![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
193 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the term for the obstruction of sinus drainage into the nasal cavity, leading to inflammation and pain over the affected area? What is the most likely affected area? |
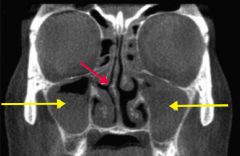
Rhinosinusitis
- Often in maxillary sinuses in adults (yellow arrows) |
|
|
What happens in Rhinosinusitis? What is the most common cause?
|
- Obstruction of sinus drainage into the nasal cavity, leading to inflammation and pain over the affected area (usually maxillary sinuses in adults)
- Most common acute cause is VIRAL URI, may cause superimposed bacterial infection (S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis) |
|
|
What is the most common acute cause of rhinosinusitis?
|
Viral URI
|
|
|
What are the most common causes of superimposed bacterial infection on rhinosinusitis?
|
- S. pneumoniae
- H. influenzae - M. catarrhalis |
|
|
What predisposes to a deep venous thrombosis?
|
Virchow's Triad:
- Stasis - Hypercoagulability - Endothelial damage |
|
|
What can cause hypercoagulability? What is this a component of?
|
- Eg, defect in coagulation cascade proteins, most commonly Factor V Leiden
- Component of Virchow's triad |
|
|
What are the characteristics of endothelial damage that is a component of Virchow's triad?
|
Exposed collagen triggers clotting cascade
|
|
|
What is the most likely location for pulmonary emboli to arise from?
|
Deep leg veins
|
|
|
What is the Homan sign?
|
Dorsiflexion of the foot → calf pain
|
|
|
What drug can be used to prevent deep vein thrombosis?
|
Heparin
|
|
|
What drug can be used for acute management of deep vein thrombosis?
|
Heparin
|
|
|
What drug can be used for long-term prevention of deep vein thrombosis recurrence?
|
Warfarin
|
|
|
What are the signs / symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism?
|
- V/Q mismatch → hypoxemia → respiratory alkalosis
- Sudden-onset dyspnea - Chest pain - Tachypnea - May present as sudden death |
|
|
What are the types of Pulmonary Emboli?
|
"An embolus moves like a FAT BAT"
- Fat - Air - Thrombus - Bacteria - Amniotic fluid - Tumor |
|
|
What are fat pulmonary emboli associated with?
|
Associated with long bone fractures and liposuction
|
|
|
What is the classic triad of fat emboli?
|
- Hypoxemia
- Neurologic abnormalities - Petechial rash |
|
|
What can an amniotic fluid emboli lead to?
|
Can lead to DIC, especially post-partum
|
|
|
Who is likely to get gas emboli? How do you treat them?
|
Nitrogen bubbles can precipitate in ascending divers; treat with hyperbaric oxygen
|
|
|
What is the best way to image a patient you think has a pulmonary embolism? What do you look for?
|
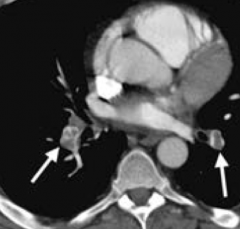
CT pulmonary angiography (look for filling defects)
|
|
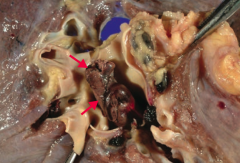
What is this gross image of?
|
Pulmonary Embolism
- Note large embolus (arrows) in the pulmonary artery |
|
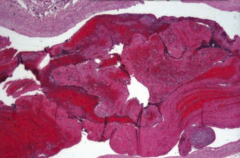
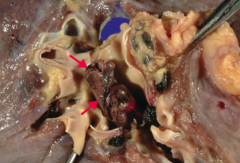
What does this image show?
|
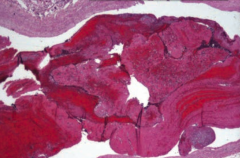
Pulmonary Thromboembolus
- Lines of Zahn are interdigitating areas of pink (platelets, fibrin) and red (RBCs) found only in thrombi formed BEFORE death - Helps distinguish pre- and post-mortem thrombi |
|
|
What can you look for to determine whether a thrombus formed pre-mortem or post-mortem?
|
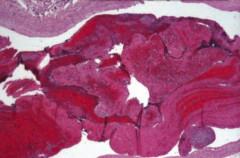
Lines of Zahn are interdigitating areas of pink (platelets, fibrin) and red (RBCs) found only in thrombi formed BEFORE death
|
|
|
What are the consequences of obstructive lung diseases?
