|
What does the MELD score consist of and what is its clinical usefulness?
|
Criteria include:
1. serum total bilirubin mg/dL 2. serum creatinine mg/dL 3. INR Clinical usefulness: 1. to determine liver transplant allocation in U.S. 2. to predict mortality in cirrhotic patients undergoing non-transplant surgical procedures -mortality increases 1% for each MELD point up to 20 and 2% for every MELD point over 20 |
|
|
|
What is a biomarker?
|
a characteristic that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological processess, pathological processess, or pharmacologic reponses to treatment
examples include GHGB or tumor markers |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2
|
|
|
What is total lung capacity (TLC)?
|
measure of total amount of gas in lungs at maximal inhalation
|
|
|
|
What is a qualitative test?
|
a test whose results are reported as either positive or negative
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2 |
|
|
What is a quantitative test?
|
a test whose results are reported as an exact numeric measurement
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2
|
|
|
What are the causes of false positive and negative of fecal occult blood?
|
false positive: aspirin, NSAIDs, fish, poultry, red meat, turnips, horseradish
false negative: vitamin C |
|
|
|
What is cephalization?
|
upper lobe vessels increase in size compared to lower lobe vessels → pulmonary venous hypertension (only if patient erect when CXR taken due to influence of gravity)
|
|
|
|
What is the definition of reference range?
|
a statistically-derived numberical range obtained by testing a sample of individuals assumed to be healthy
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2 |
|
|
The upper and lower limits of a reference range are absolute (i.e.normal vs. abnormal), true or false?
|
False
They are points beyond which the probability of clinical significance begins to increase |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2
|
|
|
In a reference range, what percent of the population falls within 1SD, 2SD, and 3SDs of the mean?
|
68% fall within 1SD
95% fall within 2SDs 99.7% fall within 3SDs |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.2
|
|
|
Reference ranges are usually established as a mean +/- 2SDs, what does this mean?
|
1 in 20 normal individuals will have test results outside the normal reference range (2.5% below lower limit and 2.5% above upper limit)
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.3
|
|
|
What is a critical value?
|
a result that is so far outside the reference range that it indicates impending mordibity
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.3 |
|
|
What is a semiquantitative test?
|
a test whose results are reported as either negative or with varying degrees of positivity (but without exact quantification)
an example includes urine ketones which are reported as 1+, 2+, or 3+ |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.3
|
|
|
What is the definition of of sensitivity?
|
1. the ability of a test to identify positive results in patients who actually have the disease
2. the ability of a test to measure low levels of a substance accurately |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.3-4
|
|
|
Does a high sensitivity lower the chance of a false positive or false negative result?
|
false negative
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.3
|
|
|
What is the definition of specificity?
|
people who do not have the disease test negative
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
Does a lower specificity have a higher or lower chance of a false positive?
|
higher
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
What does it mean if a test has a 95% specificity?
|
the disease will not be detected in 5% of people with the disease
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
Which is best for confirming a diagnosis, a test with a high sensitivity or high specificity?
|
high specificity
a test with high specificity is rarely positive in the absence of disease |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
What is the risk of a test with low sensitivity?
|
false negative
|
|
|
|
What is the risk of a test with low specificity?
|
false positive
|
|
|
|
Name examples of non-specific tests.
|
ESR
PSA |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
What may an elevated ESR indicate?
|
inflammation
infection plasma cell dyscrasias (plasma cell cancers) |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.4
|
|
|
What are diagnostic tests?
|
tests performed in presence of symptoms/signs of disease, history of disease, or positive screening results
generallymore risky and expensive than screening tests |
Interpreting Lab Data p.5
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of profile testing?
|
pro - less costly than sum of cost for each individual test
con - may generate unnecessary patient data |
Interpreting Lab Data p.6
|
|
|
What should you consider before ordering tests?
|
1. was the test recently performed; is it likely the results have changed since then?
2. were other tests performed that provide the same info? 3. can the needed info be estimated from existing data? (ex: serum osmolality can be estimated from LYTES and GLUC) 4. what will I do if the results or positive or negative; will it change my diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment? |
Interpreting Lab Data p.6
|
|
|
How does hemolysis affect lab results?
|
↑ K
↑ MG ↑ PHOS |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p6, p41
|
|
|
How does prolonged tourniquet use affect lab results?
|
causes hemoconcentration
(decrease in the plasma volume in relation to the RBCs) especially important if analyte being measured is highly protein-bound (i.e. calcium) |
Lab Data p.6
|
|
|
List factors that influence lab results.
