![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define the term isotope
|
Same atomic number, different mass number
|
|
|
Explain why the mass number of an atom is always a whole number, but RAM is not a whole number?
|
Mass number is the number of protons + neutrons whereas RAM is an average of isotopes.
|
|
|
What is half life
|
Time taken for half the radioactive nuclei to decay or radioactivity of the nuclei of substance to decrease by half.
|
|
|
What is the problem if the half life is too long?
|
May cause long term damage to cells or body tissue.
|
|
|
What is the problem if the half life is too short?
|
Not enough time for isotope to travel through the body - not enough time to detect.
|
|
|
Suggest two assumptions if a radio isotope is to be used for dating a rock.
|
Half life will stay the same, no loss or gain of parent isotope no loss or gain of daughter products.
|
|
|
What are the conditions needed for nuclear fission to take place.
|
Very high temperature and high pressure.
|
|
|
Suggest why these conditions are needed
|
to overcome repulsion between the positively charged nuclei.
|
|
|
Describe main stage in the time of flight mass spectrometer and how it can separate out the isotopes.
|
-sample is ionised.
- all ions are accelerated in an electric filed to the same kinetic energy. - move into flight region. - heavier ions move more slowly to the detector. |
|
|
What turns atoms to cations in the ionisation area?
|
begin hit by a stream of electrons, moving electrons or laser pulse. All ions in the mass spectrometer have a '+' charge.
|
|
|
What causes the acceleration of ions in the acceleration area?
|
Negative plates, electric filed or electrostatic attraction from negative charge.
|
|
|
In a mass spectrum how does a molecule produce many peaks at lower m/z value than its formula mass?
|
molecule has broken down/ fragmented.
|
|
|
Describe the appearance of an atomic absorption spectrum
|
Black lines/bands on a bright coloured background.
|
|
|
Describe the appearance of an atomic emission spectrum
|
Coloured lines/ bands on a black background - lines converge at higher frequencies.
|
|
|
Explain how the lines in the atomic emission spectrum are formed
|
Electrons drop to lower energy levels, they emit light or electromagnetic radiation. Energy is proportional to frequency E=hv
|
|
|
Explain how the lines in atomic absorption spectrum are formed
|
Electrons are excited to higher energy levels. They absorb light to EMG , E=hv , Gaps between each level are smaller as you go up, resulting to unique frequency lines for each element.
|
|
|
What feature of modern atomic structure does the occurrence of emission spectra support?
|
Electrons exist in discrete/specific energy levels.
|
|
|
By What property did Mendeleev arrange the elements in?
|
Atomic weight/mass
|
|
|
Explain why he left gaps in the periodic table?
|
Gaps were left so properties of certain elements fit their places, elements were latter discovered that fit the gaps and they had the same priorities.
|
|
|
Use your knowledge to suggest why Mg can replace Ca in carbonate shells
|
Both are group 2 ( 2 electrons on outer shell) and have a charge of 2+ , react similarly.
|
|
|
Use position of carbon and sulphur to suggest how the melting point of sulphur would differ from carbons
|
Sulfur has a simple molecular structure, but carbon has a covalent network, so melting point is sulfur would be lower.
|
|
|
Suggest why noble gases are predicted to be unreactive
|
Nobel gases have full outer electron shells so are very stable.
|
|
|
Describe the changes in bonding and structure as go from left to right in the periodic table
|
Bonding: ionic on the left, becomes covalent as you move to the right.