|
- Leads to air trapping in the lungs
- Airways close prematurely at high lung volumes → ↑ RV and ↓ FVC - PFTs: ↓↓ FEV1, ↓ FVC → ↓ FEV1/FVC ratio - V/Q mismatch |
|
|
What can chronic, hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction lead to?
|
Cor Pulmonale
|
|
|
What are the types of obstructive lung diseases?
|
- Chronic Bronchitis ("blue bloater")
- Emphysema ("pink puffer", barrel-shaped chest) - Asthma - Bronchiectasis |
|
|
What happens to the pulmonary function tests in patients with obstructive lung disease?
|
- ↓↓ FEV1
- ↓ FVC - ↓ FEV1/FVC ratio |
|
|
What are the types of COPD?
|
- Chronic Bronchitis
- Emphysema |
|
|
What happens pathologically in patients with Chronic Bronchitis?
|
Hyperplasia of mucus-secreting glands in the bronchi → Reid index >50%
|
|
|
What is the Reid Index? Utility?
|
Ratio of thickness of gland layer / total thickness of bronchial wall
>50% is supportive of Chronic Bronchitis |
|
|
What are the diagnostic criteria for Chronic Bronchitis?
|
Productive cough for >3 months / year (not necessarily consecutive) for >2 years
|
|
|
Chronic bronchitis is a disease of what airways?
|
Small airways
|
|
|
What signs and symptoms does a patient with Chronic Bronchitis have?
|
- Wheezing
- Crackles - Cyanosis (early onset hypoxemia due to shunting) - Late onset dyspnea - CO2 retention |
|
|
What happens pathologically in patients with Emphysema?
|
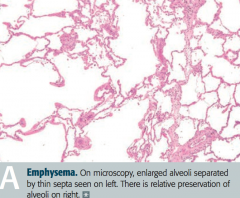
- Enlargement of air spaces
- ↓ Elastic recoil - ↑ Compliance - ↓ DLCO resulting from destruction of alveolar walls |
|
|
What are the types of emphysema? What is each associated with?
|

- Centriacinar: associated with smoking
- Panacinar: associated with α1-antitrypsin deficiency |
|
|
What causes increased lung compliance in patients with emphysema?
|
↑ Elastase activity → loss of elastic fibers → ↑ lung compliance
|
|
|
How do patients with emphysema breathe?
|
Exhale through pursed lips to increase airway pressure and prevent airway collapse during respiration
|
|
|
What is the pathology responsible for asthma?
|
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness causes reversible bronchoconstriction
|
|
|
What are the histologic findings of asthma?
|
- Smooth muscle hypertrophy
- Curschmann spirals (shed epithelium forms mucus plugs) - Charcot-Leyden crystals (formed from breakdown of eosinophils in sputum) |
|
|
What is the term for shed epithelium that forms mucus plugs? What pathology is it a sign of?
|
Curschman Spirals - sign of asthma
|
|
|
What is the term for the crystals formed by the breakdown of eosinophils in the sputum? What pathology is it a sign of?
|
Charcot-Leyden crystals - sign of asthma
|
|
|
What can trigger asthma?
|
- Viral URIs
- Allergens - Stress |
|
|
What test can you use to diagnose asthma?
|
Methacholine challenge
|
|
|
What are the findings of asthma?
|
- Cough
- Wheezing - Tachypnea - Dyspnea - Hypoxemia - ↓ I/E ratio - Pulsus paradoxus - Mucus plugging |
|
|
What pathology is seen in Bronchiectasis?
|
Chronic necrotizing infection of bronchi → permanently dilated airways, purulent sputum, recurrent infections, and hemoptysis
|
|
|
What part of the respiratory tract is affected by bronchiectasis? How is it affected?
|
Bronchi: chronic necrotizing infection
- Permanently dilates the airways - Forms purulent sputum - Recurrent infections - Hemoptysis |
|
|
What is bronchiectasis associated with?
|
- Bronchial obstruction
- Poor ciliary motility (smoking) - Kartagener syndrome (primary ciliary dyskinesia) - Cystic fibrosis - Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis |
|
|
What are the characteristics of all restrictive lung diseases?
|
Restricted lung expansion causes:
- ↓ Lung volumes (↓ FVC and TLC) - PFTs: FEV1/FVC ratio ≥ 80% |
|
|
What are the types of restrictive lung disease?
|
- Restrictive lung disease due to poor breathing mechanics
- Restrictive lung disease due to interstitial lung disease |
|
|
What are the characteristics of restrictive lung diseases due to poor breathing mechanics? Causes?
