![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Re emerging disease |
Infectious agents that have been known for some time, had fallen to such low levels that they were no longer considered public health problems & are now showing upward trends in incidence or prevalence worldwide |
|
|
Cholera |
Vibrio cholerae |
|
|
Lassa fever host |
Rodent |
|
|
Trend of infectious disease |
1. Receded in Western countries 20th century 2. Urban sanitation, improved housing, personal hygiene, antisepsis & vaccination 3. Antibiotics further suppressed morbidity & mortality 4. 20th century- new & resurgent infectious diseases 5.Unusually large number- Rotavirus, Cryptosporidiosis, HIV/AIDS, Hantaviraus, Lyme disease, Legionellosis, and Hepatitis |
|
|
Common features of infectious disease |
All were caused by zoonotic pathogens All spread by modern transportation Most had Asian origin Laboratory and clinical diagnoses were problematic Poor communication among countries Major economic impact |
|
|
After natural disaster |
Diarrhea Acute respiratory infections Malaria Leptospirosis Measles Dengue fever Viral hepatitis Typhoid fever meningitis tetanus |
|
|
Host factors to emergence |
Human demographic change (inhabiting new areas) Human behaviour (sexual & drug use) Human susceptibility to infection (Immunosuppression) Poverty & social inequality |
|
|
Environment factor emergencr |
Climate & changing ecosystems Economic development & Land use (urbanization, deforestation) Technology & industry (food processing & handling) Deterioration in surveillance systems Others Genetic drift/ genetic shift Mass immunocompromisation Economic development Breakdown of public health Poverty and social inequality Dam and irrigation system construction Interracial marriage
|
|
|
Transmission of infectious agent |
Animal/ population displacement Climate patterns Uncontrolled urbanization Human behaviour Antimicrobial drug resistance
|
|
|
Cause antibiotic resistance |
Wrong prescribing practices non-adherence by patients Counterfeit drugs Use of anti-infective drugs in animals & plants Loss of effectiveness Community-acquired (TB, Pneumococcal) & Hospital-acquired (Enterococcal) |
|
|
Consequence antibiotic resistance |
Prolonged hospital admissions Higher death rates from infections Requires more expensive, more toxic drugs Higher health care costs |
|
|
Disease spread diagram |
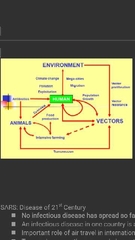
|
|
|
Bioterrorism |
Possible deliberate release of infectious agents by dissident individuals or terrorist groups Biological agents are attractive instruments of terror- easy to produce, mass casualties, difficult to detect, widespread panic & civil disruption |