Structure: metallic lattice at the start, giant covalent network in the middle and simple molecular on the right. |
|
|
What are the types of bonding
|
) Ionic - ionic lattice
) Covalent - simple molecular or covalent network ) metallic - metallic lattice |
|
|
Name two physical properties of ionic chlorides which should be different from simple covalent chlorides
|
-melting point is higher in ionic compounds
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when in solution/molten -ionic compounds usually soluble in water. |
|
|
Draw a labelled diagram to describe metallic bonding
|
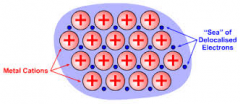
|
|
|
Explain the SF6 molecule and give the bond angle
|
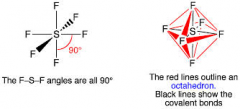
There are 6 regions of electron density around the central sulphur atom. 6 bonding pairs of electrons, electrons repel to get as far way as possible and minimise repulsion. Octahedral shape with bond angle of 90*
|
|
|
Define Molecular formula
|
The Simplest possible, the number of molecules present in each compound
|
|
|
Define Empirical formulae
|
Simplest ratio of atoms in a substance
|
|
|
Define the term aliphatic
|
hydrocarbon containing no benzene rings
|
|
|
Name the following functional groups
C=C OH O-H-(benzene ring) |
C=C - alkene
OH - alcohol O-H-(benzene ring) - Phenol |
|
|
Name the homologous series C-O-C
|
C-O-C - ethers - oxy group
|
|
|
Name the process used to spate different hydrocarbons
|
Fractional Distillation
|
|
|
What molecules are produced by reforming, what is the other products
|
cycloalkane/cycloalkane/arenes/branched alkene / benzene hydrogen also given off (H2).
|
|
|
Explain what happens in cracking process
|
Larger molecules are split to form smaller , shorter alkanes/alkenes/cycloalkanes.
|
|
|
Describe and explain the structural features of zeolites that make often effective catalysts for cracking of hydrocarbons.
|
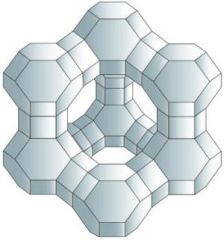
Reactants can be adsorbed on their surface, larger surface area. Can act as molecular sieves due to holes in the structure, therefore it can trap branched isomers and let straight chain trough.
|
|
|
What is isomerisation?
|
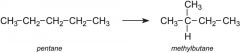
Refining process used to convert straight chain alkanes into branched chain alkanes with the same number of carbons.
|
|
|
Explain why burning old oils produces dense black clouds
|
Incomplete/partial combustion of fuel, caused by not enough O2, C is formed instead of CO/CO2.
|
|
|
Suggest one advantage and 2 disadvantage of the choice of coal as an energy source compared to cleaner fossil fuels
|
Advantage - coal has plentiful reserves/large supply of coal.
Disadvantages - Sulfur in coal burns to form SOx or acid rain and ash particles contribute bronchitis asthma |
|
|
Why is CO regarded as a dangerous pollutant?
|
Toxic/poisonous, binds to red blood cells preventing oxygen uptake.
|
|
|
Why is NOx produced from petrol engines/ forest fires?
|
due to high stability of the nitrogen-nitrogen bond.
|
|
|
Why does diesel engine produces less NOx than petrol engines?
|
In diesel engines the combustion temperature is lower than petrol engines. NOx forms in high temperatures when nitrogen and oxygen bond. Petrol engines have higher combustion temperatures than diesel so they produce more NOx
|
|
|
A substance used to make hyper rubber burns with less NOx than natural rubber due too.....
|
combustion temperature is lower
|
|
|
Give a polluting effect of NO and its consequence
|
- Causes acid rain: kills and damages plants , acidified lakes.
-Photochemical smog: eye/nose irritation, breathing problems. -Forms ozone: harmful to people/ animals, attacks plastics / rubber. |
|
|
How are sulfur oxides formed when coal and diesel engines burn?
|
Combustion of sulfur impurities
|
|
|
Give the reaction that breaks down CO + NO in catalytic converters
|
2CO (g) + 2NO (g) ---> N2(g) + 2CO2 (G)
|
|
|
Define term entropy
|
Measure of the number ways in which particles can be arranged or the amount of disorder in a system.
|
|
|
Explain why there is an increase in entropy in the equation below KNO3 (s) + C (s) ---> K2S (S) + CO2 (g) + NO (g)
|
3 solids go to 1 solid and 2 gases. Gases have higher entropy than solids as there are more ways of arranging particles in gas.