|
- Extrapulmonary, peripheral hypoventilation, normal A-a gradient
Causes: - Poor muscular effort: polio and myasthenia gravis - Poor structural apparatus: scoliosis and morbid obesity |
|
|
What are the characteristics of interstitial lung diseases?
|
- Pulmonary ↓ diffusing capacity
- ↑ A-a gradient |
|
|
What are the types of interstitial lung diseases?
|
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome - Pneumoconioses - Sarcoidosis - Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - Goodpasture syndrome - Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener) - Langerhans cell Histiocytosis - Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis - Drug toxicity |
|
|
What histologic finding is characteristic of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
Hyaline membrane (disease)
|
|
|
What are the findings in Sarcoidosis that affects the lungs?
|
Restrictive lung disease
- Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy - Non-caseating granuloma - ↑ ACE and Ca2+ |
|
|
What are the characteristics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis?
|
Restrictive lung disease
- Repeated cycles of lung injury and wound healing with increased collagen deposition |
|
|
What kind of granulomas occur in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis?
|
Eosinophilic Granulomas
|
|
|
What drugs can cause restrictive lung disease?
|
- Bleomycin
- Busulfan - Amiodarone - Methotrexate |
|
|
What type of reaction causes hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
|
Mixed type III/IV hypersensitivity reaction to environmental antigens
|
|
|
Which symptoms occur in hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
|
- Dyspnea
- Cough - Chest tightness - Headache |
|
|
Who is most likely to get hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
|
- Farmers
- Those exposed to birds |
|
|
What are the types of pneumoconioses?
|
- Asbestosis
- Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis - Silicosis |
|
|
What do Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis, Silicosis, and Asbestosis increase the risk for?
|
- Cor pulmonale
- Caplan syndrome (rheumatoid arthritis and pneumoconioses with intrapulmonary nodules) |
|
|
What is Caplan Syndrome?
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Pneumonconioses with Intrapulmonary Nodules
|
|
|
What lung pathology is associated with shipbuilding, roofing, and plumbing?
|
Asbestosis
|
|
|
What are the characteristic findings on imaging of asbestosis?
|
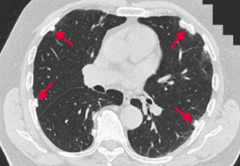
"Ivory white" calcified pleural plaques are pathognomonic of asbestos exposure, but they are not precancerous
|
|
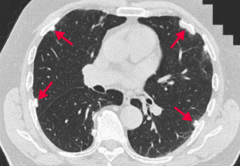
What are these findings associated with?
|
Asbestosis:
- Associated with increased risk of bronchogenic carcinoma and mesothelioma |
|
|
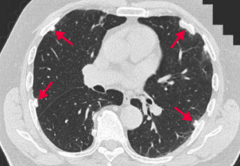
What part of the lungs are affected by asbestosis?
|
Affects lower lungs:
"Asbestos is from the roof (common in insulation), but affects the base (lower lobes)" |
|
|
What is the appearance of asbestos histologically?
|
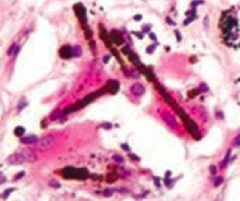
Asbestos (ferruginous) bodies are golden-brown fusiform rods resembling dumbbells
|
|
|
What part of the lungs are affected by silicosis?
|
Affects upper lobes:
"Silica is from the base (earth), but affect the roof (upper lobes)" |
|
|
What part of the lungs are affected by coal?
|
Affects upper lobes:
"Coal is from the base (earth), but affect the roof (upper lobes)" |
|
|
What is the other name for "black lung disease"?
|
Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis
|
|
|
What happens if someone has prolonged exposure to coal dust?
|
Macrophages become laden with carbon → inflammation and fibrosis → Coal Workers' Pneumoconiosis
|
|
|
What condition is found in many urban dwellers exposed to sooty air? Symptoms?
|
Anthracosis - asymptomatic
|
|
|
What is associated with foundries, sandblasting, and mines?
|
Silicosis
|
|
|
What happens if someone has exposure to silica?
|
- Macrophages respond to silica and release fibrogenic factors → fibrosis → Silicosis
- Silica may disrupt phagolysosomes and impair macrophages, increasing susceptibility to TB |
|
|
What is there increased risk of in patients with Silicosis?
|
- Increased susceptibility to TB
- Bronchogenic carcinoma |
|
|
What is the characteristic appearance of silicosis?
