![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the basal lamina of epithelia?
|
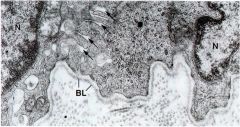
It separates the epithelia from the connective tissue
|
|
|
|
Name the 5 types of epithelium
|
Portective, Absorbtive, Secretory, Sensation, Contraction
|
|
|
|
Give brief description of protective epithelia, and an example.
|
They are multilayered or stratified. Ex: epidermis of skin or lining of the esophegus.
|
|
|
|
Give a brief description of absorptive epithelia, and an example.
|
Simple or single layer, with surface specializations to increase surface are. Ex. intestinal epithelium
|
|
|
|
Give a brief description of secretory epithelia, and an example.
|
Form glands that can be single cells (goblet) or complex. Eg. Goglet cels, pancreas
|
|
|
|
Give a brief description of Sensational epithelia, and an example.
|
specialized epithelia found in the taste buds, olfactory epithelium, and inner ear.
|
|
|
|
What are the main components of the basal lamina?
|
Collagen type IV, Laminin, Fibronectin
|
|
|
|
What other functions does the basal lamina have?
|
Structural layer for epithelia, organizes tissues, gives epithelial cells polarity (Basal vs. apical), and can serve as a filter.
|
|
|
|
What is a basement membrane?
|
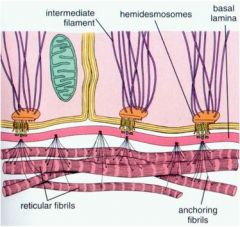
Can be two basal laminae together (in renal glomerulus), or more commonly it is a basal lamina with a reticular lamina beneath.
|
|
|
|
What is the apical domain of an epithelial cell? What are it's possible specializations?
|
It is the luminal side of the cell, away from the BL. Specializations include microvili, stereocilia, and cilia.
|
|
|
|
What is the lateral domain of the eithelial cell, and what are it's defining characteristics?
|
Middle domain in between the Basal domain and the apical domain. It contains Cell-cell junctions.
|
|
|
|
What is the basal domain?
|
It is on the BL side (abluminal-away from the lumen), where the cells attach to the BL.
|
|
|
|
What are the three domains of an epithelial cell?
|
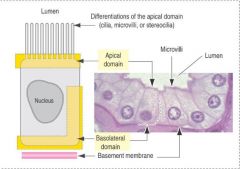
Apical, lateral, and basal domain.
|
|
|
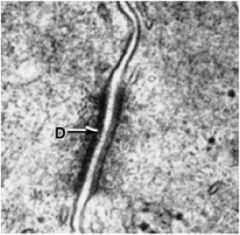
Identify the structure
|
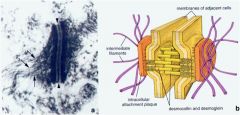
Desmosome aka Macula adherens
|
|
|
|
What tissues does hematoxylin have an affinity for?
|
Anionic components such as: Nuclei, or cytoplasmic RNA, and proteins (carboxyl groups). Hematoxylin is a semi-basic dye that stains blue.
|
|
|
|
What components of a cell stain with eosin?
|
Acidophilic molecules like collagen, cytoplasm, intracellular membranous components, and red blood cells. Eosin is an acidic dye.
|
|
|
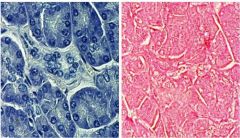
Name the stain used on the right, and the stain used on the left.
|
Right- hematoxylin, left- eosin
|
|
|
|
What is the cause of bullous pemphigoid? What are some symptoms?
|
Antibodies attact protein associated with hemidesmosomes. This causes the skin to detach from the underlying CT, which leads to blistering.
|
|
|
|
Where are connexons located?
|
Gap junctions.
|
|
|
|
What are the stains used in each side?
|
Hematoxylin - R, Eosin - L
|
hematoxylin.jpg
|
|
Identify the structure
|
Terminal bar. Used to connect adjacent apical ends of cells
|
|
|
|
What are the three sections of the terminal bar?