|
|
|
Describe and explain the entropy change that occurs when the liquid bio-butanol mixes with petrol.
|
Mixing leads to an increase in entropy, there are more ways of arranging a particle when they are mixed,
|
|
|
Define Octane number
|
Octane number is a measure of fuels tendency to auto ignite, the higher the number the less likely the fuel is to auto ignite.
|
|
|
Why is it desirable to increase the octane number of a fuel?
|
Higher octane number means less auto-ignition so less of a damage to engine and more efficient combustion.
|
|
|
What is the effect of increased branching on octane number?
|
More branching increases octane number, lowering the tendency to auto-ignite.
|
|
|
Explain in terms of bond making and bond breaking why some enthalpy change have a negative value.
|
Breaking bonds is an endothermic (+) reactions, breaking bonds absorbs in energy. Making bonds is an exothermic (-) reaction, making bonds releases energy, value of exothermic is bigger than endothermic.
|
|
|
Define Enthalpy change of formation
|
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements with both compound and elements being in their standard state.
|
|
|
Define Enthalpy Change of combustion
|
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance is completely burned in oxygen (under standard conditions).
|
|
|
What are the standard conditions?
|
-temp: 298 K ( 25*C)
-concentration: 1 mole -pressure: 1 atmospheric pressure |
|
|
Why do two isomeric hydrocarbons have very similar enthalpies of combustion?
|
The same number and types of bonds are broken, take number and types of bonds are made.
|
|
|
Describe the 2 enthalpy changes DH1 and DH2 (D = delta ) in the reaction:
8C(s) + 9H2(g) + 12.5O2 ---> 8CO2(g) + 9 H20 (g) |
DH1 - enthalpy change of combustion of 8 moles of of carbon
DH2 - enthalpy change of combustion of 9 moles of hydrogen. |
|
|
What are the main sources of error in an enthalpy of combustion based on a student experiment?
|
heat loss to the surroundings or apparatus , incomplete combustion , evaporation of fuels
|
|
|
Why might a calculated enthalpy change based on bond enthalpies differ from the true value?
|
bond enthalpies for the actual substance are not the same as the average bond enthalpy used.
|
|
|
Explain Hess' Law
|
energy change of a particular reaction is interdependent of the route taken providing the initial and finial conditions are the same.
|
|
|
Explain the term structural isomer
|
Substance with the same molecular formula but different structural formula
|
|
|
Suggest what is meant by clean burning
|
Complete combustion producing only carbon dioxide and water
|
|
|
Biodiesel molecules contain oxygen atoms - what general name is given to increase the efficiency?
|
Oxygenates - contain oxygen - increase octane number
|
|
|
Why does using a fuel with a higher percentage of carbon in it gives a yellow flame?
|

due to more incomplete combustion due to % higher carbon , gives carbon particles which burn with yellow flame.
|
|
|
Suggest one benefit and one problem associated with using hydrogen as fuel
|
Water is the only product , no CO2
difficult to store, hydrogen weakens steal. |
|
|
Give 1 disadvantage and two benefits of using biofuels
|
Benefits - less CO is produced , unburnt hydrocarbons , sustainable and replaceable.
Disadvantage - uses up land which could be used for food, agriculture. |
|
|
Define the term catalyst
|
Speeds up the reaction and chemically unchanged at the end, provides an alternative path and lowers activation enthalpy.
|
|
|
Define Heterogeneous catalyst
|
Catalyst and reactants are in different physical states
|
|
|
Explain how a catalyst is poisoned
|
Poison/ lead is very strongly adsorbed and won't ware off, prevents reactants from reaching the surface,
|
|
|
Describe how a heterogeneous catalyst works in four stages?
|
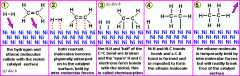
-adsorption of reactants onto catalyst surface
-bonds break within the molecule - new bonds form in products -products diffuse away from the surface. |