|
"Eggshell" calcification of hilar lymph nodes
|
|
|
What causes Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
|
Surfactant deficiency → ↑ surface tension → alveolar collapse
|
|
|
What can predict whether a neonate will have neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
Lecithin:Sphingomyelin ratio <1.5 in amniotic fluid
|
|
|
What is a potential complication of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
- Persistently low O2 tension → risk of PDA
- Therapeutic supplementation of O2 can result in RETINOPATHY of prematurity and BROCHOPULMONARY DYSPLASIA |
|
|
What are the risk factors for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
- Prematurity
- Maternal diabetes (due to ↑ fetal insulin) - C-section delivery (↓ release of fetal glucocorticoids) |
|
|
How do you treat a neonate at risk for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
Give mother steroids before birth to stimulate surfactant production
|
|
|
How do you treat an infant with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome?
|
Artificial Surfactant
|
|
|
What can cause acute respiratory distress syndrome?
|
- Trauma
- Sepsis - Shock - Gastric aspiration - Uremia - Acute pancreatitis - Amniotic fluid embolism |
|
|
What changes occur in acute respiratory distress syndrome?
|
- Diffuse alveolar damage → ↑ alveolar capillary permeability → protein-rich leakage into alveoli and non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema (normal PCWP)
- Formation of intra-alveolar hyaline membrane |
|
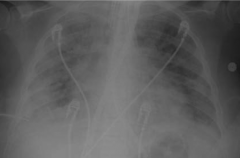
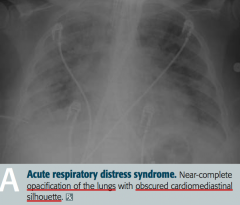
What does this x-ray show?
|
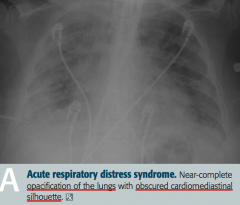
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Near complete opacification of the lungs - Obscured cardiomediastinal silhouette |
|
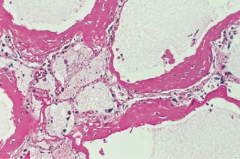
What does this histology show?
|
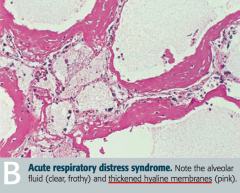
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Alveolar fluid (clear and frothy) - Thickened hyaline membranes (pink) |
|
|
What causes the initial damage in acute respiratory distress syndrome?
|
- Release of neutrophilic substances toxic to alveolar wall
- Activation of coagulation cascade - Oxygen-derived free radicals |
|
|
What is the normal FEV1/FVC ratio?
|
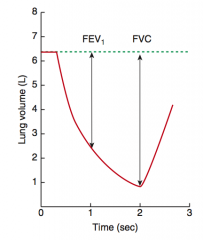
80%
|
|
|
What is the FEV1/FVC ratio in obstructive lung disease?
|
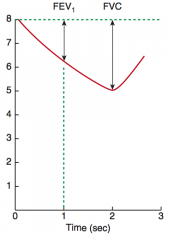
< 80%
|
|
|
What is the FEV1/FVC ratio in restrictive lung disease?
|
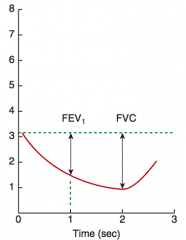
≥ 80%
|
|
|
Which lung disease has increased lung volumes (↑ TLC, ↑ FRC, and ↑ RV)?
|
Obstructive lung disease
|
|
|
Which lung disease has decreased lung volumes (↓ TLC, ↓ FRC, and ↓ RV)?
|
Restrictive lung disease
|
|
|
How does the change in FEV1 and FVC compare in obstructive vs restrictive lung disease?
|
In both obstructive and restrictive disease, FEV1 and FVC are reduced
- In obstructive, however, FEV1 is more dramatically reduced compared to FVC, resulting in ↓ FEV1/FVC ratio |
|
|
What is the normal pulmonary artery pressure?
|
10-14 mmHg
|
|
|
What is the definition of pulmonary hypertension?
|
≥ 25 mmHg at rest
|
|
|
What are the consequences of pulmonary hypertension?
|
- Arteriosclerosis
- Medial hypertrophy - Intimal fibrosis of pulmonary arteries |
|
|
What causes Primary Pulmonary Hypertension? Prognosis?
|
- Inactivating mutation in BMPR2 gene (normally functions to inhibit vascular smooth muscle proliferation)
- Poor prognosis |
|
|
What causes Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension? Prognosis?