|
1. Clinical situation - acuity, severity
2. Demographics - age, gender, ethnicity, height, weight, body surface area, pregnancy, genetics, nutrition 3. Posture - standing, sitting, supine 4. Specimen - blood, urine, stool, CSF 5. Assay - free, bound 6. Food - time of last meal, type of food ingested 7. Drugs - drug-drug interactions, drug-assay interactions 8. Timing - circadian rhythms, time of day, time of last dose 9. Organ Function 10. Altitude 11. Fluid Status |
Lab Data p.7, 11
|
|
|
How long after MI before CK is elevated and when does it return to normal?
|
elevates after 6 hours
returns to normal after 2-3 days |
Lab Data p.7
|
|
|
How long after MI before LACTIC ACID is elevated and when does it return to normal?
|
elevates after 12-24 hours
returns to normal after 10 days |
Lab Data p.7
|
|
|
How long after MI before TROP is elevated and when does it return to normal?
|
elevates after few hours
returns to normal after 5-7 days |
Lab Data p.7 |
|
|
What does cosyntropin (synthetic ACTH) test?
|
adrenal gland responsiveness
where baseline 8am cortisol level is compared to post-30min and 60min cortisol levels |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p7
|
|
|
What are signs/symptoms of dehydration?
|
dry mucous membranes
decreased skin turgor increased HR decreased urine output |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p9
|
|
|
How does dehydration affect lab results?
|
temporary hemoconcentration where RBCs and blood constituents (Na+, K+, GLUC, BUN, CREAT) are misleadingly elevated until rehydration occurs
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p9,11
|
|
|
List physiological changes associated with aging.
|
↓ height
↓ weight ↓ total body water ↓ lean muscle mass ↑ extracellular water ↑ fat leaky cell membranes decline in cardiac, pulmonary, renal, and metabolic function |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p9
|
|
|
Hereditary anemias are more common in what ethnicities?
|
African Americans
Mediterranean Middle Eastern Indian Southeast Asian |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p9
|
|
|
List examples of hereditary anemias.
|
sickle cell anemia
glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency thalassemias |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p9
|
|
|
List tests affected by old age.
|
1. Some change (unclear clinical significance) - ESR, CA2+, ALB, ALKP, URIC, TSH, T3
2. Clinically significant change - arterial PO2, 2-hr postprandial GLUC, CHOL, LDL, TRIG 3. No change but clinically significant - creatinine |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How can you minimize variation of lab results due to circadian rhythms?
|
obtain labs at same time of day
different lab results at different times of day may be due to circadian variability rather than acute physiologic changes |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
What tests are affected by circadian rhythms?
|
temperature
cortisol melatonin hormones ALT GGT LIPID CK LACTIC ACID LSH LH PROG |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How do high levels (>500mg/day) of ascorbic acid affect lab results?
|
false-negative OCCB
false-negative urine glucose |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How do thiazide and loop diuretics affect lab results?
|
↓ serum K+ due to increased renal elimination of K
↑ serum BUN due to increased fluid loss ↑ serum URIC due to decreased uric acid renal clearance or tubular secretion |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10,39
|
|
|
How do narcotics affect lab results?
|
increase serum LIPA
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How does dextran affect lab results?
|
increase urine specific gravity
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
What drugs cause a false-positive DIRECT COOMBS?
|
isoniazid
sulfonamides quinidine |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
What drugs cause a false-positive ANA?
|
penicillins
sulfonamides tetracyclines |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p10
|
|
|
How are lab results affected by pregnancy?
|
↑ hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin, prolactin, corticotropin releasing hormone, adrenocroticotropic hormone, cortisol, atrial natriuretic hormone)
↑ plasma volume by 30-50% ↓ serum Na+ ↓ Hct ↑ RBCs ↓ fasting GLUC (10-20%) ↑ CHOL (50%) ↑ TRIG (300%) ↑ cardiac output (30-50%) ↓ vascular resistance ↑ GFR (40-50%) ↓ PT ↓ PTT hyperventilation resulting in respiratory alkalosis and ↑ arterial oxygenation |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
How does unprocessed grapefruit juice affect drug bioavailability?
|
down-regulates CYP3A4 and increases bioavailability of some orally administered drugs
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What stimulates plasma renin release?
|
upright posture, low sodium diet, and diuretics
so plasma renin measured while supine after 2-4 weeks of normal sodium diet |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What does CLIA stand for?
|
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What are the 3 categories of tests established by CLIA?
|
waived tests
tests of moderate complexity tests of high complexity |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What are waived tests?
|
pose no risk to patient if used incorrectly
use simple methodologies so inaccurate results are unlikely |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of home-testing?
