![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the #1 presentation of breast diseases?
|
Pain
|
|
|
T/F
It is normal to have lumpy breasts. |
True
Apparently So, sorry nobody wants lumpy funbags |
|
|
What are common symptoms of breast disease?
|
1) Pain
2) Palpable Mass 3) Nipple Discharge or Skin Changes 4) Lumpiness |
|
|
What is the most common type of breast inflammation and what is it attributed to?
|
Acute Mastitis due to Staph. Aureus
|
|
|
What is the most common tumor of the breast?
|
Benign Fibroadenoma
|
|
|
A wide variety of benign alterations in ducts and lobules are observed in the breast. What are these benign changes grouped as?
|
1) Non-proliferative breast changes
2) Proliferative breast disease 3) Atypical hyperplasia |
|
|
What is the risk of developing breast cancer from fibrocystic changes?
|
Pretty much no risk
Fibrocystic changes = Non-proliferative breast changes |
|
|
What epithelial lesion of the breast presents as proliferation of ductal epithelium WITHOUT cellular abnormalities suggestive of cancer?
|
Proliferative breast disease WITHOUT Atypia.
|
|
|
What is the term for cancer within the epithelium but it has not invaded through the basement membrane?
|
Carcinoma in Situ
|
|
|
What is a cancer drug that affects DNA synthesis, preventing cenll division and is used in cancer chemotherapy?
|
Tamoxifen
|
|
|
What contributes the most relative risk to developing invasive carcinoma?
|
existing carcinoma in Situ
|
|
|
Risk factors for carcinoma of the cervix include which of the following?
a) Early age at first intercourse b) Persistent detection of a high-risk HPV c) Male partner with multiple sex partners d) All of the above e) A & C only |
d) all of the above
|
|
|
Cancer of the breast most commonly begins in which location?
a) around the nipple b) lower inner quadrant c) upper inner quadrant d) upper outer quadrant e) equal frequency at all sites |
d) upper outer quadrant
|
|
|
Major risk factors for breast cancer include which of the following?
a) menopause occur later than normal b) giving birth to your first child after the age of 35 c) Having multiple first degree relatives with breast cancer d) persistant detection of a high-risk HPV e) prior biopsies showing atypical hyperplasia f) having multiple sex partners |
a) menopause occur later than normal
b) giving birth to your first child after the age of 35 c) Having multiple first degree relatives with breast cancer e) prior biopsies showing atypical hyperplasia Also, Mensing early is a risk factor persistant detection of a high-risk HPV is CERVICAL cancer |
|
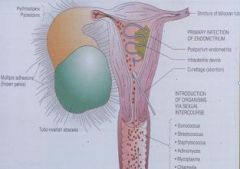
Complications of PID include which of the following?
a) peritonitis b) intestinal obstruction due to adhesions c) infertility in long-standing chronic cases d) all of the above e) A & E only |
All of the above
1) Peritonitis 2) Infertility in long-standing chronic cases 3) Intestinal obstruction due to adhesions 4) Bacteremia which may cause endocarditis, meningitis and arthritis 5) Tubo-ovarian abscesses (cysts) |
|
|
Which of the following statements is true?
a) The most common benign neoplasm of the reproductive system in females is the rhabdomyoma b) Rhabdomyomas are also known as fibroids c) carcinoma of the breast is the most common malignant tumor in females d) the ovary is the most common site for endometriosis e) patients with eclampsia often manifest hypertension edema and proteinuria |
d) the ovary is the most common site for endometriosis
e) patients with eclampsia often manifest hypertension edema and proteinuria Carcinoma is the most common malignancy of the breast and breast cancer is the most common non-skin malignancy in women |
|
|
The major risk factors for Invasive Carcinoma of the breast are hormonal and genetic. What are the major risk factors identified by Epidemiologic studies?
|
1) Age- rare before 25yrs
2) Age at Menarche- menses before age 11 and late menapause increase risk 3) First live birth- If you give birth before 20yrs you DECREASE YOUR RISK by HALF 4) First Degree Relatives with cancer 5) Breast Biopsies showing atypical hyperplasia 6) Race- Black |
|
|
What are the two major groups breast cancer is divided into?
|
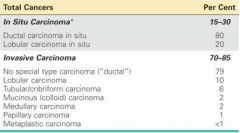
In Situ Carcinoma
Invasive Carcinoma |
|
|
What are the Major Prognostic Factors for Breast cancer?
|
1) Distant Metastases (#1 prognostic factor puts you in automatic Stage 4)
2) Lymph node metastases (#2 prognostic factor) 3) Tumor size (#3 prognostic factor) 4) Locally advanced disease 5) Inflammatory carcinoma (orange peel) 6) Invasive carcinoma or In Situ |
|
|
What is inflammation of the fallopian tube called?
|
Salpingitis
|
|
|
What are some causes of PID?
|
1) Intercourse
2) Postpartum endometritis 3) Intrauterine device 4) Curettage (abortion) |
|
|
T/F
In 1950, cervical cancer was the leading cause of cancer deaths in females but the death rate has declined to its present rank as the 8th leading cause thanks mainly to the PAP smear. The PAP smear picks up the lesion before they become invasive. |
True
|
|
|
What are other names synonomous with Cervical Cancer?
|
Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions
CIN Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasm Cervical Dysplasia |
|
|
What are these risk factors for?