|
- COPD
- Mitral stenosis - Recurrent thromboemboli - Auto-immune disease - L → R shunt - Sleep apnea - Living at high altitude |
|
|
How does COPD affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Destroys lung parenchyma → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
Which valvular problem can affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation? How?
|
Mitral Stenosis → ↑ Resistance → ↑ Pressure → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
How do thromboemboli affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Recurrent thromboemboli → ↓ cross-sectional area of pulmonary vascular bed → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
Which auto-immune diseases affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation? Implications?
|
Systemic Sclerosis
- Inflammation → Intimal Fibrosis → Medial Hypertrophy → 2° Pulmonary Hypertension |
|
|
What type of cardiac shunt can affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation? Implications?
|
Left-to-Right Shunt → ↑ shear stress → endothelial injury → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
How does sleep apnea affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Hypoxic vasoconstriction → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
How does living at a high altitude affect the pressure in the pulmonary circulation?
|
Hypoxic vasoconstriction → 2° pulmonary hypertension
|
|
|
What is the course of having pulmonary hypertension?
|
Pulmonary hypertension → severe respiratory distress → cyanosis and RVH → death from decompensated cor pulmonale
|
|
|
What happens in sleep apnea? Consequences?
|
Repeated cessation of breathing >10 seconds during sleep → disrupts sleep → daytime somnolence
|
|
|
What happens to the PaO2 during the day and night in a patient with sleep apnea?
|
- Normal PaO2 during day
- Nocturnal hypoxia |
|
|
What are the complications of sleep apnea?
|
Nocturnal hypoxia → systemic / pulmonary HTN, arrhythmias (atrial fibrillation / flutter), and sudden death
|
|
|
What are the types of sleep apnea? How do they differ?
|
- Central sleep apnea: no respiratory effort
- Obstructive sleep apnea: respiratory effort against airway obstruction, associated with obesity and loud snoring |
|
|
How do you treat sleep apnea?
|
- Weight loss
- CPAP - Surgery |
|
|
How does sleep apnea affect erythropoiesis?
|
Hypoxia → ↑ EPO release → ↑ erythropoiesis
|
|
|
What variation of sleep apnea is seen in obese patients?
|
Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome:
- Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) → hypoventilation → ↓ PaO2 and ↑ PaCO2 during waking hours |
|
|
In what lung pathology are there the following findings:
- Breath sounds: ↓ - Percussion: dull - Fremitus: ↓ - Tracheal deviation: - |
Pleural Effusion
|
|
|
In what lung pathology are there the following findings:
- Breath sounds: ↓ - Percussion: Dull - Fremitus: ↓ - Tracheal deviation: Toward side of lesion |
Atelectasis (bronchial obstruction)
|
|
|
In what lung pathology are there the following findings:
- Breath sounds: ↓ - Percussion: hyperresonant - Fremitus: ↓ - Tracheal deviation: - |
Spontaneous pneumothorax
|
|
|
In what lung pathology are there the following findings:
- Breath sounds: ↓ - Percussion: hyperresonant - Fremitus: ↓ - Tracheal deviation: away from side of lesion |
Tension pneumothorax
|
|
|
In what lung pathology are there the following findings:
- Breath sounds: bronchial breath sounds; late inspiratory crackles - Percussion: dull - Fremitus: ↑ - Tracheal deviation: - |
Consolidation (lobar pneumonia, pulmonary edema)
|
|
|
In what lung pathologies are there decreased breath sounds?
|
- Pleural effusion
- Atelectasis (bronchial obstruction) - Spontaneous pneumothorax - Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
In what lung pathologies are there bronchial breath sounds and late inspiratory crackles?
|
Consolidation (lobar pneumonia or pulmonary edema)
|
|
|
In what lung pathologies are the lungs dull to percussion?
|
- Pleural effusion
- Atelectasis (Bronchial obstruction) - Consolidation (lobar pneumonia or pulmonary edema) |
|
|
In what lung pathologies are the lungs hyperresonant to percussion?
|
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
In what lung pathologies do the lungs have decreased fremitus?
|
- Pleural effusion
- Atelectasis (bronchial obstruction) - Spontaneous pneumothorax - Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
In what lung pathologies do the lungs have increased fremitus?
|
Consolidation (lobar pneumonia or pulmonary edema)
|
|
|
In what lung pathologies is there a tracheal deviation toward the side of the lesion?
|
Atelectasis (bronchial obstruction)
|
|
|
In what lung pathologies is there a tracheal deviation away the side of the lesion?