|
misinterpretation of results
delay in seeking medical advice lack of pre- and post-test counseling lack of psychological support |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What should you consider when interpreting lab results?
|
baseline
reference range rate of change isolated results vs. trends |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p11
|
|
|
What types of testing is ELISA used for?
|
serological tests (e.g. ANA, RF, HEPB, CMV, HIV)
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p22
|
|
|
What is PCR used for?
|
to detect microorganisms (ex: EBV, HSV, chlamydia, HIV, CMV, mycobacteria)
to detect genetic diseases (ex: sickle cell anemia, CF, fragile X syndrome, Tay-Sachs disease, von Willebrand disease, drug-induced hemolytic anemia) to detect malignancies (ex: CML, pancreatic cancer, colon cancer) |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p22,35
|
|
|
What is electrophoresis used to detect?
|
genetic diseases
infectious diseases malignancies paternity testing forensic analysis tissue typing for transplantation |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p24
|
|
|
What test is used to screen for hemoglobin variants?
|
hemoglobin electrophoresis
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
What is serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP) used for?
|
to detect inflammation, protein loss, monoclonal gammopathies, dysproteinemias
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
What is immunofixation electrophoresis used to for?
|
to quantify the immunoglobulins IgA, IgM, IgG, IgD, IgE after a monoclonal immunoglobulin pattern has been detected
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
What is a southern blot?
|
electrophoresis where DNA is separated and identified with a DNA probe
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
What is a northern blot?
|
electrophoresis where RNA is separated and identified with either an RNA or DNA probe
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
What is a western blot?
|
electrophoresis where proteins are separated and identified with radioactive or enzymatically-tagged antibodies
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p25
|
|
|
Describe how agglutination immunoassay works.
|
either antibodies or antigens are added to sample
if antibodies are added to sample containing the antigen, binding will occur, and clumping will be visible if antigens are added to sample containing the antibody, binding will occur, and clumping will be visible |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
What is the simplest immunoassay?
|
agglutination
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
What is agglutination immunoassay used for?
|
to detect antibodies or antigens
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
What is agglutination immunoassay dependent on?
|
the number of binding sites on the antibody
the greater the number, the better the reaction (e.g. IgM produces better agglutination than IgG because it has more binding sites) |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
What tests can be performed using agglutination immunoassay?
|
HCG
RF ANA antigens from infectious agents like bacteria or fungi |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
How does ELISA work?
|
an antigen-enzyme complex is added to sample containing possible antibodies
if antibodies present, the antibodies and antigen-enzyme complex will bind and cause reaction to occur enzyme activity is measured |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p30
|
|
|
What is cytometry?
|
process of measuring physical, chemical, or other characteristics of cells or other biological particles
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p33
|
|
|
What is flow cytometry?
|
technology used to measure properties of cells as they flow in liquid suspension
(eg. hematology analyzer for CBC) |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p33
|
|
|
What is flow cytometry used for?
|
diagnose and develop prognosis for malignancies (ex: leukemia, lymphoma)
monitor immunodeficiency diseases (ex: HIV, AIDS) enumerate stem cells by cluster differentiation assess functional properties of cells |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p34
|
|
|
What is in situ hybridization?
|
localization of nucleic acid sequences (genes, partial chromosomes, or entire chromosomes) in cells/tissues via probes
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p34
|
|
|
What is fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)?
|
in situ hybridization using fluorescent probe
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p35
|
|
|
What is FISH used for?
|
to detect genetic anomalies
to monitor diseases at genetic level |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p35
|
|
|
What is PCR?
|
amplification of RNA or DNA using enzymes
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p35
|
|
|
What are the 3 steps of PCR?
|
1. denaturation - DNA strands separate at 94C
2. primer annealing - primers hybridize to DNA, flanking the region of interest at 50-60C 3. primer extension - DNA polymerase extends primers, generating a copy of original DNA at 72C single cycle takes 3 mintues gel electrophoresis follows PCR |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p35-36
|
|
|
What is another name for digoxin?
|
digitalis
|
|
|
|
If drug interference is suspected, what should be done?
|
1. Establish temporal relationship between drug use and change in test result
2. R/O other drugs as cause 3. R/O concurrent diseases as cause 4. if possible, D/C drug and repeat test 5. Order alternate test that provides same assessment but is unaffected by drug |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p42
|
|
|
When should a drug laboratory test interference be suspected?
|
1. Result does not match signs/symptoms
2. Results of different tests conflict with each 3. Serial results vary greatly over short period of time |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p45
|
|
|
Haptoglobin may be depressed in hemolytic disorders, true or false?
