![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is involved in the Cognition theory? |
The cognition theory, formed by theorist Piaget, involves the idea that children need to understand a concept before they can use the language that is related to that concept. Examples include seriation and object permanence. |
|
|
What is involved in the Behaviourism Theory? |
The behaviourism theory, formed by theorist skinner, involves the idea that children learn and develop language by imitation and positive-negative reinforcement. |
|
|
What is involved in the Innateness Theory? |
The innateness theory, formed by Chomsky, involves the idea that children have a device called the LAD. This helps them know basic rules for learning and developing language. |
|
|
What is involved in the Input/Interaction Theory? |
The input/interaction theory, formed by Bruner, involves the idea that children need input and interaction from parents and carers in order to develop and learn language. |
|
|
What is Seriation? |
Seriation is the ordering of objects through size. Children need to understand the concept of size before they can use language related to size, such as superlatives (e.g. biggest). |
|
|
What is Object Permanence? |
Object permanence is a child's ability to know that objects continue to exist even though they can no longer be seen or heard and once they know objects still exist when out of sight, there seems to be a leap in pronoun-usage and name things more often. |
|
|
What is positive-negative reinforcement? |
Positive-negative reinforcement is the process where children will say something accurately and be rewarded (praise or attention) and if they say something wrong they are punished (corrected or mistake is ignored). |
|
|
What is the LASS? |
LASS stands for Language Acquisition Support System and is used in the input/interaction theory as interaction "scaffolds" children's language development. The LASS was a rejoinder to Chomsky's LAD. |
|
|
What is child-directed speech? |
CDS is the language used by parents and caregivers when talking to children. |
|
|
What is the LAD? |
The LAD is the Language Acquisition Device. It is believed to be an inbuilt device that contains the rules of their particular language. |
|
|
What is universal grammar? |
Universal grammar is the theory that all languages share a similar grammatical structure under the surface. It is universal grammar that is in the LAD, as [proposed by Chomsky. |
|
|
What are virtuous errors? |
Virtuous errors are mistakes made by children, but that are used with underlying logic. For example, a child may say "runned" but means "ran". So the child has realised that "-ed" usually means a word is past tense and has used, just incorrectly for the time being. |
|
|
What is the regression curve? |
The regression curve is a U-shaped curve that shows the basic progression of children's language. |
|
|
How does the regression curve and virtuous errors link? |
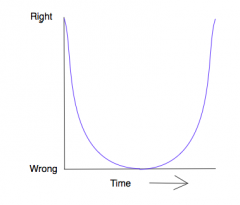
A child says something correctly at first ("held") probably by imitation. Then use it incorrectly ("helded") most likely when deductive processes play a part in learning. Over time they learn and use rules correctly ("held"). |
|
|
What is the critical period? |
The critical period is the optimal time when children need to learn and develop their language. |
|
|
What is the case study of Genie? |
Genie was a "feral child" whose language development was stunted. |
|
|
Which theories does the Genie case study support or oppose? |
As Genie didn't receive much interaction or had no one to imitate it shows she the support of the interaction and behaviourism theories. It also shows that although she learnt some language later in life, she needed to learn during the critical period. It opposes the innateness theory, because she didn't learn language on her own with the LAD. |
|
|
What is the case study of Jim? |
Jim was the hearing child of deaf parents. He was sat in front of a TV to learn language and didn't interact with parents vocally. |
|
|
Which theories does the case study of Jim support of oppose? |
As Jim didn't receive much interaction until later in life, it shows he needed interaction to learn language (supports interaction theory). He learnt some language from watching TV, so the behaviourism theory is supported as he imitated to learn minimal language. The innateness theory is opposed as he didn't learn language using the LAD only. |
|
|
What is derivational morphology? |
The study of how morphemes are used to help create new words. |
|
|
What is addition? |
When an extra vowel sound is added to create a CVCV structure (e.g. dog becomes doggie) |
|
|
What is deletion? |
When the last consonant of a word is left out. (e.g. cat becomes ca) |
|
|
What is reduplication? |
The repetition of particular sounds and structures (e.g. choochoo) |
|
|
What is substitution? |
When one sound is swapped for another, easier sound (e.g. rabbit becomes wabbit) |
|
|
What is consonant cluster reduction? |
When finding it difficult to produce consonant clusters, children will reduce them to smaller units (e.g. frog becomes fog) |
|
|
What is deletion of unstressed syllables? |
It is the removal of an entire unstressed syllable from a word (e.g. banana becomes nana) |
|
|
What is assimilation? |
It is a process in which substitution occurs but the sound changes because of other sounds around it (e.g. doggie becomes goggie) |
|
|
What is the telegraphic stage? |
It is when the child speaks in utterances consisting of two or three words in a range of patterns (e.g. daddy go means where did daddy go) |
|
|
What is the holophrastic stage? |
It is when a child uses single words that relate consistently to identifiable referents (e.g. daddy) |
|
|
What is the post-telegraphic stage? |
When a child speaks in utterances using words that were previously omitted during the telegraphic stage (e.g. that baddy got eaten by the dragon) |
|
|
What is over-generalisation? |
It is the over-application of a grammatical rule; a form of virtuous error (e.g. adding -ed to words for past tense effect, so runned) |