|
Tension pneumothorax
|
|
|
What is the leading cause of cancer death?
|
Lung cancer
|
|
|
What is the classic presentation of lung cancer?
|
- Cough
- Hemoptysis - Bronchial obstruction - Wheezing - Pneumonic "coin" lesion on x-ray film or non-calcified nodule on CT |
|
|
What finding on x-ray is characteristic of lung cancer?
|
Pneumonic "coin" lesion
|
|
|
What finding on CT is characteristic of lung cancer?
|
Non-calcified nodule
|
|
|
What is more common: primary neoplasms or metastases to the lungs?
|
In the lung, metastases (usually multiple lesions) are more common than 1° lesions
|
|
|
What are the most common sites that metastasize to the lungs?
|
Cancer of:
- Breast - Colon - Prostate - Bladder |
|
|
What are the most common sites of metastases from the lungs?
|
- Adrenals
- Brain - Bone (pathologic fracture) - Liver (jaundice, hepatomegaly) |
|
|
What are the types of lung cancer?
|
- Adenocarcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma - Small cell (oat cell) carcinoma - Large cell carcinoma - Bronchial carcinoid tumor |
|
|
What types of lung cancer are located peripherally?
|
- Adenocarcinoma
- Large cell carcinoma - Bronchial carcinoid tumor (either peripheral or central) |
|
|
What types of lung cancer are located centrally?
|
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Small cell (oat cell) carcinoma - Bronchial carcinoid tumor (either peripheral or central) |
|
|
What is the most common type of lung cancer (except for metastases)?
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What is the most common type of lung cancer in non-smokers?
|
Adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
What genetic changes are associated with Lung Adenocarcinoma?
|
Activating mutations:
- k-ras - EGFR - ALK |
|
|
What is a specific physical sign of Lung Adenocarcinoma?
|
Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (clubbing)
|
|
|
Which subtype of lung adenocarcinoma is associated with hazy infiltrates on CXR (similar to pneumonia)? Why this appearance? Prognosis?
|
Bronchioloalveolar Subtype of Adenocarcinoma:
- Tumor grows along alveolar septa giving an apparent "thickening" to the alveolar walls - Excellent prognosis |
|
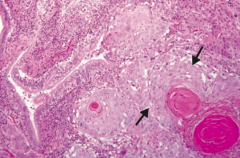
What type of cancer does this show? What are the characteristics of it that tell you that?
|
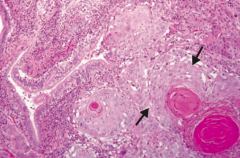
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Keratin pearls and intercellular bridges - Sheets of large dysplastic squamous cells (arrows) surrounding dark, pink keratin pearls (lower right) |
|
|
What is the location of lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma? Other characteristics indicative of it?
|
- Central location
- Hilar mass arising from bronchus - Cavitation, Cigarettes, and HyperCalcemia |
|
|
What type of lung cancer is associated with hypercalcemia? How?
|
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Hypercalcemia because tumor produces PTHrP |
|
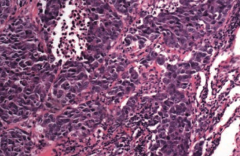
What type of cancer does this show? What are the characteristics of it that tell you that?
|
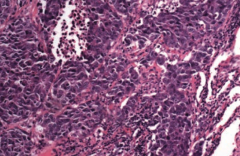
Small Cell (Oat Cell) Carcinoma
- Sheets of dark purple tumor cells with nuclear molding, high mitotic rate, necrosis, and "salt and pepper" neuroendocrine-type chromatin - Neoplasm of neuroendocrine Kulchitsky cells → small dark blue cells |
|
|
What type of lung cancer is known for producing certain substances that can cause seemingly unrelated symptoms? What substances?
|
Small Cell (Oat Cell) Carcinoma:
- May produce ACTH or ADH - May also produce Antibodies against pre-synaptic Ca2+ channels causing Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome |
|
|
What genetic change is sometimes associated with Small Cell (Oat Cell) Carcinoma?
|
Ampification of myc oncogenes common
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of Small Cell (Oat Cell) Carcinoma? How do you treat it?
|
- Undifferentiated → very aggressive
- Inoperable, treat with chemotherapy |
|
|
Which type of lung cancer is associated with pleomorphic giant cells?
|
Large Cell Carcinoma
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of a Large Cell Carcinoma of the lung? Location?
|
- Peripheral locatoin
- Highly anaplastic undifferentiated tumor |
|
|
What is the prognosis for Large Cell Carcinoma? How do you treat?