|
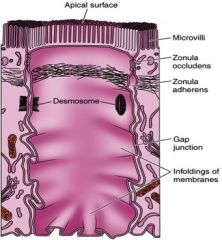
Zonula occludens or tight junctions, Zonula adherens, Macula adherens.
|
|
|
|
What are some common bacteria or pathogens that interfere with the terminal bar?
|
Clostridium perfigens that produces enterotoxin that attacks the zonulae occludens. This allows mass movement of fluid causing dehydration/diarrhea.
|
|
|
|
What is the purpose of microvilli? What are they made of?
|
They are specialized for absorbtion, i.e. in the kidney or small intestine. They are made of actin microfilaments that is anchored to the terminal web in the apical web of the cell.
|
|
|
|
What is the function of cilia? What is their structure?
|
They are used for movement, i.e. in the trachea to move mucous. They are made of 9 doublets of microtubules, with a central pair, and are anchored to basal bodies in the apical cytoplasm.
|
|
|
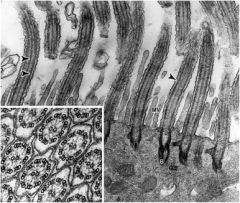
Identify the stricture
|
Cillia
|
|
|
|
What is the main pathological feature of Kartegener's Syndrome?
|
Absence of dyenin, can case infertility in males and females.
|
|
|
|
What is the main function of stereocilia?
|
used in mechanical sensation, found in epididymis and the inner ear. Similar structure to microvillus, but longer.
|
|
|
|
What are the 4 classifications of epithelial tissue by cell number?
|
Simple - 1 layer, Strattfied two or more layers, Transitional - stratified found in urinary tract, PSeudostratified - looks stratified, but actually simple.
|
|
|
|
What are the three classifications of cell type by shape?
|
Squamous - flattened, Cuboidal - height=width, Columnar - height > width.
|
|
|
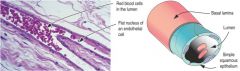
Identify the tissue type on the left
|
Simple squamus
|
|
|
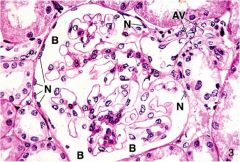
Identify the issue type where the Nuclei are labeled.
|
Simple squamus found in the bowmans capsule of the kidney.
|
|
|
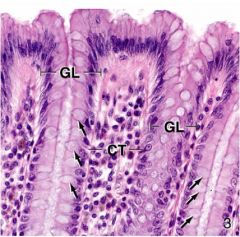
Identify the tissue type
|
Simple columnar, GL - Intestinal gland
|
|
|
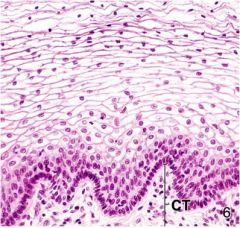
Identify the tissue type
|
Stratified squamous found in the vagina
|
|
|
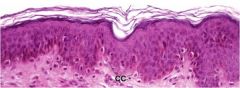
Identify the tissue type
|
Stratified squamous Keratinized - found in the skin
|
|
|
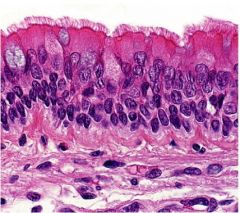
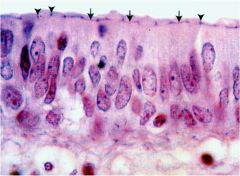
Identify the tissue type, as well as the arrows
|
Pseudostratified columnar, with cilia found in the trachea
|
|
|
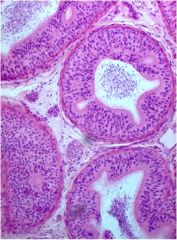
Identify the tissue type
|
Pseudostratified columnar cells, with stereocillia. The small dots in the lumen are sperm, inside the epididymis
|
|
|
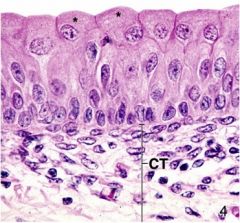
Identify the tissue type, and the stared cell type
|
Transitional epitheliem of the urinary tract. The stared cells are dome shaped cells that are reacting to distention.