|
true
|
Current p447
|
|
|
Which is more temporary and which is long-term, IgM or IgG?
|
IgM is temporary
IgG is long-term |
|
|
|
What are screening tests?
|
tests performed in absence of symptoms/signs of disease in order to detect disease early when interventions are most effective
generally easy to perform, quick, inexpensive, and reliable but require confirmation testing |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p.5
|
|
|
List examples of screening tests.
|
sickle cell tests
chemistry tests LIPID PSA coagulation tests OCCB Pap smear PPD |
Interpreting Lab Data p.5
|
|
|
Describe the physiology of bilirubin.
|
old/damaged RBCs broken down by spleen → releasing hemoglobin → broken down into heme → turned into unconjugated bilirubin by spleen → bound to albumin and sent to liver → turned into conjugated bilirubin by liver → most excreted through bile, small amount excreted through urine
|
|
|
|
Is unconjucated bilirubin soluble in water?
|
no
must be bound to albumin and sent to liver to be conjugated and then excreted |
|
|
|
Bilirubin circulates in what forms?
|
indirect (unconjugated bilirubin)
irreversibly bound to albumin (delta bilirubin) direct (conjugated bilirbuin) |
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
What does DIRECT BILIRUBIN measure?
|
sum of bilirubin that is bound to albumin and bilirubin that is conjugated
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p1
|
|
|
How is indirect bilirubin measured?
|
calculated from total bilirubin and direct bilirubin
|
|
|
|
If TOTAL BILIRUBIN is abnormally high but jaundice or conjunctival icterus are absent, what should be considered?
|
drug interference
|
Interpreting Laboratory Data p42
|
|
|
List 3 diseases where DC is positive.
|
hemolytic disease of newborn
autoimmune hemolytic anemia hemolytic transfusion reaction |
Antrim
|
|
|
What are the HDL CHOLESTEROL ranges for increased risk, average risk, and less than average risk for coronary heart disease?
|
increased: <40 mg/dL for men or <50 mg/dL for women
average: 40-50 mg/dL for men and 50-59 mg/dL for women less than average: ≥60 for both men and women |
http://tiny.cc/lipid
|
|
|
When is a lipid profile ordered?
|
to determine risk of coronary artery disease
|
http://tiny.cc/lipid
|
|
|
When is HS-CRP ordered?
|
cardiac risk assessment
|
http://tiny.cc/hscrp
|
|
|
Where is CRP synthesized and then secreted?
|
liver then secreted into bloodstream
|
http://tiny.cc/hscrp
|
|
|
Which is more sensitive, CRP or HS-CRP?
|
HS-CRP
more accurately detects lower concentrations of CRP |
http://tiny.cc/hscrp
|
|
|
What does an elevated CRP indicate?
|
non-specific inflammation
|
http://tiny.cc/hscrp
|
|
|
What is the difference b/w CRP and HS-CRP?
|
CRP detects elevated levels of CRP in patients w/ inflammation or infection
HS-CRP distinguishes b/w low normal and high normal levels of CRP in patients who are otherwise healthy |
http://tiny.cc/hscrp
|
|
|
Should HS-CRP be ordered to determine cardiac risk in a patient w/ chronic inflammation?
|
no
HS-CRP only meaningful in patients who are otherwise healthy |
http://tiny.cc/hscrp1
|
|
|
What is BNP and where is it stored and secreted?
|
17 amino-acid peptide stored and secreted from membrane granules in heart ventricles into bloodstream
|
Antrim
|
|
|
BNP is secreted in response to what?
|
ventricular volume expansion and pressure overload
|
Antrim
|
|
|
What does BNP secretion cause?
|
increase in Na and H2O excretion by kidneys via increased glomerular filtration and inhibition of Na reabsoprtion
counteracts renin-angiotensin |
Antrim
|
|
|
What disorder displays elevated BNP?
|
CHF
(the higher the BNP, the more severe the CHF) |
Antrim
|
|
|
When do initial elevation, peak elevation, and normalization occur for MYGB, CK, CKMB, and TROP?
|
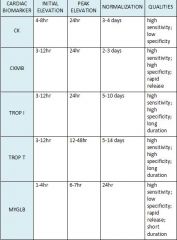
|
|
|
|
List procedures used in diagnosis of cardiac disorders.
|
CXR
CT of heart MRI with gadolinium contrast resting EKG stress EKG ambulatory EKG (Holter/event monitoring transthoracic ECHO transesophageal ECHO stress ECHO doppler US of extremities MUGA scan scintigraphy with thallium scan angiography cardiac catheterization |
|