|
- Poor prognosis
- Less responsive to chemotherapy, removed surgically |
|
|
What type of lung cancer is composed of nests of neuroendocrine cells and is chromogranin A positive?
|
Bronchial Carcinoid Tumor
|
|
|
What is the prognosis for Bronchial Carcinoid Tumor? Symptoms?
|
- Excellent prognosis, metastasis rare
- Symptoms usually due to mass effect - Occasionally causes carcinoid syndrome (5-HT secretion → flushing, diarrhea, wheezing) |
|
|
What type of lung cancer is associated with Carcinoid Syndrome? What does that mean?
|
Bronchial Carcinoid Tumor
- 5-HT secretion → flushing, diarrhea, wheezing |
|
|
Which types of lung cancer have a good prognosis?
|
- Bronchioalveolar subtype of Adenocarcinoma
- Bronchial Carcinoid Tumor |
|
|
What is the name of the malignancy of the pleura? What is it associated with?
|
Mesothelioma
- Associated with asbestosis |
|
|
What are the complications of a Mesothelioma?
|
Results in hemorrhagic pleural effusion and pleural thickening
|
|
|
What are the histologic signs of Mesothelioma?
|
Psamomma bodies
|
|
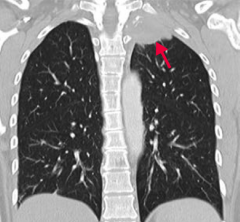
What type of lung cancer occurs in the apex of the lung? What can it do?
|
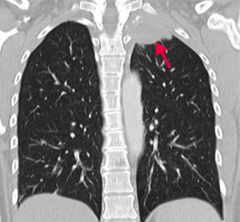
Pancoast tumor:
May affect cervical sympathetic plexus causing: - Horner syndrome (ipsilateral ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis) - SVC syndrome - Sensorimotor deficits - Hoarseness |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Horner syndrome?
|
Ipsilateral ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis
|
|
|
What happens in Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
|
Obstruction of the SVC impairs blood drainage from the head, neck, and upper extremities
|
|
|
What are the implications of the blood drainage obstruction of the head, neck, and upper extremities in superior vena cava syndrome?
|
- Head → facial plethora
- Neck → jugular venous distention - Upper extremities → edema Medical emergency |
|
|
What can cause Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
|
Commonly caused by malignancy and thrombosis from indwelling catheters
|
|
|
What can Superior Vena Cava Syndrome cause if the obstruction is severe?
|
Can raise intracranial pressure → headaches, dizziness, and ↑ risk of aneurysm / rupture of intracranial arteries
|
|
|
What are the types of pneumonia?
|
- Lobar
- Bronchopneumonia - Interstitial (atypical) pneumonia |
|
|
What are the typical causative organisms responsible for lobar pneumonia?
|
- S. pneumoniae most frequently
- Also Legionella and Klebsiella |
|
|
What are the typical causative organisms responsible for bronchopneumonia?
|
- S. pneumoniae
- S. aureus - H. influenzae - Klebsiella |
|
|
What are the typical causative organisms responsible for interstitial (atypical) pneumonia?
|
- Viruses (influenza, RSV, adenoviruses)
- Mycoplasma - Legionella - Chlamydia |
|
|
What are the characteristics of lobar pneumonia?
|
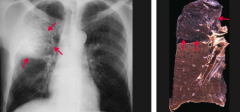
Intra-alveolar exudate → consolidation
- May involve entire lung |
|
|
What are the characteristics of bronchopneumonia?
|
- Acute inflammatory infiltrates from bronchioles into adjacent alveoli
- Patchy distribution involving ≥ 1 lobe |
|
|
What is the histologic appearance of bronchopneumonia?
|
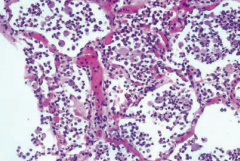
Neutrophils in alveolar space
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of interstitial (atypical) pneumonia?
|
- Diffuse patchy inflammation localized to interstitial areas at alveolar walls
- Distribution involving ≥ 1 lobe - Generally follows a more indolent course |
|
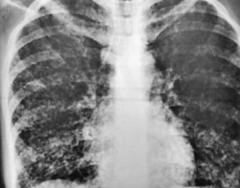
What does this chest x-ray show?
|
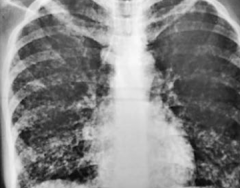
Interstitial Pneumonia: coarse bilateral reticular opacities, worse on the right side
|
|
|
What is wrong in a lung abscess?