|
|
|
|
What is the difference between exocrine and endocrine glands
|
Exocrine glands secrete substances onto the epithelial surface via ducts. Endocrince glands have no ducts and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
|
|
|
|
What are the three main modes of secretion for exocrine glands?
|
Holocrine - entire cell fills and is shed as in sebaceous and tarsal glands.
Apocrine - apical end fills with product is shed - mammary glands Merocrine (eccrine) - secretory cells (vesicles) are formed and released by exocytosis - Pancreatic acinar. |
|
|
|
What type of gland is a goblet cell
|
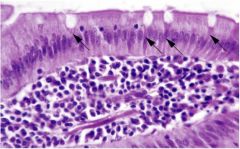
Unicellular
|
|
|
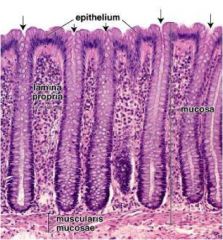
Identify the gland type
|
Simple tubular - found in colon known as crypt of Lieberkuhn
|
|
|
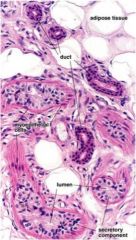
Identify the tissue type of the ducts
|
stratified cuboidal- found in the coiled tubular sweat glands
|
|
|
|
Name the 8 types of multicellular exocrine glands. Draw a picture of each. And give an example.
|
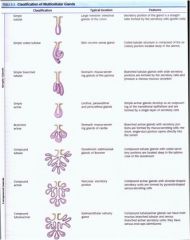
1. Simple tubular - Large intestine, colon
2. Simple coiled tubular - skin sweat glands 3. Simple tubular branched - stomach - gland of pylorus 4. Simple acinar - urethra 5. Branched acinar - stomach: glands of cardia 6. Compound tubular - Duodenum: glands of Brunner 7. Compound acinar - Pancreas - excretory 8. Compound tubuloacinar - Submandibular salivary gland |
|
|
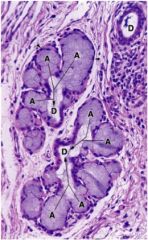
Identify the gland type
|
Compound acinar - a mucus secreting gland in the larynx. A- acinus, D - duct
|
|
|
|
What are the pathological characteristics of epithelial cells?
|
1. Dysplasia - size, shape, organizational changes.
2. Hyperplasia - increased # of cells 3. Hypertrophy - enlarged cells 4. Hypoplasia - decreased # of cells 5. Hypotrophy (atrophy) - Smaller cells 6. Pleomorphism - many diff. size/shapes of cells 7. Anaplasia - a decrease in differentiation of cells - malignancy marker 8. Metaplasia - A change from one tissue type to another |
|
|
|
What are the two different forms of hypertrophy?
|
Physiological (hormonal) - puberty or steroids
Increased functional demand - exercise, or hypertension (left ventricular size) |
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of cancerous epithelial cells?
|
Dysplasia, hyperplasia, anaplasia.
|
|
|
|
What is an example of metaplasia?
|
Chronic gastic reflux causes stratified squamous cells in the lower esophogus to become a gastric-like epithelium that secretes mucus.
|
|
|
|
What are the two forms of benign tumors?
|
Papiloma - from surface epithelium
Adenoma - from glandular epithelium |
|
|
|
What are some faactors affecting malignancy?
|
Anaplasia, Mitotic activity (Increased), Invasion - breach BL, Metastases - spread to distant tissue.
|
|
|
|
What are epithelial cancers called?
|
Carcinomas
|
|