1) Early age at first intercourse 2) Multiple sex partners 3) Increased parity (having children) 4) Male partner with multiple sex partners 5) Presence of a cancer-associated HPV 6) Persistent detection of a high-risk HPV 7) Certain HLA and viral subtypes 8) Exposure to nicotine and oral contraceptives 9) Genital infections |
Cervical Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the most common tumor in women?
|
Uterine Leiomyomas (Fibroids)
|
|
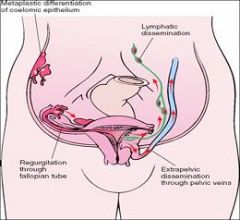
What are some signs or symptoms of endometriosis?
|
Dysmenorrhea (painful menses)
Infertility |
|
|
What are some theories of Endometriosis pathogenesis?
|
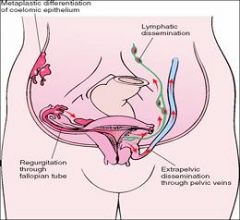
1) Regurgitation of menstrual endometrium through the fallopian tubes and implantation at various sites
2) hematogenous spread of menstrual endometrium to sites such as the lungs or kidneys 3) lymphatogenous spread 4) Celomic metaplasia of the peritoneum |
|
|
Where is the most common site for endometriosis?
|
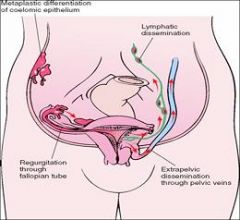
The Ovary
endometriosis implies the presence of benign endometrial glands and stroma in a location outside the uterus. |
|
|
What is another name for PCOD polycystic Ovarian Disease
|
Stein-Leventhal Syndrome
|
|
|
T/F
The most common types of lesions observed in the ovary include functional or benign cysts and tumors. |
True
Cystic follicles in the ovary are so common as to be virtually physiologic. These cysts tend to rupture, seal and heal |
|
|
What are the msot common form of neoplasia in women?
|
Tumors of the ovary
|
|
|
What are three categories of teratomas?
|
1) Mature (benign)teratomas
2) Immature (Malignant) 3) Monodermal or highly specialized (struma avarii and carcinoid) |
|
|
What are the most common monodermal teratomas that may develop?
|
Struma Ovarii
Carcinoid Syndrome |
|
|
What type of tissue composes Struma ovarii teratomas?
|
mature thyroid tissue which may cause hyperthyroidism with hyperfunction
|
|
|
What gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is characterized by cystic swelling of the chorionic villi accompanied by variable trophoblastic proliferation?
|
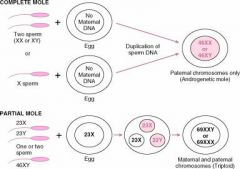
Hydatidform moles (complete and partial)
|
|
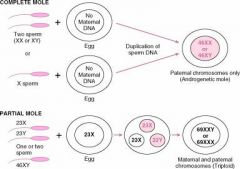
Which type of GTD Hydatidiform mole can undergo malignant change into choriocarcinoma?
|
Complete Hydatidform Mole
|
|
|
Which mole is composed of nothing other than swollen chorionic villi - there is no fetal tissue present?
|
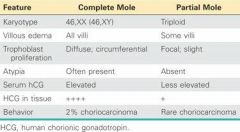
Complete Hydatidiform Mole
|
|
Which mole may have some fetal parts present?
|
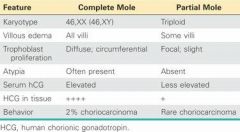
Partial Hydatiform Mole
|
|
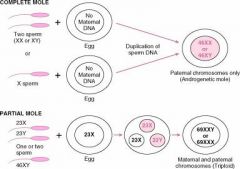
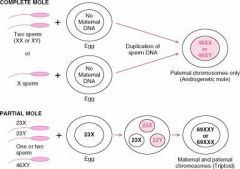
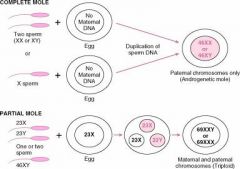
In Complete Hydatidiform mole where do all 46 chromosomes come from?
|
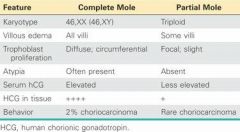
The father
|
|
|
Which type of Hydatidiform mole may have 69 or 92 chromosomes?
|
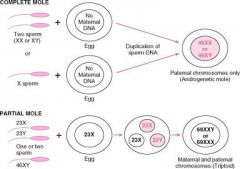
Partial Hydatiform Mole
|
|
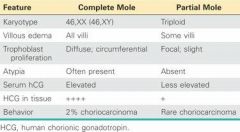
How would you test to see if a mole is complete or partial?
|
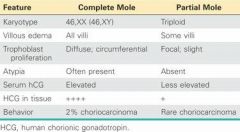
Serum hCG elevated indicates Complete Mole
|
|
|
What are three different categories of GTD Gestational Trophoblastic Disease?
|
1) Hydatidiform Moles
2) Invasive Moles 3) Choriocarcinomas |