|
Localized collection of pus within the parenchyma
|
|
|
What can cause a lung abscess?
|
Bronchial obstruction (eg, cancer) or aspiration of oropharyngeal contents (especially in patients predisposed to loss of consciousness [eg, alcoholics or epileptics])
|
|
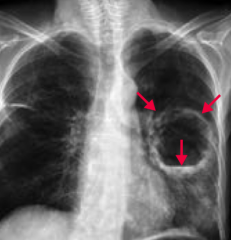
What does this chest x-ray show?
|
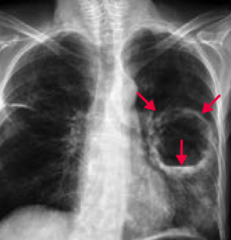
Lung Abscess
- Localized collection of pus within parenchyma - Air-fluid levels can be seen by arrows |
|
|
What are the most common causes of lung abscesses?
|
- S. aureus
- Anaerobes (Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, or Peptostreptococcus) |
|
|
What is wrong in a pleural effusion?
|
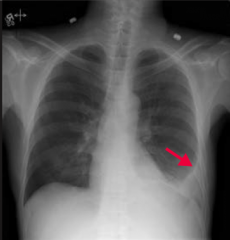
Excess accumulation of fluid between the two pleural layers → restricts lung expansion during inspiration
|
|
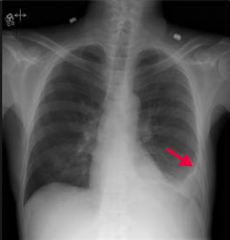
What does this chest x-ray show? How would you describe it?
|
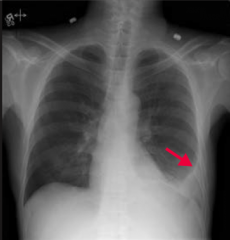
Pleural Effusion
- Blunting of the left costophrenic angle (arrow) due to fluid in the pleural space |
|
|
What are the types of pleural effusions?
|
- Transudate
- Exudate - Lymphatic |
|
|
What are the components of transudative pleural effusions? What can cause this?
|
- ↓ Protein content
- Due to CHF, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis |
|
|
What are the components of exudative pleural effusions? What can cause this?
|
- ↑ Protein content
- Due to malignancy, pneumonia, collagen vascular disease, trauma (occurs in states of ↑ vascular permeability) |
|
|
What are the components of lymphatic pleural effusions / chylthorax? What can cause this?
|
- ↑ Triglycerides, milky-appearing fluid
- Due to thoracic duct injury from trauma or malignancy |
|
|
What type of pleural effusion needs to be drained? Why?
|
Exudative: must be drained due to risk of infection
|
|
|
Which type of fluid is found in a pleural effusion caused by CHF, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis?
|
Transudate: ↓ protein content
|
|
|
Which type of fluid is found in a pleural effusion caused by malignancy, pneumonia, collagen vascular disease, or trauma?
|
Exudate: ↑ protein content
|
|
|
Which type of fluid is found in a pleural effusion caused by thoracic duct injury from trauma or malignancy?
|
Lymphatic / Chylothorax: ↑ triglycerides (milky-appearing)
|
|
|
What is wrong in a pneumothorax?
|
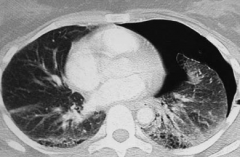
Accumulation of air in the pleural space
|
|
|
What signs and symptoms occur in patients with pneumothorax?
|
All on affected side:
- Unilateral chest pain - Dyspnea - Unilateral chest expansion - ↓ Tactile fremitus - Hyperresonance - Diminished breath sounds |
|
|
What are the types of pneumothorax?
|
- Spontaneous pneumothorax
- Tension pneumothorax |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a spontaneous pneumothorax? Cause?
|
- Accumulation of air in the pleural space
- Occurs most frequently in tall, thin, young males because of rupture of apical blebs |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a tension pneumothorax? Cause?
|
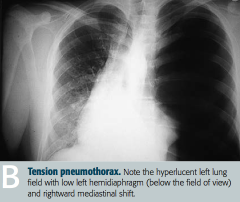
- Air is capable of entering pleural space but not exiting
- Trachea deviates AWAY from the affected lung - Usually occurs in setting of trauma or lung infection |
|
|
A rupture of an apical bleb in a tall, thin, young male is likely to cause what?
|
Spontaneous Pneumothorax: accumulation of air in pleural space
|

